Paraguay facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Paraguay
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: Paz y justicia (Spanish)
"Peace and justice" |
|
|
Anthem:
Himno Nacional Paraguayo (Spanish) "Paraguayan National Anthem" |
|
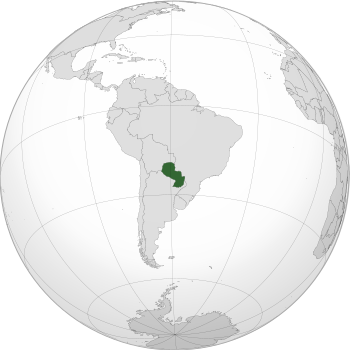
Location of Paraguay (dark green)
in South America (grey) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Asunción 25°16′S 57°40′W / 25.267°S 57.667°W |
| Official languages |
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Paraguayan |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| Santiago Peña | |
| Pedro Alliana | |
|
• President of the Senate
|
Silvio Ovelar |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Independence from Spain | |
|
• Declared
|
14 May 1811 |
|
• Recognized
|
25 November 1842 |
| 20 June 1992 | |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
406,752 km2 (157,048 sq mi) (59th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
2.6 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
6,218,879 (113th) |
|
• 2022 census
|
6,109,903 |
|
• Density
|
39/sq mi (15.1/km2) (223rd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2022) | 45.1 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 105th |
| Currency | Guaraní (PYG) |
| Time zone | UTC–3 (PYT) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +595 |
| ISO 3166 code | PY |
| Internet TLD | .py |
Paraguay, officially known as the Republic of Paraguay, is a country in South America. It is a landlocked country, meaning it has no coastlines. Paraguay shares borders with Argentina to the south, Brazil to the east, and Bolivia to the northwest.
About 6.1 million people live in Paraguay. Nearly 2.3 million of them live in the capital city, Asunción, and its surrounding areas. Paraguay is a developing country, ranking 105th in the Human Development Index. It is a founding member of important groups like Mercosur and the United Nations.
Even though Paraguay is landlocked, it has ports on the Paraguay and Paraná rivers. These rivers connect to the Atlantic Ocean through the Paraná-Paraguay Waterway. Most of Paraguay's people are mestizo, which means they have mixed European and Indigenous heritage. The Guarani culture is very important here. More than 90% of people speak different types of Guarani along with Spanish.
Contents
- Paraguay's Past: A Look at History
- What's in a Name? The Meaning of Paraguay
- Exploring Paraguay's Geography
- Paraguay's Climate and Weather
- How Paraguay is Governed
- Paraguay's Regions and Departments
- Paraguay's Economy: How People Make a Living
- Paraguayan Culture: A Mix of Traditions
- Delicious Paraguayan Cuisine
- Images for kids
- See also
Paraguay's Past: A Look at History
The Guaraní lived in eastern Paraguay for at least 1,000 years before the Spanish arrived. In western Paraguay, the Gran Chaco region was home to nomadic groups. The Paraguay River generally separated the farming Guarani people in the east from the nomadic groups in the west. These nomadic groups were known for being strong warriors. They were not fully settled until the late 1800s.
Spanish explorers arrived in 1524. In 1537, they founded Asunción, which became an important city. During the 1600s, Jesuit missions were set up in Paraguay. Here, the native Guaraní people learned about Christianity and European culture. After the Jesuits left in 1767, Paraguay became less central to the Spanish Empire.
Paraguay gained independence from Spain in the early 1800s. After independence, the country was led by a series of strong governments. This period ended with the difficult Paraguayan War (1864–1870). During this war, Paraguay lost about half of its people and a lot of its land.
In the 1900s, Paraguay had another big conflict called the Chaco War (1932–1935) against Bolivia. Paraguay won this war. Later, the country was led by military leaders, including Alfredo Stroessner for 35 years. He was removed from power in 1989, which started Paraguay's current democratic period.
What's in a Name? The Meaning of Paraguay
The name Paraguay comes from the Guarani words paraguá and y. Paraguá means "feather crown" and y means "water". So, Paraguaí means "feather crown of waters".
Exploring Paraguay's Geography

Paraguay is divided into two main areas by the Río Paraguay. The eastern part is called the Región Oriental. The western part is officially called Western Paraguay (Región Occidental) and is also known as the Gran Chaco. The country is located between 19° and 28° South latitude, and 54° and 63° West longitude.
The eastern region has mostly grassy plains and wooded hills. The western part has low, marshy plains.
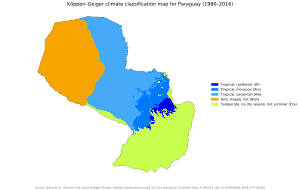
Paraguay's Climate and Weather
Paraguay has a tropical to subtropical climate. Like many places in this region, it has wet and dry seasons. Winds greatly affect Paraguay's weather. From October to March, warm winds blow from the Amazon Basin in the North. From May to August, cold winds come from the Andes mountains.
There are no large mountain ranges to block the winds, so they can reach speeds of up to 161 km/h (100 mph). This also means temperatures can change a lot very quickly. Between April and September, temperatures can sometimes drop below freezing. January is the hottest summer month, with an average daily temperature of 28.9 degrees Celsius (84 degrees F).
Rainfall varies across the country. The eastern forests get a lot of rain, about 170 cm (67 inches) annually. The western Chaco region gets much less, usually no more than 50 cm (20 inches) a year. The rain in the west is often irregular and dries up quickly, making the area quite dry.
Amazing Animals of Paraguay
Paraguay is home to many interesting animals. These include marsh deer, monkeys, armadillos, anteaters, otters, wild boars, tapirs, jaguars, ocelots, bats, and the coypu.
How Paraguay is Governed
Paraguay is a representative democratic republic. This means that citizens elect people to represent them in government. The government has a multi-party system, where different political parties can exist. Power is divided into three main parts:
- Executive Power: This is held by the President, who is both the head of state and the head of government.
- Legislative Power: This power belongs to the National Congress, which has two parts: the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. They make the laws.
- Judicial Power: This is held by tribunals and Courts, including a nine-member Supreme Court of Justice. They make sure laws are followed and are independent of the other two branches.
Paraguay's Regions and Departments
Paraguay is divided into 17 departments and one special capital district (Distrito Capital). These departments are further divided into smaller areas called districts.
The departments are grouped into two geographic regions, separated by the Paraguay river:
- Occidental (Western) region or Chaco: This is to the north of the Paraguay river. It includes the departments of Alto Paraguay, Boquerón, and Presidente Hayes.
- Oriental (Eastern) region: This is to the south of the Paraguay river. It includes many departments like Alto Paraná, Amambay, and Central. The capital district is also part of this region.
Paraguay's Economy: How People Make a Living
100% of Paraguay's electricity comes from hydroelectricity, which uses the power of water. This makes it one of the cleanest energy producers in the world!
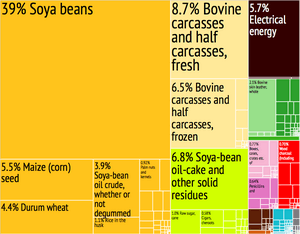
Paraguay is a big producer of several important crops and goods:
- It's the sixth-largest producer of soybeans in the world.
- It's the second-largest producer of stevia (a natural sweetener).
- It's the second-largest producer of tung oil.
- It's the sixth-largest exporter of corn.
- It's the tenth-largest exporter of wheat.
- It's the eighth-largest exporter of beef.
The city of Ciudad del Este has one of the world's most important free trade zones. Many people in Paraguay, especially in rural areas, earn their living from farming.
Industries and Factories in Paraguay

The mineral industry of Paraguay makes up about 25% of the country's total economic output (GDP). It also employs about 31% of the workers. Factories in Paraguay commonly produce cement, iron ore, and steel.
In the pharmaceutical industry (making medicines), Paraguayan companies now produce 70% of the medicines needed in the country. They have even started to export drugs to other countries. Paraguay is quickly becoming a major supplier for its own medicine needs. Other areas showing strong growth include making edible oils, clothes, organic sugar, processed meat, and steel.
Paraguayan Culture: A Mix of Traditions
Paraguay's culture comes from a mix of Spanish settlers and native Guaraní women. It is also influenced by other European countries. So, Paraguayan culture is a blend of European and Southern Guaraní traditions. More than 93% of Paraguayans are mestizos, making Paraguay one of the most culturally similar countries in Latin America.
A special part of this cultural mix is that most people speak two languages. More than 80% of Paraguayans speak both Spanish and the native language, Guaraní. Jopara, a mix of Guaraní and Spanish, is also widely spoken.
This cultural blend can be seen in arts like embroidery (ao po'í) and lace making (ñandutí). The music of Paraguay includes lively polkas, bouncy galopas, and gentle guaranias, often played on the native harp.
Paraguay's food also shows this cultural mix. Many popular dishes use manioc, a local root crop similar to yuca. A famous dish is sopa paraguaya, which is like a thick corn bread. Another well-known food is chipa, a bread similar to a bagel made from cornmeal, manioc, and cheese. Many other dishes use different kinds of cheeses, onions, bell peppers, milk, and fresh corn.
In the 1950s and 1960s, new Paraguayan writers and poets became famous. These included José Ricardo Mazó, Roque Vallejos, and Augusto Roa Bastos, who was nominated for a Nobel Prize. Several Paraguayan films have also been made.
Delicious Paraguayan Cuisine
Popular Dishes to Try

- Dumplings are a common food.
- Chipa is a bread made with manioc, egg, and cheese. In Argentina, it's called chipá, and in Bolivia, cuñapé.
- Chipa Guasú is a cake made with corn grains. It's a traditional and common food in Paraguay, often served at barbecues (asado).
- Chipa so'o is another type of cake.
- A traditional kiveve is made with pumpkin, water, salt, oil, onion, milk, sugar, corn flour, and fresh cheese.
- Lampreado, also known as Payaguá Mascada, is a fried cake made from manioc flour.
- Mazamorra is a cooked corn mush dish.
- Mbaipy-so-ó is a corn pudding with meat.
- Mbejú is a starch cake and a very common food in the Paraguayan diet.
- Milanesa is a breaded meat cutlet that can be fried, baked, or sautéed.
- Authentic Paraguay cheese is a local specialty.
- Parrillada is a dish of meat cooked over hot banana leaves and coals.
- Pira caldo is a fish soup that is part of the traditional cuisine.
- Sopa paraguaya is a traditional Paraguayan dish. Even though it's called "Paraguayan soup," it's actually similar to corn bread. It's made with corn flour, pig fat (lard) or butter, cheese, and milk. It's a spongy cake rich in calories and protein, and it's the national dish of Paraguay. You can also find this dish in other Spanish-speaking countries.
- Soyo is a thick soup made from meat crushed in a mortar, seasoned with different spices and vegetables.
- Vori vori is a thick, yellow soup with small balls made of cornmeal, corn flour, and cheese.
Sweet Treats and Desserts
- There are many different kinds of cakes.
- Kosereva is a common candy native to Paraguay. It's made from the hardened skin of the sour orange, cooked in black molasses. It has a bittersweet and tangy taste and is high in protein.
- Mbaipy-he-é is a dessert made with milk, molasses, and corn.
- Dulce de leche means "sweet [made] of milk." It's used to fill cakes, spread on toast for breakfast, or with other baked goods. It's especially good with small coconut candies or buttered biscuits.
Images for kids
-
José Gaspar Rodríguez de Francia, Paraguay's first leader.
-
The Gran Chaco was where the Chaco War (1932–35) happened.
-
Inauguration of former President Horacio Cartes, 15 August 2013.
-
Nacunday National Park, Southern Paraguay.
-
San Bernardino, Paraguay is an important resort town in Paraguay.
-
A gathering in Caacupé.
-
Main Catholic Chapel in Concepción, Paraguay.
See also
 In Spanish: Paraguay para niños
In Spanish: Paraguay para niños