Armenia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Armenia
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: Մեկ ազգ, մեկ մշակույթ
Mek Azg, Mek Mshakouyt "One nation, one culture" |
|
Location of Armenia
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Yerevan 40°11′N 44°31′E / 40.183°N 44.517°E |
| Official languages | Armenian |
| Recognized languages | |
| Ethnic groups
(2022)
|
|
| Religion
(2022)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Armenian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| Vahagn Khachaturyan | |
| Nikol Pashinyan | |
|
• President of the National Assembly
|
Alen Simonyan |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Establishment | |
| 16th century BC - 13th century BC | |
|
• Urartu
|
860 BC – 590 BC |
| 6th century BC | |
| 321 BC–428 AD | |
|
• Principality of Hamamshen
|
790–1486 |
| 885–1045 | |
|
• Kingdom of Vaspurakan
|
908–1021 |
|
• Kingdom of Vanand
|
963–1064 |
|
• Kingdom of Tashir-Dzoraget
|
979–1118 |
|
• Kingdom of Syunik
|
987–1170 |
|
• Kingdom of Artsakh
|
1000–1261 |
| 1198–1375 | |
| 1261–1603 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
29,743 km2 (11,484 sq mi) (138th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
4.71 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
3,015,400 (138th) |
|
• Density
|
101.5/km2 (262.9/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | low |
| HDI (2022) | high · 76th |
| Currency | Dram (֏) (AMD) |
| Time zone | UTC+4 (AMT) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +374 |
| ISO 3166 code | AM |
| Internet TLD |
|
Armenia, officially known as the Republic of Armenia, is a country located in the western part of Asia. Its capital city is Yerevan. Armenia became an independent country in 1991, after the Soviet Union broke apart.
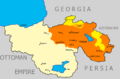
Armenia shares its borders with Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Iran.
Most people in Armenia are ethnic Armenians, making up over 90% of the population. There are also smaller groups like Greeks and Russians. The main religion in Armenia is the Armenian Apostolic Church, which is a type of Christianity. Some Christians believe that Noah's Ark landed in Armenia, and Noah's family settled there. The Armenian name for Armenia, Hayastan, means "Land of Haik," named after a great-great-grandson of Noah.
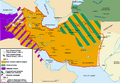
Throughout history, Armenia's size has changed a lot. It was once much larger, covering parts of what are now Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Iran, Iraq, and Azerbaijan around 80 BCE. From 1920 to 1991, Armenia was part of the Soviet Union.
Today, Armenia has some border issues with Turkey and Azerbaijan. In 1992, Armenia and Azerbaijan had a conflict over a region called Nagorno-Karabakh. The fighting stopped in 1994, and Armenia gained control of this land, but Azerbaijan still claims it.
Contents
Exploring Armenia's Geography
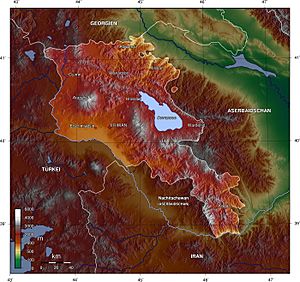
Armenia is a landlocked country, meaning it has no coastline. It is located in the South Caucasus region, between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. To the north and east, it borders Georgia and Azerbaijan. To the south and west, it borders Iran and Turkey.
The country covers an area of about 29,743 square kilometers (11,484 square miles). The land is mostly mountainous, with many fast-flowing rivers and not many forests. Armenia experiences hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters.
Mount Ararat is a very important symbol for Armenians. It used to be part of Armenia and is the highest mountain in the region. Even though it is now in Turkey, it is clearly visible from Armenia. Because of its importance, Mount Ararat is shown on the Armenian national emblem.
Provinces and Cities of Armenia
Armenia is divided into ten main areas called provinces, plus the capital city of Yerevan. As of 2007, Armenia has 915 communities. Out of these, 49 are considered urban (cities or towns), and 866 are considered rural (villages). You can find a full list of communities at List of settlements in Armenia.
| Province | Capital | Area | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aragatsotn (Արագածոտն) | Ashtarak (Աշտարակ) | 2,753 km² | 126,278 |
| Ararat (Արարատ) | Artashat (Արտաշատ) | 2,096 km² | 252,665 |
| Armavir (Արմավիր) | Armavir (Արմավիր) | 1,242 km² | 255,861 |
| Gegharkunik (Գեղարքունիք) | Gavar (Գավառ) | 5,348 km² | 215,371 |
| Kotayk (Կոտայք) | Hrazdan (Հրազդան) | 2,089 km² | 241,337 |
| Lori (Լոռի) | Vanadzor (Վանաձոր) | 3,789 km² | 253,351 |
| Shirak (Շիրակ) | Gyumri (Գյումրի) | 2,681 km² | 257,242 |
| Syunik (Սյունիք) | Kapan (Կապան) | 4,506 km² | 134,061 |
| Tavush (Տավուշ) | Ijevan (Իջևան) | 2,704 km² | 121,963 |
| Vayots Dzor (Վայոց Ձոր) | Yeghegnadzor (Եղեգնաձոր) | 2,308 km² | 53,230 |
| Yerevan (Երևան) | – | 227 km² | 1,091,235 |
Largest Cities in Armenia
Armenia has many cities. Here are the ten biggest ones:
- Yerevan (with about 1,121,900 people)
- Vanadzor
- Gyumri
- Vagharshapat
- Hrazdan
- Abovyan
- Armavir
- Kapan
- Gavar
- Artashat (with about 20,562 people)
Armenia's Climate

Armenia has a continental climate. This means it has distinct seasons. Summers are usually dry and sunny, lasting from June to mid-September. Temperatures can range from 22 to 36 degrees Celsius (72 to 97 degrees Fahrenheit). The low humidity makes the heat more bearable. Cool breezes often blow down from the mountains in the evenings.
Springs are short, while autumns are long and known for their beautiful, colorful trees. Winters are quite cold with lots of snow. Temperatures typically range from -10 to -5 degrees Celsius (14 to 23 degrees Fahrenheit). If you like Winter sports, you can go skiing in Tsakhkadzor, which is about 30 minutes from Yerevan. Lake Sevan, located high in the Armenian mountains, is the second largest lake in the world for its altitude, sitting about 1,900 meters (6,234 feet) above sea level.
Armenia's Economy
Armenia's economy gets a lot of help from Armenians living in other countries. Before Armenia became independent, its economy was mostly based on industry. This included making things like chemicals, electronics, machinery, processed food, and textiles. It relied heavily on resources from outside the country.
Before the Soviet Union broke apart in 1991, agriculture was a smaller part of the economy. After independence, farming became much more important.
Armenian mines produce valuable metals like copper, zinc, gold, and lead. Most of Armenia's energy comes from fuel imported from Russia, including gas and nuclear fuel for its single nuclear power plant. The main energy source within Armenia is hydroelectric power, which uses water. There are also small amounts of coal, gas, and petroleum, but these have not been developed much yet.
People and Population
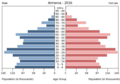
Armenia has a population of about 3,238,000 people (as of 2008). It is one of the most densely populated countries that used to be part of the Soviet Union. After the USSR broke up, many people left Armenia, causing the population to decrease. However, in recent years, fewer people have been leaving, and some Armenians have even returned. This trend is expected to continue, and Armenia's population is predicted to start growing again by 2010.
Most of the people in Armenia are ethnic Armenians, making up 97.9% of the population. Other groups include Yazidis (1.3%) and Russians (0.5%). There are also smaller groups like Assyrians, Ukrainians, Greeks, Kurds, Georgians, and Belarusians.
During the Soviet era, Azerbaijanis were the second largest group in Armenia. However, because of the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh, almost all of them moved from Armenia to Azerbaijan.
Armenian is the only official language. However, Russian is also widely used, especially in schools. Many adult Armenians (94%) think it is important for their children to learn Russian.
Armenian Culture and Traditions
Armenians have their own unique alphabet and language. The alphabet was created in AD 405 by Saint Mesrob Mashtots. It has thirty-eight letters, with two letters added later. About 96% of people in Armenia speak Armenian. Also, 75.8% of the population speaks Russian, and English is becoming more and more popular.
Music and Dance in Armenia
Armenian music is a blend of traditional folk music and modern pop. A famous example of Armenian folk music is the sound of the duduk, a traditional Armenian woodwind instrument, often played by artists like Djivan Gasparyan.
Instruments commonly found in Armenian folk music include the duduk, the dhol (a drum), the zurna (a wind instrument), and the kanun (a string instrument). Artists like Sayat Nova are well-known for their important role in developing Armenian folk music.
One of the oldest forms of Armenian music is the Armenian chant. This is the most common type of religious music in Armenia. Many of these chants are very old, some even from before Christianity. Others are more recent, including some written by Saint Mesrop Mashtots, who invented the Armenian alphabet.
See Also
Images for kids
-
Armenian soldier of the Achaemenid army, circa 470 BC. Xerxes I tomb relief.
-
In 1501–02, most of the Eastern Armenian territories including Yerevan were conquered by the emerging Safavid dynasty of Iran led by Shah Ismail I.
-
Capture of Erivan fortress by Russian troops in 1827 during the Russo-Persian War (1826–28) by Franz Roubaud.
-
Territory held by Armenia and the Karabakh Council at some point Area given to Armenia by the Treaty of Sèvres, which was never enforced.
-
The Government house of the First Republic of Armenia (1918–1920)
-
Armenians gather at Theater Square in central Yerevan to claim unification of Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Oblast with the Armenian SSR.
-
Armenian soldiers in 2008, during the ongoing and unresolved Nagorno-Karabakh conflict.
-
Yerevan is the economic and cultural centre of Armenia.
-
Ancient Armenian Khachkars (cross-stones)
-
Queen Zabel's Return to the Palace, Vardges Sureniants (1909)
-
The Armenia national football team in Dublin, Ireland
-
Chess Grandmaster Levon Aronian is a former FIDE No. 2 rated player and the fourth-highest rated player in history.
See also
 In Spanish: Armenia para niños
In Spanish: Armenia para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |