Namibia facts for kids
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country located on the west coast of Southern Africa. It shares borders with the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east, and South Africa to the south. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek.
Namibia is known as the driest country in sub-Saharan Africa. People have lived here for a very long time, including the Khoi, San, Damara, and Nama people. Later, around the 14th century, Bantu peoples moved into the area.
In 1884, the German Empire took control of most of the land, calling it German South West Africa. This period included a very sad and difficult time between 1904 and 1908, where many Herero and Nama people lost their lives. German rule ended during the First World War in 1915 when South African forces took over. In 2021, Germany and Namibia agreed to work towards healing from the past.
After the war, the League of Nations gave South Africa the job of looking after the territory. From 1948, South Africa applied apartheid (a system of unfair rules based on race) to the area, which was then called South West Africa.
Later, in the 1960s, people in Namibia started to demand their freedom. The United Nations (UN) became involved and, in 1966, took responsibility for the territory. The UN recognized the South West Africa People's Organisation (SWAPO) as the group representing the Namibian people.
Namibia finally gained its independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, after a long struggle. Today, Namibia is a stable parliamentary democracy. Its economy relies on farming, tourism, and mining (especially for diamonds and uranium). Even with economic growth, many people still face poverty and inequality.
With about 3.1 million people, Namibia is one of the most sparsely populated countries in the world. It is a member of the United Nations, the African Union, and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Namibia
Name in national languages
|
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Motto: "Unity, Liberty, Justice"
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: "Namibia, Land of the Brave"
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city
|
Windhoek 22°34′S 17°5′E / 22.567°S 17.083°E |
||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | English | ||||||||||||||||
| Recognised national languages |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Recognised regional languages |
|
||||||||||||||||
| Ethnic groups
(2023)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Religion
(2023)
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Namibian | ||||||||||||||||
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic | ||||||||||||||||
| Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah | |||||||||||||||||
| Lucia Witbooi | |||||||||||||||||
| Elijah Ngurare | |||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament | ||||||||||||||||
| National Council | |||||||||||||||||
| National Assembly | |||||||||||||||||
| Independence from South Africa | |||||||||||||||||
|
• Constitution
|
9 February 1990 | ||||||||||||||||
| 21 March 1990 | |||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
825,615 km2 (318,772 sq mi) (34th) | ||||||||||||||||
|
• Water (%)
|
negligible | ||||||||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||||||||
|
• 2025 census
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
• Density
|
3.7/km2 (9.6/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2025 estimate | ||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
• Per capita
|
|||||||||||||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2025 estimate | ||||||||||||||||
|
• Total
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
• Per capita
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Gini (2015) | 59.1 high |
||||||||||||||||
| HDI (2023) | medium · 136th |
||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Namibian dollar (NAD) South African rand (ZAR) |
||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+2 (CAT) | ||||||||||||||||
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy | ||||||||||||||||
| Driving side | left | ||||||||||||||||
| Calling code | +264 | ||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | NA | ||||||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .na | ||||||||||||||||
Contents
Namibia's Past
How Namibia Got Its Name
The name Namibia comes from the Namib desert, which is the oldest desert in the world. The word Namib means "vast place" in the Khoi language. Before 1990, the country was known as German South-West Africa and then South West Africa, showing its history of being ruled by Germany and South Africa.
Early History of Namibia
Namibia's dry lands have been home to people like the San, Damara, and Nama people for thousands of years. These groups lived a nomadic life, moving around to find food and water. Around the 14th century, Bantu people started to arrive from central Africa.
In the late 18th century, the Oorlam people moved into southern Namibia. They met the Nama tribes peacefully. However, further north, the Oorlam met the OvaHerero people, which led to conflicts.
In 1878, the British took control of Walvis Bay and the nearby islands. These areas later became part of South Africa. The first Europeans to explore the coast were Portuguese sailors in the late 1400s, but they didn't claim the land. Later, in the 19th century, traders and settlers from Germany and Sweden arrived. Finnish missionaries also came to spread the Lutheran religion.
German Rule in Namibia
In 1884, Namibia became a German colony called German South West Africa. From 1904 to 1907, the Herero and Nama fought against the German settlers. During this time, a very sad event occurred where many Herero and Nama people were killed. This period is known as the "first genocide of the 20th century." The survivors faced harsh rules, including being forced to work and live in separate areas.
German rule ended during World War I when South African troops took over in 1915. In 2021, the German government officially recognized the genocide and agreed to provide financial support for development projects in Namibia.
South African Control
After World War I, the League of Nations gave South Africa the responsibility to manage South West Africa. South Africa treated the territory as its own and did not prepare it for independence.
In the late 1940s, South Africa started to apply its apartheid system to South West Africa. This meant unfair laws that separated people by race and limited the freedom of Black South West Africans.
During the 1950s and 1960s, groups like the South West African People's Organisation (SWAPO) began to push for Namibia's independence. In 1966, SWAPO started an armed struggle. The United Nations declared South Africa's control over Namibia illegal in 1969. On 12 June 1968, the UN General Assembly officially renamed the territory Namibia.
Namibia's Independence
Namibia gained its independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990. This followed a long period of conflict and negotiations. Walvis Bay and the Penguin Islands, which had remained under South African control, were finally given to Namibia in 1994.
Since independence, Namibia has become a stable parliamentary democracy. The country holds regular elections, and the SWAPO party has won every election since 1990. The transfer of power from one president to the next has been peaceful. For example, Sam Nujoma was the first president, followed by Hifikepunye Pohamba in 2005. In 2014, Hage Geingob became president and was re-elected in 2019. After his passing in February 2024, Nangolo Mbumba became president. In March 2025, Netumbo Nandi-Ndaitwah was sworn in as Namibia's new president, becoming the first female president.
The Namibian government has worked to bring people together after the liberation war. In 1999, a rebel group tried to separate the Caprivi Strip region, but the government stopped this attempt.
Namibia's Land and Environment
Geography of Namibia
Namibia is a large country, covering about 825,615 square kilometers. It has five main geographical areas: the Central Plateau, the Namib Desert, the Great Escarpment, the Bushveld, and the Kalahari Desert.
The Namib Desert is a wide area of dry plains and dunes along Namibia's coast. It is one of the oldest deserts in the world. The Central Plateau runs through the middle of the country and includes Namibia's highest point, Königstein, which is 2,573 meters high.
The Great Escarpment is a steep rise in land that goes up to over 2,000 meters. The Bushveld is in the northeast and gets more rain than other parts of the country. The Kalahari Desert is another well-known feature, extending into South Africa and Botswana. It has different environments, including some green areas.
Namibia's Coastal Desert is famous for its very tall sand dunes, shaped by strong winds. Dense fog often forms along the coast because of the cold Atlantic Ocean water meeting the hot climate.
Major Cities and Towns
Namibia has 13 cities and 26 towns. The capital city, Windhoek, is the largest urban area. Other important cities include Rundu, Walvis Bay, and Swakopmund.
|
Largest cities or towns in Namibia
According to the 2023 Census |
||
|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Pop. |
| 1 | Windhoek | 486,169 |
| 2 | Rundu | 118,625 |
| 3 | Walvis Bay | 102,704 |
| 4 | Swakopmund | 75,921 |
| 5 | Oshakati | 58,696 |
| 6 | Otjiwarongo | 49,022 |
| 7 | Katima Mulilo | 46,401 |
| 8 | Okahandja | 45,159 |
| 9 | Rehoboth | 40,788 |
| 10 | Tsumeb | 34,960 |
Climate and Weather
Namibia has a very dry climate. It gets the least rainfall of any country in sub-Saharan Africa. Most of the country has over 300 sunny days a year. Winter (June–August) is dry. There are two rainy seasons in summer: a small one from September to November, and a bigger one from February to April. Rainfall can vary a lot, and droughts are common. In May 2019, Namibia declared a state of emergency because of a severe drought.
The coastal area's weather is affected by the cold Benguela Current from the Atlantic Ocean. This causes very little rain, frequent dense fog, and cooler temperatures. Sometimes, a hot, dry wind called Bergwind blows from inland to the coast, creating sandstorms.
Water Resources
Namibia is one of the driest countries in Africa and relies heavily on water from underground. The average rainfall is about 350 mm per year. The only rivers that flow all year round are on the country's borders. Inside the country, surface water is only available during the summer rainy months. People who don't live near these rivers depend on groundwater.
Over 100,000 boreholes have been drilled in Namibia. In 2012, a large underground water source called Ohangwena II was found near the border with Angola. Experts believe it could supply water to 800,000 people for 400 years. Namibia also has a project that turns sewage water into safe drinking water, using advanced cleaning methods. In June 2023, Namibia joined an international agreement to protect and use shared water resources.
Wildlife Conservation
Namibia is one of the few countries that has specific rules in its constitution to protect its natural resources and wildlife. The government works with organizations like USAID to help local communities manage wildlife and tourism in a way that helps both people and nature. This is called Community-Based Natural Resource Management (CBNRM).
Animals of Namibia
Namibia is home to many different animals, including the wild dog, dik dik, and the critically endangered black rhino. There are over 200 types of mammals, 645 bird species, and 115 fish species.
Government and People
How Namibia is Governed
Namibia is a democratic republic with a President who is both the head of state and the head of government. The President is elected for a five-year term.
Namibia's government has three main parts:
- Executive: The President and the Cabinet make and carry out laws.
- Legislature: The Parliament has two parts: the National Assembly (lower house) and the National Council (upper house). They make the laws.
- Judiciary: The courts interpret and apply the laws.
While Namibia has a system with many political parties, the SWAPO party has been the main party since independence in 1990. Namibia is considered one of the most democratic countries in Africa.
Namibia's Place in the World

Namibia has its own independent foreign policy. It has strong ties with countries that helped it gain independence, like Cuba. Because it has a small army and economy, Namibia focuses on building strong relationships with other countries in Southern Africa. It is a member of the United Nations and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Military of Namibia
Namibia's military, called the Namibian Defence Force (NDF), was formed by combining former opposing groups after the war. Its job is to protect the country's territory and interests. The NDF is relatively small, with about 7,500 members. In 2017, Namibia signed a UN treaty to ban nuclear weapons.
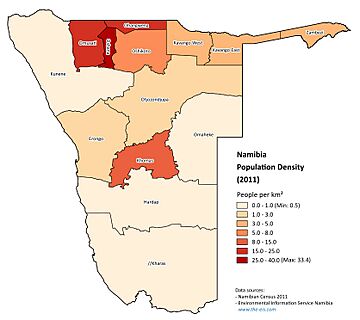
Regions of Namibia
Namibia is divided into 14 regions, which are then split into 121 smaller areas called constituencies. The Khomas and Erongo regions are the most developed, with Khomas being home to the capital, Windhoek.
The table below shows population data from the 2023 census:
| Region | Population (2023) | People per km2 | Average household size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khomas | 494,605 | 13.4 | 3.3 |
| Ohangwena | 337,729 | 31.5 | 4.8 |
| Omusati | 316,671 | 11.9 | 4.2 |
| Oshikoto | 257,302 | 6.7 | 4.1 |
| Erongo | 240,206 | 3.8 | 3.1 |
| Oshana | 230,801 | 26.7 | 3.7 |
| Otjozondjupa | 220,811 | 2.1 | 3.6 |
| Kavango East | 218,421 | 9.1 | 5.3 |
| Zambezi | 142,373 | 9.7 | 3.7 |
| Kavango West | 123,266 | 5.0 | 5.5 |
| Kunene | 120,762 | 1.0 | 3.8 |
| Hardap | 106,680 | 1.0 | 3.6 |
| ǁKaras | 109,893 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| Omaheke | 102,881 | 1.2 | 3.3 |
Human Rights in Namibia
Namibia is known for protecting human rights and freedoms. However, there are still challenges like government corruption and crowded prisons. The country's constitution ensures equal rights for women.
Population and People
Namibia has one of the lowest population densities in the world, with only about 3.08 people per square kilometer in 2017. The country conducts a census every ten years to count its population. The 2023 census counted 3,022,401 people.
Ethnic Groups in Namibia
Namibia has many different ethnic groups. Most of the population belongs to Bantu and Khoisan groups. The Bantu groups include the Ovambo, Herero, and Himba. The Khoisan groups include the Damara, Nama, and San. There are also people of mixed ancestry and a small Chinese minority.
White Namibians, mostly of South African, German, British, and Portuguese descent, make up a small part of the population. Many white Namibians and those of mixed race speak Afrikaans.
Education in Namibia
Namibia offers free primary and secondary education. Primary school is from Grades 1–7, and secondary school is from Grades 8–12. In 1998, there were over 400,000 primary students and over 115,000 secondary students. Namibia spends about 8% of its GDP on education. The country has one of the highest literacy rates in sub-Saharan Africa, with 91.5% of people aged 15 and over able to read and write as of 2018.
Most schools are run by the state, but there are also private schools. Namibia has several universities, including the University of Namibia (UNAM) and the Namibia University of Science and Technology (NUST). Education helps people find jobs, with higher education leading to better employment rates.
Religions in Namibia
Most Namibians (80%–90%) are Christian, with Lutherans being the largest group. This is because of missionary work during colonial times. About 10%–20% of the population follow traditional African beliefs. There are also small communities of Muslims and Jews.
Languages Spoken in Namibia
| Home Languages in Namibia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Languages | percent | |||
| Oshiwambo Languages | 49.7% | |||
| Khoekhoegowab | 11.0% | |||
| Kavango Languages | 10.4% | |||
| Afrikaans | 9.4% | |||
| Herero Languages | 9.2% | |||
| Lozi Languages | 4.9% | |||
| English | 2.3% | |||
| Other | 1.0% | |||
| San Languages | 0.7% | |||
| German | 0.6% | |||
| Other African Languages | 0.5% | |||
| Tswana | 0.3% | |||
| Other European Languages | 0.1% | |||
Most Namibians can speak and understand English and Afrikaans. Before independence in 1990, English, German, and Afrikaans were official languages. After independence, English became the only official language, even though only 2.3% of the population speaks it at home. This was done to unite the country. Some other languages are used in primary schools.
According to a 2016 survey, Oshiwambo is the most spoken language in homes (49.7%). Khoekhoegowab is next at 11.0%, followed by Kavango Languages at 10.4%. Afrikaans is widely used as a common language, spoken by 9.4% of households. German is still used in business. Many people also speak Portuguese due to the country's closeness to Angola.
Health in Namibia
Life expectancy in Namibia was estimated to be 64 years in 2017. The country has a National Health Extension Programme to train health workers who help communities with health activities like first aid and disease prevention.
Namibia faces health challenges like high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity. The country has also made progress in fighting the HIV epidemic, with efforts to expand treatment services.
Namibia's Economy

Namibia's economy is closely linked to South Africa's. In 2023, the biggest parts of the economy were mining (18.0% of GDP), public administration (12.9%), and manufacturing (10.1%).
Namibia has a modern banking system. However, there's a big difference between the formal economy (with jobs and businesses) and the informal economy (where people might trade goods or services without official records).
Unemployment is a challenge, especially for young people. In 2018, the overall unemployment rate was 33.4%, and youth unemployment was 38.4% in 2023. The government is trying to encourage businesses to offer more internships to help young people find jobs.
Poverty and inequality are still big issues. In 2015, Namibia had one of the highest rates of income inequality in the world. The government is working to attract foreign investment by making it easier to do business in the country.
The cost of living in Namibia is a bit higher than average because many goods have to be imported. Taxes in Namibia are generally lower than in South Africa, especially for higher incomes.
Namibia has good transportation networks, including seaports, airports, highways, and railways. It's an important hub for trade with its landlocked neighbors.
Farming in Namibia

About half of Namibia's population depends on farming for their living, mostly growing food for themselves. However, Namibia still needs to import some of its food. A small number of commercial farmers own almost half of the country's farmland. The government is working on land reform to give land to more Black Namibians.
Mining and Energy

Mining is very important to Namibia's economy, providing 25% of the country's income. Namibia is a major exporter of minerals, especially uranium and high-quality diamonds. Other minerals mined include lead, gold, copper, and zinc. There are also offshore gas deposits that might be extracted in the future.
Namibia has managed to develop its diamond mining industry without the conflicts seen in some other African countries. This is due to good agreements between the government and the diamond company De Beers. Recent discoveries of oil in the Orange Basin could bring significant revenue to Namibia.
Most of Namibia's electricity comes from thermal and hydroelectric power plants. The country also has plans to build its first nuclear power station.
Tourism in Namibia

Tourism is a big part of Namibia's economy, creating many jobs and attracting over a million tourists each year. Namibia is known for ecotourism, which focuses on enjoying the country's amazing wildlife and natural beauty.
There are many lodges and reserves for ecotourists. Hunting is also a growing part of the tourism economy. People also enjoy extreme sports like sandboarding and skydiving. Popular places to visit include Windhoek, the Fish River Canyon, Sossusvlei, the Skeleton Coast Park, and the coastal towns of Swakopmund and Walvis Bay.
Windhoek is important for tourism because of its central location and closeness to the main international airport. The Namibia Tourism Board (NTB) helps regulate the tourism industry and promotes Namibia as a tourist destination.
Water Supply and Sanitation
NamWater is the main supplier of water in Namibia, selling it to cities and towns. In rural areas, the government helps provide drinking water. The UN has noted that Namibia has improved its water access since 1990. However, the cost of water and long distances to water points can still be a problem for many people.
Compared to water access, sanitation (toilets and waste disposal) is still a challenge in Namibia. Many schools lack toilets, and poor sanitation contributes to health problems. In rural areas, many people still don't have proper toilets.
Culture and Sports
Namibian Culture
Namibian culture is similar to South African culture because of their shared history. Namibians generally prefer to stay in their home country and have a strong national identity. They are known for being very social.
Sports in Namibia
The most popular sport in Namibia is association football. The Namibia national football team has played in the Africa Cup of Nations several times.
The Namibian rugby team is very successful, having competed in the last seven Rugby World Cups. Cricket in Namibia is also popular, with the national team playing in the 2003 Cricket World Cup and other international tournaments.
Individual athletes from Namibia have also achieved great success. Frankie Fredericks is a famous sprinter who won four Olympic silver medals. Golfer Trevor Dodds and boxer Julius Indongo are other notable Namibian athletes.
Media in Namibia
Namibia has a good level of media freedom compared to its neighbors. It often ranks high in the Press Freedom Index. The country has two TV stations, 19 radio stations, and 5 daily newspapers. Many foreign media outlets, especially from South Africa, are also available.
The first newspaper in Namibia was the German-language Windhoeker Anzeiger, started in 1898. During colonial times, newspapers mostly showed the views of the white minority. Today, daily newspapers include The Namibian (English and other languages), Die Republikein (Afrikaans), Allgemeine Zeitung (German), and Namibian Sun (English). The state-owned Namibian Broadcasting Corporation (NBC) runs a TV station and several radio services in local languages.
Art in Namibia
The National Art Gallery of Namibia displays Namibian, African, and European art. In 2022, Namibia participated in the Venice Biennale, a major international art exhibition, for the first time.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Namibia para niños
In Spanish: Namibia para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |