Iran facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Islamic Republic of Iran
جمهوری اسلامی ایران (Persian)
Jomhuri-ye Eslâmi-ye Irân |
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: مهر خاوران
Mehr-e Khâvarân "Eastern Sun" |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Tehran 35°41′N 51°25′E / 35.683°N 51.417°E |
| Official languages | Persian |
| Demonym(s) | Iranian |
| Government | Unitary presidential theocratic Islamic republic |
| Mojtaba Khamenei | |
| Masoud Pezeshkian | |
| Mohammad Reza Aref | |
| Legislature | Islamic Consultative Assembly |
| Formation | |
|
• Median kingdom
|
c. 678 BC |
| 550 BC | |
| 247 BC | |
| 224 AD | |
|
• Iranian Intermezzo
|
821 |
| 22 December 1501 | |
| 22 January 1736 | |
|
• Zand Iran
|
1751 |
| 20 March 1794 | |
| 12 December 1905 | |
|
• Pahlavi Iran
|
15 December 1925 |
| 11 February 1979 | |
|
• Current constitution
|
3 December 1979 |
|
• Constitution amendment
|
28 July 1989 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,648,195 km2 (636,372 sq mi) (17th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
1.63 (as of 2015) |
| Population | |
|
• 2025 estimate
|
|
|
• Density
|
52/km2 (134.7/sq mi) (163rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2023) | ▲ 35.9 medium |
| HDI (2023) | high · 75th |
| Currency | Iranian rial (ریال) (IRR) |
| Time zone | UTC+3:30 (IRST) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +98 |
| ISO 3166 code | IR |
| Internet TLD | |
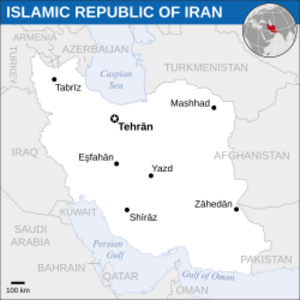
Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a country in Western Asia. It's part of the Middle East region. Iran shares its borders with several countries, including Afghanistan, Iraq, Pakistan, and Turkey.
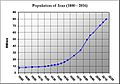
Tehran is the capital city and also the largest city in Iran. Iran is the 18th biggest country in the world. It has a population of over 84.9 million people. Iran has been a member of the United Nations since 1945. It is also part of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). Iran is an Islamic Republic, which means its government is based on Islamic laws.
In Iran, there are many different ethnic groups. The main group is Persians. Other groups include Azerbaijanis, Kurds, and Lurs.
Contents
Iran's History
In the past, people outside the country often called Iran "Persia". However, the people living there always called it "Iran". The name "Persia" was used more in official papers and when dealing with other countries.
In 1935, Reza Shāh Pahlavi, who was the Shah (king) of Iran, officially asked other countries to use the name "Iran". This was to show that the country belonged to all its people, not just the Persian ethnic group. The word "Iran" means land of the Aryans. This name comes from an ancient religious book called the Avesta. The word "Aryan" means "noble" in Iranian languages.
Ancient Empires of Iran
Around 500 BC, the area that is now Iran was the heart of the Achaemenid Empire. This was a very powerful empire. The Greek city-states even fought against the Persian armies led by famous kings like Darius the Great and Xerxes.
Later, Alexander the Great conquered the Achaemenid Empire. After he died, the Greek Seleucids ruled. Then, the Parthian Empire took over and even fought against the Roman Empire. After the Parthians, the Sassanian dynasty ruled for many centuries (224-651 AD).
Over time, other groups also conquered parts of Iran. These included the Arabs in the 7th century, the Turks in the 10th century, and the Mongols in the 13th century. Despite these invasions, Iran has always kept its unique culture and identity.
Modern History of Iran
After World War II, there were some big changes in Iran. In 1953, the Prime Minister Mosaddegh was removed from power. The United States and Great Britain helped the Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi become the most powerful leader again.
However, the Shah left Iran in 1979 because of a big revolt. This event is known as the Iranian Revolution. After this, Iran became an Islamic Republic. Soon after, a group of students took over the U.S. Embassy in Tehran. They held many diplomats as hostages for 444 days.
Since then, relations between Iran and the United States have often been difficult. For example, the U.S. has concerns about Iran's support for certain groups. Iran also fought a long war with Iraq in the 1980s, called the Iran–Iraq War. Many other countries supported Iraq during this time.
Today, there are discussions about Iran's nuclear technology. Iran is a member of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, which means it agrees not to develop nuclear weapons. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) checks Iran's nuclear activities. They have reported that there is no evidence Iran is making nuclear weapons. However, they also say they cannot be completely sure about secret activities.
A report from the CIA in 2007 said that Iran's secret program to get nuclear weapons technology was stopped in 2003. It also said that Iran would probably not be able to build a nuclear weapon anytime soon.
In late 2025, there were significant public demonstrations in Iran due to economic challenges. International tensions also led to military actions involving the United States and Israel. As of early 2026, the position of Supreme Leader was vacant.
Iran's Economy
Iran has a lot of natural resources, especially oil. It is a major oil producer and exporter. Oil is one of the country's main exports.
Besides oil, Iran also produces and exports other important goods. These include Rice, handicrafts, beautiful carpets, and crocus (which is used to make saffron). Iran is the world's largest exporter of caviar, which is a special type of fish eggs. It is also one of the biggest exporters of pistachio nuts.
Iran has many factories that make industrial products. The country is also making progress in biomedical sciences, which involves using biology and medicine to create new treatments.
The money used in Iran is called the Rial.
Religion in Iran
Most people in Iran are Muslim. About 90% of Iranians follow Islam. The official religion of the country is Shia Islam. This has been the state religion since the 16th century, during the Safavid dynasty. About 75% of Iranians who are Muslim belong to the Twelver branch of Shia Islam.
About 9% of Iranians who are Muslim belong to the Sunni branch of Islam. The remaining 9% of Iranians follow other religions. These include Bahá'ís, Mandeans, Zoroastrians, Christians, and Jews. There are thought to be between 300,000 and 350,000 Iranian Jews.
Regions and Provinces
Iran is divided into 31 provinces. Each province has its own capital city. Here are some of the provinces:
Languages Spoken in Iran
The main language spoken in Iran is Persian. It is the official language of the country. Many other Iranian languages are also spoken. These languages are part of the larger Indo-European language family.
The CIA's World Factbook provides percentages for the languages spoken. About 53% of the population speaks Persian. Other languages include 16% Azerbaijani, 10% Kurdish, and 7% Mazenderani and Gilaki. About 7% speak Luri. Smaller groups speak Turkmen, Balochi, and Arabic. There are also speakers of Armenian, Georgian, and Neo-Aramaic.
Iranian Architecture

Iranian architecture has a very long history, going back at least 5,000 years. You can find examples of it across a huge area, from modern-day Turkey to Uzbekistan. Iranians were very good at using mathematics, geometry, and astronomy in their buildings. This led to a style that is both strong and beautiful.
Iranian architecture is known for its unique look. It has a great sense of shape and size. Builders were very clever with vault and dome construction. They also had a special talent for decoration that is not seen in other types of architecture.
Besides old gates, palaces, and mosques, new buildings are constantly being built in cities like Tehran. Iran is ranked seventh in the world for the number of ancient ruins and attractions listed by UNESCO.
World Heritage Sites in Iran
Iran has many amazing places recognized by UNESCO as World Heritage Sites. It ranks 10th globally with 27 such sites. These include famous places like Persepolis, Naghsh-e Jahan Square, and Pasargadae. Other sites are Golestan Palace, Arg-e Bam, and the ancient city of Yazd.
Iran also has 24 "Human treasures," which are examples of Intangible Cultural Heritage. This ranks Iran 5th worldwide for these cultural traditions.
Museums in Iran
The National Museum of Iran in Tehran is the most important cultural place in the country. It is the first and largest museum in Iran. The museum has two main parts: the Museum of Ancient Iran and the Museum of the Islamic Era. This museum is very important for showing and studying Iran's ancient collections. It is one of the most respected museums in the world because of its many diverse and high-quality artifacts.
