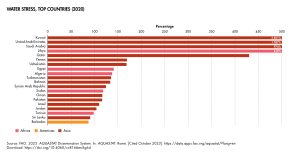Tunisia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Republic of Tunisia
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: حرية، نظام، عدالة
"Ḥurrīyah, Niẓām, 'Adālah" "Freedom, Order, Justice" |
|
Location of Tunisia in North Africa
|
|
 |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Tunis 36°49′N 10°11′E / 36.817°N 10.183°E |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Local vernacular | Tunisian Arabic |
| Foreign languages | French and English |
| Ethnic groups
(2021)
|
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Tunisian |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| Kais Saied | |
| Sara Zaafarani | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| National Council of Regions and Districts | |
| Assembly of the Representatives of the People | |
| Establishment | |
| 814 BC | |
|
• Husainids
|
15 July 1705 |
|
• Independence and Kingdom
|
20 March 1956 |
| 25 July 1957 | |
|
• Current Constitution
|
25 July 2022 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
163,610 km2 (63,170 sq mi) (91st) |
|
• Water (%)
|
5.04 |
| Population | |
|
• 2020 estimate
|
11,708,370 (81st) |
|
• Density
|
71.65/km2 (185.6/sq mi) (144th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2021) | ▼ 33.7 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 101st |
| Currency | Tunisian dinar (TND) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +216 |
| ISO 3166 code | TN |
| Internet TLD |
|
Tunisia, officially known as the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in North Africa. Its capital city is Tunis.
Tunisia is part of many important international groups. These include the United Nations, the Arab League, and the African Union. It also has strong ties with European countries like France and Italy. This is because they are close geographically. Tunisia also has a special agreement with the European Union. It is also a major non-NATO ally of the United States. This means it's a close friend to the U.S. even though it's not part of the NATO military alliance.
Contents
History of Tunisia
Ancient Times
For a very long time, Berber tribes lived in the area that is now Tunisia. Many of them built small towns and ports along the coast. This helped them trade with travelers from all over the Mediterranean Sea.
Around the 10th Century BC, people called Phoenicians started to settle on the Tunisian coast. Later, in the 8th Century BC, they built the famous city of Carthage. After many wars, Carthage became very powerful in the Mediterranean Sea by the 6th Century BC.
However, Carthage had big wars with the Roman Empire. These wars are known as the Punic Wars. During the Second Punic War, a famous Carthaginian general named Hannibal even invaded Italy. The wars ended in the 2nd Century BC with the Romans destroying Carthage. After that, the region became part of the Roman Empire.
When the Roman Empire became weak, a group called the Vandals took control in the 5th Century AD. About 100 years later, the Byzantine Empire took over.
The Start of Islam
In the 7th Century, Arab Muslims conquered the region. They built a new city called Kairouan. Kairouan was the first Arab Muslim city in Tunisia.
Many Muslim ruling families, called dynasties, ruled Tunisia. One important dynasty was the Zirids. They were a Berber dynasty who followed the rules of the Fatimids, a larger dynasty based in Cairo. When the Zirids angered the Fatimids, the Fatimids sent tribes who caused a lot of destruction in Tunisia.
Later, the Normans from Sicily briefly occupied Tunisia in the 12th Century. Then, the Almohad dynasty took control. After them came the Hafsids. As the Hafsids became weaker, Spain took over many coastal cities. Finally, the Ottoman Empire took full control.
In 1705, Tunisia became almost independent under the Hussein dynasty. However, they still had to follow some orders from the Ottoman Empire.
French Control
In the mid-1800s, the ruler of Tunisia made some financial decisions that led the country into debt. This allowed France to gain control. Tunisia officially became a French protectorate on May 12, 1881. This meant France protected and controlled Tunisia's foreign affairs.
Tunisia in World War II
Important battles of World War II happened in Tunisia. General Rommel, a German leader, wanted to defeat the Allies there.
On February 19, 1943, General Rommel attacked U.S. forces. This was a difficult time for the United States. Many U.S. soldiers who died in these battles are buried in war graves in western Tunisia.
After this, the Allies learned how important tank warfare was. They then broke through German lines in southern Tunisia on March 20, 1943.
Independence and Revolution
Tunisia gained its independence in 1956. Habib Bourguiba became the first president. In 1957, Tunisia became a republic. Bourguiba focused on improving education and the economy. He also supported women's rights. However, he held most of the power himself.
In 1987, Zine el Abidine Ben Ali took power from Bourguiba. Ben Ali ruled as a dictator until 2011. In 2011, a revolution overthrew him. This revolution was the first big event of the Arab Spring, a series of protests across the Arab world. After the revolution, Tunisia started to become more democratic. In 2014, the country held its first free presidential election.
Geography and Climate
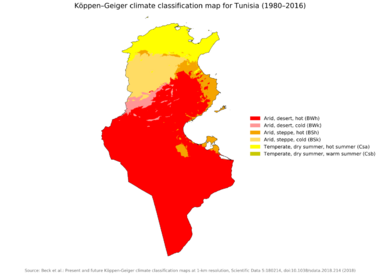
Tunisia is located on the Mediterranean Sea coast in Northwest Africa. It is between the Atlantic Ocean and the Nile Delta. Algeria borders it to the west, and Libya to the southeast.
Even though it's a relatively small country, Tunisia has many different environments. This is because it stretches from north to south. The northern part of Tunisia has a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers. Most of the country to the south is desert.
The Atlas Mountains extend into Tunisia, forming a range called the Dorsal. North of the Dorsal are low hills and plains. In the northwest, elevations can reach 1,050 meters (3,440 feet), and it snows in winter.
The Sahel, a coastal plain along Tunisia's eastern Mediterranean coast, is famous for growing olives. Inland from the Sahel are the Steppes. Much of the southern region is semi-arid and desert.
Tunisia has a long coastline, about 1,148 kilometers (713 miles) long. The city of Tunis is built on a hill that slopes down to Lake Tunis.
Water Resources
Tunisia faces challenges with water supply. It is ranked as one of the most water-stressed countries in the world.
Nature and Wildlife
Tunisia has five main types of natural environments. These include Mediterranean forests, dry woodlands, and steppes. There are also areas of desert and semi-desert plants.
People and Languages
Standard Arabic is the official language of Tunisia. However, most Tunisians speak Tunisian Arabic. This local language is a mix of many languages from people who have lived in Tunisia over time. It is also called Darija or Tunsi.
A small number of people in Tunisia still speak a Berber language called Shelha.
Most people living in Tunisia today are Maghrebin Arabs. However, there are also small groups of Berbers and Jews.
The Tunisian constitution states that Islam is the official state religion. It also says that the President must be a Muslim.
Government and Politics
Tunisia is a presidential republic. This means it has a president who is the head of the country. There is also a prime minister who leads the government. The country has a two-house parliament and a civil law court system.
After gaining independence in 1956, Tunisia adopted a "Code of Personal Status." This set of laws gave women full legal rights. For example, women could own businesses, have bank accounts, and get passports on their own. The code also made polygamy (having more than one spouse) illegal. It also stopped husbands from divorcing their wives without a good reason. In 1993, more changes allowed Tunisian women to pass on their citizenship to their children, even if they were married to a foreigner. This Code of Personal Status is one of the most advanced civil laws in North Africa and the Muslim world.
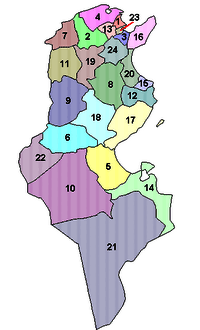
Regions of Tunisia
Tunisia is divided into 24 areas called governorates. These are:
Major Cities

Here are the largest cities in Tunisia:
| Nr. | City | Population | Governatorate |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Tunis |
983,861
|
Tunis |
|
|
Sfax |
855,256
|
Sfax |
|
|
Kairouan |
546,209
|
Kairouan |
|
|
Sousse |
544,413
|
Sousse |
|
|
Ettadhamen |
422,246
|
Ariana |
|
|
Gabès |
342,630
|
Gabès |
|
|
Bizerte |
114,371
|
Bizerte |
|
|
Aryanah |
97,687
|
Ariana |
|
|
Gafsa |
84,676
|
Gafsa |
|
|
El Mourouj |
81,986
|
Ben Arous |
Economy and Trade
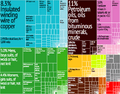
Tunisia has a varied economy. It includes farming, mining, and making things like clothes and car parts. Tourism is also a big part of the economy. In 2009, tourism made up 7% of the country's total income. It also created 370,000 jobs.
The farming sector makes up about 11.6% of the economy. Industry makes up 25.7%, and services (like tourism and banking) make up 62.8%. Even though Tunisia's economy has grown by about 5% each year, many young people still struggle to find jobs.
The European Union is Tunisia's main trading partner. About 72.5% of what Tunisia buys comes from the EU. And 75% of what Tunisia sells goes to the EU. Tunisia is one of the EU's most important trading partners in the Mediterranean region.
In 2024, Tunisia was ranked 81st in the Global Innovation Index. This index measures how innovative countries are.
Culture and Arts
Tunisia's culture is a mix of many influences. Over a long history, different groups of people have left their mark. These include Phoenicians, Romans, Arabs, Turks, and the French.
Painting and Art
Modern Tunisian painting started with the School of Tunis in 1949. This group of artists wanted to use local themes in their art. They did not want to copy European styles. The group included French, Tunisian Muslim, Christian, and Jewish artists.
After Tunisia became independent in 1956, the government supported the arts. A Ministry of Culture was created. Many Tunisian artists became famous around the world. Today, there are about fifty art galleries in Tunisia. They show works by both Tunisian and international artists.
Literature and Books

Tunisian literature is written in two languages: Arabic and French. Arabic literature has been around since the 7th century. French literature started when France controlled Tunisia from 1881. Arabic literature is generally more important in Tunisia.
Famous Tunisian writers include Ali Douagi, who wrote many radio stories and poems. Khraief Bashir wrote novels that caused a stir because they used the Tunisian dialect.
Tunisian poetry often tries new things. A well-known poet is Aboul-Qacem Echebbi.
Many Tunisian writers who write in French live outside Tunisia. Their stories often talk about travel, being away from home, and memories.
In 2007, about 1,700 non-school books were published in Tunisia. Almost a third of these books were for children.
Music and Sounds
In the early 1900s, Tunisian music included religious songs and traditional Andalusian styles. In 1930, a group called The Rachidia was formed. They helped bring back Arab Andalusian music. This was important for Tunisian national identity.
When Radio Tunis started in 1938, it helped musicians share their work. The station played mostly Tunisian music.
Some famous Tunisian musicians are Saber Rebaï, Dhafer Youssef, and Emel Mathlouthi.
Festivals and Celebrations
Tunisia has many festivals throughout the year. Music and theater festivals are very popular.
Some big festivals happen every summer:
- The International Festival of Carthage in July.
- The International Festival of Arts of Mahr from late July to early August.
- The International Festival of Hammamet in July and August.
The Carthage Film Festival happens every other year in October and November. It shows films from the Maghreb, Africa, and the Middle East. The top prize is the Tanit d'or, named after an ancient goddess.
The International Festival of the Sahara is held every December. It celebrates the traditions of the Tunisian desert. Many tourists and musicians come to this festival.
The Carnival of Awussu is an annual event in Sousse on July 24. It's a parade with chariots and folk groups. It happens before the hottest part of August. This festival has ancient roots, possibly going back to Pagan times.
Omek Tannou is an old Tunisian rainmaking festival. It comes from ancient Punic and Berber traditions. Children carry a doll-like figure through villages during dry times. They sing a song asking for rain. Each housewife then pours a little water on the figure.
Sports and Games
Football (soccer) is the most popular sport in Tunisia. The Tunisia national football team, also called "The Eagles of Carthage," won the 2004 African Cup of Nations (ACN). They also played in the 2005 FIFA Confederations Cup.
Tunisia's top football league is the Tunisian Ligue Professionnelle 1. Some of the main clubs are Espérance Sportive de Tunis and Étoile Sportive du Sahel.
The Tunisia men's national handball team is very strong. They came fourth in the 2005 World Championship. The national league has about 12 teams. The most famous Tunisian handball player is Wissem Hmam. He was the top scorer in the 2005 Handball Championship. The Tunisian national handball team has won the African Cup ten times.
Tunisia's national basketball team is also one of the best in Africa. They won the 2011 Afrobasket tournament. Tunisia was one of the first countries in Africa to have a competitive basketball league.
In boxing, Victor Perez was a world champion in 1931 and 1932.
In swimming, Oussama Mellouli won a gold medal at the 2008 Summer Olympics. He won another gold medal and a bronze medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Tunisia's Paralympic team has also done very well. In the 2012 Summer Paralympics, they won 19 medals, including 9 gold medals. They were ranked 14th overall.
Recently, tennis has become very popular in Tunisia. This is thanks to tennis player Ons Jabeur. She reached a high ranking of number 3 in the world. She also made it to three Grand Slam finals, including two at Wimbledon.
Images for kids
-
Ruins of Dougga's World Heritage Site.
-
Carthaginian-held territory before the first First Punic War
-
Ruins of Carthage
-
Domes of the Great Mosque of Kairouan. Founded in 670, it dates in its present form largely from the Aghlabid period (9th century). It is the oldest mosque in the Maghreb.
-
Conquest of Tunis by Charles V and liberation of Christian galley slaves in 1535
-
Tunis on 14 January 2011 during the Tunisian Revolution.
-
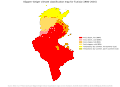
Köppen climate classification in Tunisia. The climate is Mediterranean towards the coast in the north, while most of the country is desert.
-
Sadiki College in Tunis.
See also
 In Spanish: Túnez para niños
In Spanish: Túnez para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |