Eilat facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Eilat
אילת
إيلات |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
From upper left: Eilat coastline at night (×2), evening view of Eilat marina, view of Eilat North Beach, view from the promenade to the outskirts and the surrounding mountains of Eilat.
|
|||
|
|||
| Country | |||
| District | Southern | ||
| Founded | 7000 BCE (Earliest settlements) 1951 (Israeli city) |
||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 84,789 dunams (84.789 km2 or 32.737 sq mi) | ||
| Population
(2017)
|
|||
| • Total | 50,724 | ||
| Website | www.eilat.muni.il | ||
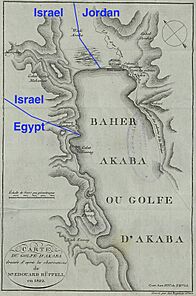
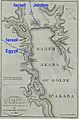
Eilat is Israel's southernmost city. It has a busy port and is a very popular vacation spot. Eilat is located at the northern tip of the Red Sea. In Israel, this part of the sea is called the Gulf of Eilat. In Jordan, it's known as the Gulf of Aqaba.
Eilat is found at the very bottom of Israel. It sits at the end of the Arabah and the Negev Desert. To the south, it's next to Taba, a resort city in Egypt. To the east, it's near Aqaba, a port city in Jordan. You can even see Haql, Saudi Arabia, across the gulf.
This city has many hotels, resorts, and beaches. Its famous coral reefs make it a top spot for diving tourism. People love to go snorkeling and scuba diving here. Eilat is also a tax-free zone, which means shopping can be cheaper!
Fun places to visit include the Dolphin Reef, where you can swim with dolphins. The Coral Beach Nature Reserve has the world's northernmost shallow coral reef. You can also explore the Coral World Underwater Observatory, the Ice Mall, and the city's marina. The promenade by the sea has many restaurants and shops. For outdoor adventures, you can hike in nearby places like Timna Valley Park and the Eilat Mountains.
Eilat has a dry desert climate with low humidity. The nearby warm sea helps to make the weather milder. Summer temperatures often go above 40°C (104°F). In winter, they are usually around 21°C (70°F). The water temperature stays between 20°C and 26°C (68-79°F). Eilat enjoys about 360 sunny days each year!
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Eilat was given to the area in 1949. Before that, it was called Umm al-Rashrāsh. The name Eilat comes from a place mentioned many times in the Hebrew Bible. This ancient place was a stop for the Israelites when they left Egypt. King Solomon also built ships there. The old site might be at Tell el-Kheleifeh, which is between modern Eilat and Aqaba.
Eilat's Landscape
Eilat's land is very diverse. You can find different kinds of rocks, like igneous, metamorphic, sandstone, and limestone. There are mountains as high as 892 meters (2,927 feet) above sea level. Wide valleys, like the Arava, and a seashore on the Gulf of Aqaba are also part of the landscape.
Eilat gets very little rain, only about 28 mm (1.1 inches) per year. Summer temperatures can reach 40°C (104°F) or higher. Because of this, water resources and plants are limited. However, the area has always been important due to its copper and other minerals. Ancient trade routes also crossed through here. This made people settle in the area despite the tough environment.
A Look Back in Time
Ancient Times
Archaeologists have found amazing ancient tombs near Eilat. These tombs date back to about 7,000 BCE (the Neolithic period). Nearby, in Timna Valley, are some of the oldest copper mines in the world.
During the Umayyad period (around the 8th century CE), a small Islamic community lived in the area. They farmed, mined copper, and traded with pilgrims. Their village was found and dug up in 1989.
Modern Eilat Grows
During the time of the British Mandate, there was a British police post here called Umm Al-Rashrash. In 1947, the UN Partition Plan said this area would be part of a Jewish state. On March 10, 1949, during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Israeli soldiers took over the abandoned police post without a fight. This event, called Operation Uvda, marked the end of Israel's war for independence. The place where the Ink Flag was raised is now a National Heritage Site.
Eilat grew a lot in the years that followed. An airport was built in 1949. Ships started arriving in the 1950s, but there wasn't a proper port yet. In the early 1950s, Eilat was a small, quiet town. Its population was mostly port workers, soldiers, and former prisoners.
The town's growth sped up in 1955. The Timna Copper Mines and the Port of Eilat opened that year. The Israeli government worked hard to get more people to live in Eilat. Jewish families from Morocco were among the first to resettle there.
Eilat really started to develop after the Suez Crisis in 1956. Its tourism industry began to boom. The Israeli Navy's Eilat naval base was also built that year. By 1961, the town's population had grown to 5,300 people. The Yoseftal Medical Center and the Eilat-Ashkelon oil pipeline were finished in 1968. The population kept growing, reaching 13,100 in 1972 and 18,900 in 1983.
After the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, some Arab countries blocked land routes to Israel. This meant Israel had to rely on air and sea for trade. Egypt also stopped Israeli ships from using the Suez Canal. This made Eilat and its seaport extremely important for Israel's trade with Africa and Asia. Without a port on the Red Sea, Israel couldn't have developed strong ties beyond the Mediterranean region.
In 1956 and again in 1967, Egypt closed the Straits of Tiran to Israeli ships. This blocked the port of Eilat. In 1967, this closure was a major reason for the start of the Six-Day War. After peace treaties were signed with Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994, Eilat's borders with its neighbors finally opened.
Safety in Eilat
Eilat has a special forces unit called Lotar Eilat. This unit is made up of reservists, who are citizens trained in fighting terrorism and rescuing hostages. They are always ready in case of an attack on the city. They have taken part in many missions since 1974.
In 2007, a bombing at an Eilat bakery killed three people. This was the first attack of its kind right in Eilat. In 2011, terrorists attacked people on Highway 12, just north of Eilat.
To help prevent such attacks, Israel built the Egypt–Israel barrier. This is a strong steel fence along the southern border. It has cameras, radar, and motion sensors. The fence was finished in 2013.
Recently, during the Israel-Hamas War and Red Sea crisis, the port of Eilat saw a huge drop in its activity. By July 2024, the port had almost no economic activity for eight months.
Eilat's Future Plans
In 2012, Israel and China agreed to work together to build a high-speed railway to Eilat. This train line will carry both people and goods. It will connect Eilat with Beersheba and Tel Aviv.
The old Eilat Airport closed in March 2019. This happened after the new Ramon Airport opened in January 2019. Ramon Airport is about 18 km (11 miles) north of Eilat. It replaced both the old Eilat Airport and the civilian use of Ovda Airport. The land where the old airport was will be redeveloped. Plans include new hotels, apartments, public spaces, and walking paths. There will also be space for the new railway line and an underground train station. The goal is to connect the city center and North Beach better.
There are also plans to move the Port of Eilat and the oil pipeline terminal to the northern part of the city. Eilat also aims to become a university town for science and research. It also wants to be known as an international sports city. All these projects are part of a plan to grow Eilat's population to 150,000 people. They also plan to build 35,000 new hotel rooms.
Eilat's Weather
Eilat has a hot desert climate. This means it has very hot, dry summers and warm, dry winters. Winter temperatures are usually between 11°C and 23°C (52-73°F). Summers are usually between 26°C and 40°C (79-104°F). Eilat has small coral reefs. They were much larger about 50 years ago.
| Climate data for Eilat (Temperature: 1987–2010, Precipitation: 1980–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 32.2 (90.0) |
35.8 (96.4) |
38.7 (101.7) |
43.4 (110.1) |
45.2 (113.4) |
47.4 (117.3) |
48.3 (118.9) |
48.0 (118.4) |
45.0 (113.0) |
44.3 (111.7) |
38.1 (100.6) |
33.6 (92.5) |
48.3 (118.9) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 26.3 (79.3) |
29.3 (84.7) |
32.8 (91.0) |
38.2 (100.8) |
42.1 (107.8) |
43.6 (110.5) |
44.1 (111.4) |
43.2 (109.8) |
41.9 (107.4) |
39.7 (103.5) |
33.4 (92.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
44.1 (111.4) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 21.3 (70.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
31.0 (87.8) |
35.7 (96.3) |
38.9 (102.0) |
40.4 (104.7) |
40.0 (104.0) |
37.3 (99.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
27.7 (81.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
31.5 (88.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 15.8 (60.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
24.7 (76.5) |
29.1 (84.4) |
32.0 (89.6) |
33.8 (92.8) |
33.7 (92.7) |
31.3 (88.3) |
27.4 (81.3) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
25.4 (77.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 10.4 (50.7) |
11.8 (53.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
18.4 (65.1) |
22.5 (72.5) |
25.2 (77.4) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.4 (81.3) |
25.2 (77.4) |
21.8 (71.2) |
16.3 (61.3) |
11.9 (53.4) |
19.4 (66.9) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 5.9 (42.6) |
7.4 (45.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.7 (63.9) |
21.5 (70.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
24.8 (76.6) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.4 (63.3) |
11.5 (52.7) |
7.5 (45.5) |
5.9 (42.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
0.9 (33.6) |
3.0 (37.4) |
8.4 (47.1) |
12.1 (53.8) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.4 (66.9) |
18.6 (65.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
5.3 (41.5) |
2.5 (36.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 4 (0.2) |
3 (0.1) |
3 (0.1) |
2 (0.1) |
1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
4 (0.2) |
2 (0.1) |
5 (0.2) |
24 (1) |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.9 | 10.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 32 | 28 | 25 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 17 | 18 | 23 | 27 | 29 | 33 | 24 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 229.4 | 237.3 | 251.1 | 273 | 319.3 | 324 | 347.2 | 347.2 | 291 | 282.1 | 246 | 217 | 3,364.6 |
| Source: Israel Meteorological Service | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22 °C (72 °F) | 21 °C (70 °F) | 21 °C (70 °F) | 23 °C (73 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) | 26 °C (79 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 28 °C (82 °F) | 27 °C (81 °F) | 25 °C (77 °F) | 23 °C (73 °F) |
Who Lives in Eilat?
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1955 | 500 | — |
| 1961 | 5,300 | +960.0% |
| 1972 | 13,100 | +147.2% |
| 1983 | 18,900 | +44.3% |
| 1995 | 32,500 | +72.0% |
| 2008 | 47,300 | +45.5% |
| 2017 | 50,724 | +7.2% |
| Source: CBS | ||
Most people living in Eilat are Jews. About 4% of the population are Arabs. Eilat also has many foreign workers. They work in jobs like caregiving, hotels, and construction. Many wealthy Jordanians and Egyptians visit Eilat in the summer.
In 2007, over 200 Sudanese refugees came to Eilat from Egypt. They were given jobs and allowed to stay.
Learning in Eilat
Eilat's schools teach more than 9,000 young people. There are eight day-care centers, 67 kindergartens, 10 elementary schools, and 3 high schools. There are also special education schools and religious schools.
Ben Gurion University of the Negev has a campus in Eilat. About 1,100 students study there. Most of them come from outside the city. In 2010, a new student dormitory was built. The SPNI's Eilat Field School offers special hiking tours. These tours teach about desert ecology, the Red Sea, and bird migration. The Hesder Yeshiva Ayelet Hashachar, a religious school, was started in Eilat in 1997.
Healthcare in Eilat
Yoseftal Medical Center, opened in 1968, is Israel's southernmost hospital. It is the only hospital covering the southern Negev region. With 65 beds, it is Israel's smallest hospital. It offers special services for the Red Sea area. These include a hyperbaric chamber for diving accidents. It also has kidney dialysis for tourists on vacation.
Getting Around Eilat
By Air
Since 2019, Ramon International Airport handles all flights to Eilat. This includes both flights within Israel and international flights.
Old Airports
- The old Eilat Airport was in the city center. It was mostly used for flights within Israel. The land where it was will be redeveloped.
- Ovda International Airport was about 50 km (31 miles) northwest of Eilat. It was used for international flights. Now, no civilian flights use it. It is still used as a military airbase.
By Road
Eilat has two main roads that connect it to central Israel. Route 12 goes northwest. Route 90 goes northeast. It also goes southwest to the border with Egypt.
By Bus
Egged, the national bus company, has regular bus service. Buses go north almost every hour. Buses within the city run every half hour during the day. Because trips to Eilat can be long, you can book tickets in advance.
Border Crossings
- The Taba Border Crossing lets you cross between Eilat and Taba, Egypt.
- The Wadi Araba Crossing, also called the Yitzhak Rabin Border Crossing, lets you cross between Eilat and Aqaba, Jordan.
By Sea
The Port of Eilat and Eilat Marina allow travel by sea.
By Train
There are future plans for a train link, sometimes called the Med-Red. This train would greatly reduce travel times from Eilat to Tel Aviv and Jerusalem. It would connect through the existing line at Beer Sheba. As of 2021, Dimona railway station is the southernmost passenger train station in Israel.
Eilat's Economy
In the 1970s, tourism became very important to Eilat's economy. Other industries either closed or became much smaller. Today, tourism is the city's main source of money. Eilat also became a free trade zone in 1985. This means some goods can be bought without certain taxes.
Tourism in Eilat
Eilat offers many places to stay, from hostels to fancy hotels. You can even experience Bedouin hospitality. In recent years, Eilat has seen fewer tourists sometimes. This is due to security concerns in the region.
Here are some popular attractions:
- Birdwatching and ringing station: Eilat is on a major route for birds migrating between Africa and Europe.
- Camel tours: Explore the desert on a camel!
- Coral Beach Nature Reserve: An underwater park with amazing tropical plants and animals.
- Coral World Underwater Observatory: Located at Coral Beach, it has aquariums, a museum, and tanks with sharks, turtles, and stingrays. It's the biggest public aquarium in the Middle East.
- Dolphin Reef: A place where you can swim and interact with dolphins.
- Freefall parachuting: For those who love adventure.
- Yotvata Hai-Bar Nature Reserve: This reserve helps protect endangered species, including animals mentioned in the Bible. They help desert animals get used to the wild before releasing them.
- Marina: With space for about 250 yachts.
- Timna Valley Park: Home to the world's oldest copper mines. You can see ancient temples, rock formations, and old rock art.
- "What's Up": A portable astronomical observatory that offers stargazing programs in the desert.
- Ice Mall: A shopping mall with an ice skating rink.
Diving Fun
You can rent scuba diving and snorkeling gear at or near all major beaches. Diving clubs and schools offer equipment and air all year. Eilat is in the Gulf of Aqaba, which is one of the most popular diving spots in the world.
The coral reefs along Eilat's coast are still beautiful. The area is known as one of the best diving locations globally. About 250,000 dives happen each year along Eilat's 11 km (6.8 miles) coastline. Diving brings in 10% of the tourism money for this area. Many reefs are close to the shore, so even non-divers can easily see the Red Sea's reefs. Diving conditions are good all year. Water temperatures are around 21–25°C (70-77°F). There are usually no strong currents, and the water is clear. You can often see 20–30 meters (66-98 feet) underwater.
Museums to Visit
- Eilat City Museum
- Eilat Art Gallery
Eilat on Screen
Eilat has been used as a filming location for movies and TV shows since the 1960s. It was used in films like She, Madron, Ashanti, and Rambo III.
Archaeological Discoveries
Even though conditions are harsh, people have lived in the Eilat region for a very long time. Some findings date back to 8,000 BCE. Several Neolithic sites have been found in and around Eilat. One site has ancient burial places from 5410-4250 BCE.
People started exploring ancient sites here in 1861. However, only about 7% of the area has been properly dug up by archaeologists. There are about 1,500 ancient sites in a 1,200 square kilometer (460 sq mi) area. Unlike other nearby regions, these sites show that people have lived here continuously for the past 10,000 years.
Famous People from Eilat
- Shawn Dawson (born 1993), a basketball player.
- Gadi Eizenkot (born 1960), a former military chief.
- Eden Harel (born 1976), an actress.
- Amit Ivry (born 1989), an Olympic swimmer.
- Keren Karolina Avratz (born 1971), a singer and songwriter.
- Shaul Mofaz (born 1948), a former government minister.
- Ziki Shaked (born 1955), the first Israeli ship captain to sail around the world.
- Shahar Tzuberi (born 1986), an Israeli Olympic bronze-medal-winning windsurfer.
- Raviv Ullman (born 1986), an Israeli-American actor and musician.
- Ghil'ad Zuckermann (born 1971), a linguist who works on bringing languages back to life.
Sister Cities
Eilat is connected with these cities around the world:
 Acapulco, Mexico
Acapulco, Mexico Antibes, France
Antibes, France Arica, Chile
Arica, Chile Durban, South Africa
Durban, South Africa Kamen, Germany
Kamen, Germany Kampen, Netherlands
Kampen, Netherlands Karlovy Vary, Czech Republic
Karlovy Vary, Czech Republic Los Angeles, United States
Los Angeles, United States Palanga, Lithuania
Palanga, Lithuania Piešťany, Slovakia
Piešťany, Slovakia Sopron, Hungary
Sopron, Hungary Sorrento, Italy
Sorrento, Italy Yalta, Ukraine
Yalta, Ukraine Yinchuan, China
Yinchuan, China Ushuaia, Argentina
Ushuaia, Argentina
Eilat has streets named after some of its sister cities, like Antibes, Durban, Kamen, Kampen, and Los Angeles. There is also a Canada Park.
Panoramic Views
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Eilat para niños
In Spanish: Eilat para niños