1948 Arab-Israeli War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids 1948 Arab–Israeli War |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of 1947–1949 Palestine war | |||||||||
 Captain Avraham "Bren" Adan raising the Ink Flag at Umm Rashrash (a site now in Eilat), marking the end of the war |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
Before 26 May 1948: Paramilitary groups: After 26 May 1948: Foreign volunteers: Mahal |
Irregulars: Foreign volunteers: |
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Israel: 29,677 (initially) 117,500 (finally) |
Egypt: 10,000 initially, rising to 20,000 Transjordan: 7,500–10,000 Iraq: 2,000 initially, rising to 15,000–18,000 Syria: 2,500–5,000 Lebanon: 1,000 Saudi Arabia: 800–1,200 (Egyptian command) Yemen: 300 Arab Liberation Army: 3,500–6,000. Total: 13,000 (initial) 51,100 (minimum) 63,500 (maximum) |
||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| 6,373 killed (about 4,000 fighters and 2,400 civilians) Around 2,000 were Holocaust survivors. | Arab armies: 3,700–7,000 killed Palestinian Arabs: 3,000–13,000 killed (both fighters and civilians) |
||||||||
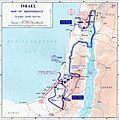
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War was a major conflict in the Middle East. It was the second and final part of the 1947–49 Palestine war. The war started right after the British ended their control over Palestine. This happened at midnight on May 14, 1948.
Earlier that same day, Israel declared itself an independent country. On May 15, 1948, a group of Arab countries sent their armies into the area. They attacked Israeli forces and some Jewish settlements. The fighting lasted for about ten months. It took place mostly in the former British Mandate area, the Sinai Peninsula, and southern Lebanon. There were also several times when the fighting stopped for a truce.
Contents
What Caused the War?
The first deaths in this conflict happened on November 30, 1947. Two buses carrying Jewish people were attacked. There had been tension between Arabs and Jews for a long time. This tension grew after the 1917 Balfour Declaration. It also increased when the British Mandate of Palestine was created in 1920.
Neither the Arabs nor the Jews were happy with British rules. The Arabs' unhappiness led to a revolt from 1936 to 1939. Jewish groups also resisted British rule from 1944 to 1947. These tensions eventually led to a civil war in 1947.
The United Nations Plan
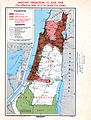
On November 29, 1947, the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was approved. This plan aimed to divide Palestine into three parts:
Who Fought in the War?
One day after Israel declared its independence, the civil war turned into a bigger conflict. This was between the new state of Israel and several Arab countries.
- Israel: The newly formed Israel Defense Forces (IDF) fought for Israel. Before the IDF was officially created, groups like the Haganah, Irgun, and Lehi were involved.
- Arab Countries: Armies from Egypt, Transjordan (now Jordan), Syria, and Iraq entered Palestine. Forces from Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen also joined.
- Other Groups: Irregular fighters like the Army of the Holy War and the Arab Liberation Army also participated.
Results of the War
After the war, the State of Israel controlled more land than the UN plan had suggested for the Jewish state. Israel gained control of areas like Jaffa, Lydda, Ramle, Galilee, parts of the Negev desert, and West Jerusalem. They also controlled a wide strip of land along the road between Tel Aviv and Jerusalem.
Transjordan took control of the remaining parts of the former British mandate. They later officially joined this land to their country. The Egyptian military took control of the Gaza Strip.
Impact on People
The war caused big changes for many people in the Middle East. About 700,000 Palestinian Arabs left or were forced to leave their homes in the area that became Israel. They became Palestinian refugees. Many refer to this event as Al-Nakba, which means "the catastrophe."
In the three years after the war, about 700,000 Jewish people moved to Israel. Many of them had been forced to leave their homes in other Middle Eastern countries.
Images for kids
-
IDF soldiers of the Samson's Foxes unit advance in a captured Egyptian Bren Gun carrier.
-
A "Butterfly" improvised armoured car of the Haganah at Kibbutz Dorot in the Negev, Israel 1948. The armoured car is based on CMP-15 truck. The car has brought supply to the kibbutz. The Negev Kibbutz's children were later evacuated by those cars from their kibbutz, before an expected Egyptian Army attack.
-
Mathematics professor Michael Fekete, the Provost of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, with his water quota, during the siege of Jerusalem
-
Kaukji, the Arab Liberation Army commander
-
Northland in Greenland circa 1944 which became the Israeli INS Eilat
-
Israeli armoured vehicles in Lydda airport after the town's capture by Israeli forces
-
Arab prisoners of war captured by Israeli forces in Ramla.
-
Beit Horon Battalion soldiers in the Russian Compound in Jerusalem, 1948
-
IDF forces in Beersheba during Operation Yoav
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra árabe-israelí de 1948 para niños
In Spanish: Guerra árabe-israelí de 1948 para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |