Arabs facts for kids
| Arabic: عَرَب (ʿarab) | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Total population | |
c. 400 million to 420+ million
|
|
| Regions with significant populations | |
| 350,000,000 | |
| 11,600,000–20,000,000 | |
| 5,500,000–7,000,000 | |
| 5,000,000 | |
| 3,700,000 | |
| 3,500,000 | |
| 3,200,000 | |
| 2,080,000 | |
| 1,800,000 | |
| 1,600,000–4,000,000 | |
| 1,600,000 | |
| 1,401,950 | |
| 1,350,000 | |
| 1,100,000 | |
| 800,000 | |
| 750,925 | |
| 705,968 | |
| 543,350 | |
| 500,000 | |
| 500,000 | |
| 480,000–613,800 | |
| 300,000 | |
| 280,000 | |
| 170,000 | |
| 150,000 (2006) | |
| 121,000 | |
| 118,866 (2010) | |
| 100,000 | |
| 80,000 (2010) | |
| 75,000 | |
| 70,000 | |
| 59,021 (2019) | |
| 30,000 | |
| Languages | |
| Arabic | |
| Religion | |
Predominantly:
|
|
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Other peoples of the Middle East and North Africa | |
The Arabs (Arabic: عَرَب) are a large group of people who mostly live in the Arab world, which stretches across West Asia and North Africa. Many Arabs also live in other parts of the world, forming what is known as the Arab diaspora.
Arabs have a very long history, going back thousands of years. Ancient writings from the 9th century BCE mention Arabs living in places like the Levant and Mesopotamia. Over time, Arabs built important civilizations such as Dilmun and Gerrha. They played a big role in trade across ancient regions. Some famous ancient tribes like Midian and Thamud are even mentioned in the Bible and Quran.
Later, powerful kingdoms like Saba and Himyar grew in Arabia. In ancient times, groups like the Nabataeans and the Palmyrene Empire (led by Queen Zenobia) built impressive kingdoms. Many Arab tribes in later ancient times, such as the Tanukhids and Ghassanids, became Christian.
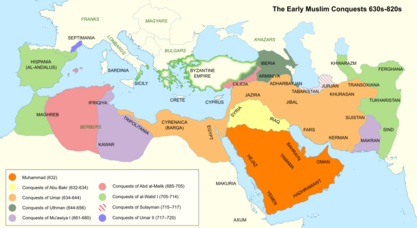
During the Middle Ages, the rise of Islam brought Arabs together. This led to the creation of large Arab empires like the Rashidun, Umayyad, and Abbasid empires. These empires spread from southern France to western China, becoming some of the biggest in history. In the early 1900s, the Arab Revolt helped break up the Ottoman Empire. This led to the formation of the Arab League in 1945, which aimed for a "unified Arab homeland."
Today, Arabs from Morocco to Iraq share many things in common. These include their language (Arabic), culture, history, and identity. They also share customs, literature, music, dance, food, and architecture. Arabs have made huge contributions to human progress in many areas, like science, technology, philosophy, and literature. Before Islam, most Arabs followed ancient polytheistic religions, but some tribes were Jewish or Christian. Now, about 93% of Arabs are Muslims, and most of the rest are Arab Christians.
Contents
What Does "Arab" Mean?

The first time the word Arab was written down was in the 9th century BCE. An ancient record from Assyria used the term to describe Bedouin people from the Arabian Peninsula. It mentioned a king named Gindibu who fought against Assyria with 1,000 camels.
The word ʾaʿrāb is still used today to mean Bedouins, while ʿArab refers to Arabs in general. Both words appear in ancient inscriptions from the Sabaeans. The oldest sign of an Arab national identity is an inscription from 328 CE. It uses an old form of Arabic to call Imru' al-Qays ibn 'Amr the 'King of all the Arabs'.
Ancient Greek historians like Herodotus also wrote about Arabs living in different regions. Some Arab stories say the word Arab comes from a father named Ya'rub, who was the first to speak Arabic. Another idea is that Mesopotamians called Arabs gharab (meaning 'westerners') because they lived west of Mesopotamia. This word then changed to Arab.
Where Did Arabs Come From?

Arabic is a Semitic language, part of the Afroasiatic language family. Many experts believe that the Arabian Peninsula is where Semitic languages first began. From there, these languages spread to other areas. Old Arabic started to become different from other Semitic languages around 1000 BCE.
Abrahamic Traditions
According to Jewish, Christian, and Islamic traditions, Ishmael is seen as the father of the Arabs. He was the son of Abraham and Hagar. The Bible says that God promised Hagar that Ishmael would have many descendants and become a "great nation."
In Islam, Ishmael (called Ibrahim) is believed to be an ancestor of the prophet Muhammad. The Quran tells how Ibrahim brought Hagar and Ishmael to Mecca. There, God provided them with water. Later, Ibrahim and Ishmael built the Kaaba in Mecca, which is a very important holy site in Islam.
A Look at Arab History
Arabs have lived in the desert areas around the Fertile Crescent since at least 3000 BCE. The first clear mention of Arabs as a group is from an Assyrian record in 853 BCE. This record describes a battle.
Ancient civilizations like Dilmun and Gerrha were important trading centers. They helped connect Mesopotamia with the Mediterranean Sea. The Thamud tribe was known for its wealth and advanced technology. The Qedarites were a powerful group of nomadic Arabs. Their kingdom covered a large area in northern Arabia and southern Palestine.

The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who settled around Petra in modern-day Jordan. They were among the first to write in Arabic. Their alphabet later developed into the modern Arabic script. The Palmyrene Empire, led by Queen Zenobia, was another powerful Arab kingdom in Syria. It briefly controlled a large area before being defeated by the Romans.
Arab Empires and the Spread of Islam
The rise of Islam began in the 7th century with the prophet Muhammad. After his death, the Rashidun Caliphate was formed. This was a new kind of state that grew very quickly. Under its leaders, the Arab community expanded, conquering vast territories like Egypt, Syria, and Iraq. This marked the start of the Arab empire.
The Umayyad Empire (661–750 CE)
After the Rashidun era, the Umayyad dynasty took control. They made Damascus their capital. The Umayyads were proud of their Arab heritage. They made Arabic the official language of the empire in 686 CE. The Umayyad Empire expanded west, taking over North Africa and parts of Spain. In Spain, their last kingdom became the Caliphate of Córdoba, which was a center of trade, culture, and knowledge.
The Abbasid Empire (750–1258 CE)
The Abbasids took over from the Umayyads. They moved the capital to Baghdad. The Abbasids were supported by many non-Arab people. This period is often called the "Islamic Golden Age." Baghdad became a major center for science, philosophy, medicine, and education. The Abbasids built the "House of Wisdom" in Baghdad, where scholars translated and studied many important texts.
During this time, Arab scholars made huge advancements in many fields. Other cities like Cairo and Córdoba also became important centers of learning. The Abbasid Empire eventually weakened and was conquered by the Mongols in 1258.
The Fatimid Empire (909–1171 CE)
The Fatimid Caliphate was a Shia Islamic empire that started in North Africa and later moved its capital to Cairo. The Fatimids were known for being religiously tolerant and for their intellectual achievements. They built universities and libraries that became important learning centers. One of their most famous achievements is the Al-Azhar Mosque and University in Cairo, which is one of the oldest universities in the world.
The Ottoman Era (1517–1918 CE)
From 1517, the Ottoman Empire took control of much of the Arab world. For centuries, Arabs lived under Ottoman rule. In the early 1900s, Arab thinkers and politicians started a movement called Arab nationalism. They wanted more freedom or even full independence from the Ottoman Empire.

During World War I, the Arab Revolt began in 1916. It was led by Sherif Hussein bin Ali. The goal was to gain independence for Arab lands. This revolt helped weaken the Ottoman Empire. After the war, the Sykes–Picot Agreement divided Arab territories between France and Britain, which ignored the Arab people's wish for independence.
The Modern Period
The modern period of Arab history began in the late 1800s. The collapse of the Ottoman Empire led to the creation of new Arab nations. Arab nationalism grew, aiming to unite all Arabs. This led to the formation of the Arab League after World War II.
Many attempts were made to create a single Arab state, like the United Arab Republic (Egypt and Syria). However, these unions often faced challenges and did not last. In recent years, the Arab world has faced new issues, including economic problems and political changes. The Arab Spring in 2010-2011 saw protests for democracy, which led to big changes and sometimes conflict in many Arab countries.
Arab Identity
Being Arab is about more than just religion. There were Arab Christian kingdoms and Arab Jewish tribes long before Islam spread widely. Today, most Arabs are Muslim, but many are Christian, and smaller groups are Druze or Baháʼí.
Arab identity is shaped by many things: shared family history, common language, customs, and traditions. The rich history of Arabs, including the rise and fall of empires, has helped keep a strong sense of unity and pride. Arab identity continues to change as Arab communities deal with modern challenges. Still, it remains a very important part of the Arab world's culture and history.
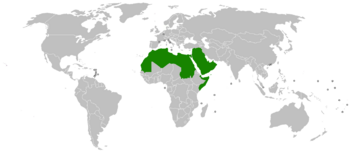
Where Do Arabs Live?
Most Arabs live in the 22 countries of the Arab League, which stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east. The total number of Arabs in these countries is about 366 million.
Arabs Around the World
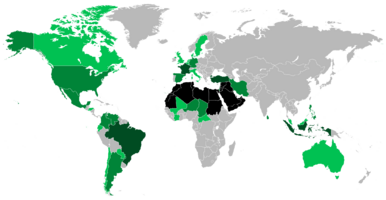
Many Arabs also live outside the Arab world. This is called the Arab diaspora. Large groups of Arabs have moved to places like East Africa, South America, Europe, North America, and Australia.
Arabs in Europe
Millions of Arabs live in Europe, especially in France (around 6 million). Most Arabs in France come from North Africa. There are also large Arab populations in Germany, the United Kingdom, and Spain. Many Arabs came to Spain in the 8th century during the Muslim conquest.
Arabs in the Americas

Arab immigration to the United States began in the 1880s. Today, about 3.7 million Americans have some Arab background. Most Arab Americans were born in the US. Large Arab communities also live in Latin America, especially in Brazil (millions of people of Lebanese and Syrian descent), Argentina, Colombia, and Venezuela. Many famous people, like singer Shakira and Apple co-founder Steve Jobs, have Arab heritage.
Arab Culture
Arab culture has a long and rich history, shaped by thousands of years of different religions, empires, and kingdoms. It includes language, literature, food, art, architecture, music, and philosophy.
Language

Arabic is a Semitic language spoken by over 500 million people. It is also the religious language for 1.7 billion Muslims, as it is the language of the Quran. Arabic is one of the six official languages of the United Nations.
There are two main forms of Arabic. Classical Arabic was used in ancient literary texts. Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is used today in writing and formal speaking across the Arab world. However, there are also many different spoken Arabic dialects that vary greatly from region to region.
Literature

The Quran had a huge impact on the Arabic language and marked the beginning of Arabic literature. As Islam spread, the Quran helped to unite and standardize Arabic.
Much of Arabic literature before the 20th century was poetry. Even prose often included poetry or rhymed sections. Love poems, called ghazal, were very popular. Arabic literature saw a decline after the 13th century but had a big revival in the 19th century, known as the al-Nahda or Arab Renaissance. This movement focused on rediscovering old literary traditions and translating Western works. Famous writers like Khalil Gibran emerged during this time.
Cuisine
Arab cuisine is diverse, with different styles in the Khaleeji, Levantine, and Maghrebi regions. It uses many herbs and spices like cumin, coriander, cinnamon, and mint. Arab food is also known for its delicious sweets and desserts, such as Baklava. Arabic coffee is a traditional drink often served with dates.
Art
Arabic art includes jewelry, textiles, and architecture. Arabic writing itself is often decorated with beautiful Arabic calligraphy. Arabic miniatures are small paintings, often found in books or manuscripts. These paintings flourished between 1000 and 1200 CE. They influenced other Islamic art forms like Persian and Ottoman miniatures.
Arabesque is a common art style in Arab culture. It uses beautiful patterns of scrolling lines and leaves, often combined with other designs. These patterns can be repeated endlessly, creating stunning decorations.
Architecture
The Arab world has many UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Ancient Arab architecture includes the buildings of the Nabataeans, who carved impressive structures like the city of Petra out of sandstone cliffs.
When the Arab empire expanded, it brought together many different architectural styles. Famous examples include the Great Mosque of Damascus and the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem. These buildings combine elements from Byzantine and Roman architecture with unique Arab designs.
Music

Arabic music has a long history and has influenced many other musical styles. Before Islam, Arab music was similar to other ancient Middle Eastern music. Many musical instruments used in classical music today, like the lute and rebec, came from Arabic instruments.
In the 1950s and 1960s, Arabic music started to use more Western instruments. Artists like Umm Kulthum helped create a new style of Arabic pop music, which mixes Eastern and Western melodies.
Science
Arabic science made huge progress during the Middle Ages (8th to 13th centuries CE). This knowledge later spread to Europe and greatly influenced medicine and education. The language of science was Arabic.
During the "Islamic Golden Age", Arab scholars made big discoveries in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. They also studied physics, chemistry, and geography.
- Al-Battani was an astronomer who accurately calculated the length of the solar year.
- Al-Zahrawi was a famous surgeon whose book "De chirurgia" was the first illustrated guide to surgery.
- Ibn al-Haytham is called the "world's first true scientist" for his work in optics and developing analytic geometry.
- Ismail al-Jazari invented many clever mechanical devices.
Many universities in the Arab world, like the University of Al Quaraouiyine in Fez, are among the oldest in the world. They have been giving out degrees for centuries. Many scientific words in English, like alchemy, algebra, and algorithm, come from Arabic.
See Also
 In Spanish: Pueblo árabe para niños
In Spanish: Pueblo árabe para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |