The Bahamas facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Commonwealth of The Bahamas
|
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: "Forward, Upward, Onward, Together"
|
|
|
Anthem: "March On, Bahamaland"
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Nassau 25°04′41″N 77°20′19″W / 25.07806°N 77.33861°W |
| Official languages | English |
| Vernacular language | Bahamian Creole |
| Ethnic groups
(2020)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Bahamian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Charles III |
| Cynthia A. Pratt | |
| Philip Davis | |
| Legislature | Parliament |
| Senate | |
| House of Assembly | |
| Independence
from the United Kingdom
|
|
|
• Realm
|
10 July 1973 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
13,943 km2 (5,383 sq mi) (155th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
28% |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 census
|
412,628 |
|
• Density
|
25.21/km2 (65.3/sq mi) (181st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| HDI (2022) | very high · 57th |
| Currency | Bahamian dollar (BSD) United States dollar (USD) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +1 242 |
| ISO 3166 code | BS |
| Internet TLD | .bs |
|
|
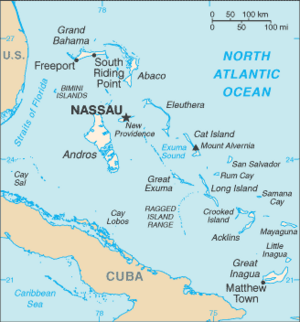
The Bahamas (bə-HAH-məz), officially called the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lucayan Archipelago. The Bahamas has over 3,000 islands and small cays.
It is located north of Cuba and northwest of Hispaniola. The U.S. state of Florida is to its southeast. The capital city is Nassau, found on New Providence island. The country's ocean territory covers a huge area of about 180,000 square miles (470,000 km²).
Contents
History of The Bahamas
Early Settlers and European Arrival
The first people to live in The Bahamas were the Lucayans. They came from South America around the 11th century AD. They settled in the southern Bahamas after traveling from Hispaniola and Cuba.
About 30,000 Lucayans lived there when Christopher Columbus arrived in 1492. Columbus's first stop in the New World was on an island he named San Salvador. Some experts believe this is today's San Salvador Island.
Spanish Rule and Decline of Lucayans
The Spanish forced many Lucayans to move to Hispaniola. They were made to do hard labor. Also, new diseases from Europe, like smallpox, caused many Lucayans to die. This led to most of the Lucayan population disappearing.
British Control and Pirates
In 1670, King Charles II of England leased the islands. He gave rights to trade, tax, and govern to the Carolinas. During this time, The Bahamas became a safe place for pirates. Famous pirates like Blackbeard used the islands as a base.
To bring order, Britain made The Bahamas a crown colony in 1718. The first governor was Woodes Rogers.
Loyalists and Independence
After the American Revolutionary War, many British supporters, called Loyalists, moved to The Bahamas. They came from New York, Florida, and the Carolinas. They brought about 7,300 enslaved people with them. These Loyalists started large farms called plantations on several islands. The number of enslaved Africans soon became higher than the number of Europeans.
The Bahamas became fully independent from the United Kingdom in 1973. Sir Lynden O. Pindling led the country to independence. The King of the United Kingdom is also the monarch of The Bahamas.
People and Languages
| DNA estimates of The Bahamas | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | % approx. | |||
| Black African | 70% | |||
| Mulatto | 13.8% | |||
| White | 12.4% | |||
| Asian | 3.8% | |||
Nearly 500,000 people live in The Bahamas. Most people are of African descent. About 82% of the population has African roots. Around 15% are of European and mixed descent. About 3% are of Asian and other backgrounds.
Languages Spoken
The official language of The Bahamas is English. However, many Bahamians also speak a local dialect. This dialect is called Bahamianese. It mixes English accents from West Country England and South Hiberno English. It also has strong influences from West African languages.
Geography and Climate
The Bahamas is made up of many islands. In 1864, there were 29 main islands, 661 cays, and 2,387 rocks.
Bimini is the closest island to the United States. Inagua is the southeasternmost island. The largest island is Andros Island. The capital city, Nassau, is on New Providence island.
All the islands are low and flat. The highest point is Mount Alvernia on Cat Island. It is 63 meters (207 feet) high.
Climate and Hurricanes
The climate in The Bahamas is warm, from subtropical to tropical. The Gulf Stream can be dangerous in summer and autumn. This is when hurricanes often pass near or through the islands.
Hurricane Andrew hit the northern islands in 1992. Hurricane Floyd affected most of the islands in 1999. It has never frozen in The Bahamas. Temperatures can drop to about 2–3°C (36–37°F).
Districts of The Bahamas
The Bahamas is divided into 32 districts. There is also the town of New Providence.
The districts are:
National Symbols
The Bahamian Flag
The flag of The Bahamas was chosen in 1973. Its colors show the strength of the Bahamian people. The design also reflects the sun, sea, and the country's growth. The flag has a black triangle on the left. It sits on a background of three equal stripes: aquamarine, gold, and aquamarine.
Coat of Arms
The coat of arms has a shield in the middle. A marlin and a flamingo support the shield. These are the national animals. The flamingo stands on land, and the marlin is in the sea. This shows the islands' geography.
Above the shield is a conch shell. This represents the sea life around the islands. The conch shell sits on a helmet. The shield itself shows a ship, the Santa María, sailing under the sun. This ship belonged to Christopher Columbus. Below the shield is a banner with the national motto:
Forward, Upward, Onward Together.
National Flower
The national flower of The Bahamas is the yellow elder. This flower grows naturally on the Bahama islands. It blooms all year round.
Garden clubs in New Providence chose the yellow elder in the 1970s. They picked it because other flowers, like bougainvillea and hibiscus, were already national flowers of other countries. The yellow elder was unique to The Bahamas. It is also native to the family islands.
Bahamian Food
Bahamian food includes lots of seafood. You can find fish, lobster, crab, and conch. They also eat tropical fruits, rice, and peas. Common seasonings are chilies, lime, tomatoes, onions, and garlic. Spices like allspice, ginger, and cinnamon are also used. Rum and coconut are popular ingredients.
Since The Bahamas has many islands, the food can be a bit different from island to island. Bahamian food is similar to that in the American South. For example, both places enjoy "fish 'n' grits."
Popular Dishes
Bahamians enjoy many soups. These include conch chowder and stewed conch. Stewed fish and split pea soup (made with ham) are also popular. Peas are used in many soups, even with dumplings and salt beef.
Seafood is a main part of the diet. Conch, a large sea snail, is the national dish. Conch can be eaten raw with lime juice and vegetables. It can also be steamed, stewed, or deep-fried. Deep-fried conch is called "cracked conch" or conch fritters. It is also used in soups and salads. Other popular seafood includes crab, often served baked.
Meat dishes often use chicken, pork, and goat. Iguana is still hunted and eaten on some islands. However, some types, like the Northern Bahamian rock iguana, are endangered.
Fruits and Desserts
Bahamian food uses many tropical fruits. Guavas are used to make duff (dessert). Ice cream is popular, especially with fruit flavors like soursop. Puddings are also eaten, including sapodilla pudding.
Papaya is a very famous Bahamian fruit. It is used in desserts, chutneys, and "Goombay" marmalade. This marmalade is made with papaya, pineapple, and green ginger. Papaya is also eaten fresh for breakfast. It can even be used to tenderize meat or in tropical drinks like the Bahama Mama. Other fruits grown there include melons, pineapples, passion fruit, and mangoes.
Military and Defense
The Bahamas does not have an army or an air force. The country's defense is handled by the Royal Bahamas Defence Force (RBDF). This is their navy.
The Defence Force has 26 patrol boats and 2 aircraft. It has over 850 people, including 65 officers and 74 women.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Continental Marines land at New Providence during the Battle of Nassau in 1776
-
The Duke of Windsor (briefly King Edward VIII) and Governor of The Bahamas from 1940 to 1945
-
Damaged homes in The Bahamas in the aftermath of Hurricane Dorian in September 2019
-
Dean's Blue Hole in Clarence Town on Long Island, Bahamas.
-
The Bahamian Parliament, located in Nassau
-
Bahamian Prime Minister Hubert Minnis with US President Donald Trump on 22 March 2019
-
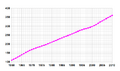
Demographics of Bahamas, data of FAO; number of inhabitants in thousands
-
White Bahamians on the island of New Providence
-
Junkanoo celebration in Nassau
-
Thomas Robinson Stadium in Nassau.
See also
 In Spanish: Bahamas para niños
In Spanish: Bahamas para niños