There are many other popular museums across Iran. Some of these include the Golestan Palace (a World Heritage Site), The Treasury of National Jewels, and the Tehran Museum of Contemporary Art. Other notable museums are the The Carpet Museum and the Abgineh Museum. In 2019, about 25 million people visited museums in Iran.
Iranian Cuisine
Iranian main dishes often include different kinds of kebab, pilaf (rice dishes), stews (called khoresh), and soups. Lunch and dinner meals are usually served with side dishes. These can be plain yogurt, salad Shirazi, or torshi (pickled vegetables).
Tea is a very popular drink in Iranian culture. Iran is the world's seventh largest producer of tea. For dessert, one popular choice is falude, which is a frozen noodle dessert. Another favorite is saffron ice cream, known as Bastani Sonnati (traditional ice cream). Iran is also famous for its caviar.
Typical Iranian main dishes combine rice with meat, vegetables, and nuts. Herbs are used a lot, along with fruits like plums, pomegranates, and apricots. Common Iranian spices include saffron, cardamom, cinnamon, and turmeric.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Inscription of Ardeshir Babakan (r. 224–242) in Naqsh-e Rostam: "This is the figure of Mazdaworshiper, the lord Ardashir, Shahanshah of Iran..."
-
An Ashrafi Coin of Nader Shah (r. 1736–1747), reverse:"Coined on gold the word of kingdom in the world, Nader of Greater Iran and the world-conquerer king."
-
A cave painting in Doushe cave, Lorestan, from the 8th millennium BC
-
A bas-relief at Persepolis, depicting the united Medes and Persians
-
Tomb of Cyrus the Great, founder of the Achaemenid Empire, in Pasargadae
-
Tomb of Hafez, a medieval Persian poet whose works are regarded as a pinnacle in Persian literature and have left a considerable mark on later Western writers, most notably Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Henry David Thoreau, and Emerson
-
Venetian portrait, kept at the Uffizi, of Ismail I, the founder of the Safavid Empire
-
Statue of Nader Shah, the first Afsharid ruler of Iran, at his Tomb
-
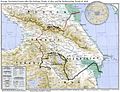
A map showing the 19th-century northwestern borders of Iran, comprising modern-day eastern Georgia, Dagestan, Armenia, and the Republic of Azerbaijan, before being ceded to the neighboring Russian Empire by the Russo-Iranian wars
-
The first national Iranian Parliament was established in 1906 during the Persian Constitutional Revolution
-
Reza Shah, the first Pahlavi king of Iran, in military uniform
-
The Allied "Big Three" at the 1943 Tehran Conference.
-
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi and the Imperial Family during the coronation ceremony of the Shah of Iran in 1967.
-
An Iranian soldier wearing a gas mask on the front line during the Iran–Iraq War
-
The Green Movement's Silent Demonstration during the 2009–10 Iranian election protests
-
The 2017–18 Iranian protests were initiated on 31 December 2017 and continued for months.
-
Mount Damavand, Iran's highest point, is located in Amol, Mazenderan.
-
Persian leopard, listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List.
-
Iran holds 10% of the world's proven oil reserves and 15% of its gas. It is OPEC's second-largest exporter and the world's 7th largest oil producer.
-
Iron Age gold cup from Marlik, kept at New York City's Metropolitan Museum of Art
-
Kamal-ol-Molk's Mirror Hall, often considered a starting point in Iranian modern art
-
Zoroaster, the founder of Zoroastrianism, depicted on Raphael's The School of Athens
-
The Roudaki Hall, constructed between 1957 and 1967 in Tehran
-
Abbas Kiarostami (1940–2016), an acclaimed Iranian film director
-
Behrouz Vossoughi, a well-known Iranian actor who has appeared in more than 90 films
-
Haft-Seen, a customary of Nowruz, the Iranian New Year
-
An Iranian tea (čāy) tray served near Garden of Mausoleum of Omar Khayyam in Nishapur
-
The Azadi Stadium in Tehran is West Asia's largest football stadium.
See also
 In Spanish: Irán para niños
In Spanish: Irán para niños