Monaco facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Principality of Monaco
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Anthem: "Hymne Monégasque"
(English: "Hymn of Monaco") |
|
Location of Monaco (green)
on the European continent (dark grey) |
|
| Capital | Monaco (city-state) 43°43′52″N 07°25′12″E / 43.73111°N 7.42000°E |
| Largest quarter | Monte Carlo |
| Official languages | French |
| Common languages |
|
| Ethnic groups | |
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Unitary parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy |
|
• Monarch
|
Albert II |
| Isabelle Berro-Lefèvre (acting) | |
| Legislature | National Council |
| Independence | |
|
• House of Grimaldi (under the sovereignty of the Republic of Genoa)
|
8 January 1297 |
|
• from the French Empire
|
17 May 1814 |
|
• from occupation of the Sixth Coalition
|
17 June 1814 |
|
• Franco-Monégasque Treaty
|
2 February 1861 |
|
• Constitution
|
5 January 1911 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
2.08 km2 (0.80 sq mi) (194th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
negligible |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 census
|
|
|
• Density
|
18,446/km2 (47,774.9/sq mi) (1st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2015 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$7.672 billion (165th) |
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +377 |
| ISO 3166 code | MC |
| Internet TLD | .mc |
|
|
Monaco, officially called the Principality of Monaco, is a tiny country in Western Europe. It is a city-state located on the French Riviera, very close to Italy. Monaco is surrounded by France on three sides and has a beautiful coastline along the Mediterranean Sea.
Monaco is home to about 38,682 people. Only a small part of them (about 9,486) are Monégasque citizens. It is known as one of the richest and most expensive places in the world. The main language spoken is French. Many people also speak Monégasque, English, and Italian.
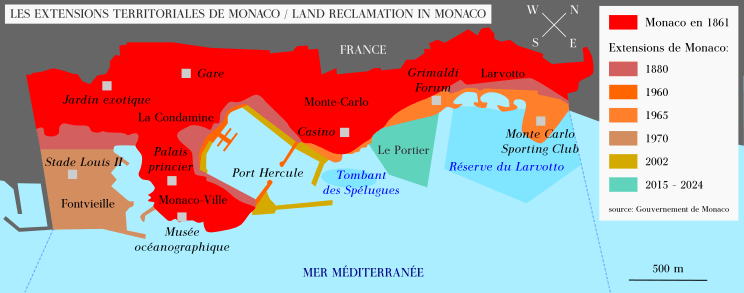
With an area of just 2.08 square kilometers, Monaco is the second-smallest country in the world, right after Vatican City. It is also the most densely populated country, meaning a lot of people live in a small space. Monaco has the world's shortest coastline, only 3.83 kilometers long. The country is divided into nine areas, and the largest is Monte Carlo.
Monaco is a constitutional monarchy, which means it has a ruler, Prince Albert II, who is the head of state. He has political power, but also follows a constitution. The prime minister leads the government and can be from Monaco or France. The House of Grimaldi family has ruled Monaco for a very long time, since 1297. Monaco became a full member of the United Nations in 1993. Even though Monaco is independent, France is responsible for its defense.
Monaco's economy grew a lot in the late 1800s when the first casino, the Monte Carlo Casino, opened. A train line to Paris also helped. Monaco's nice weather, beautiful views, and casinos make it a popular place for tourists and wealthy people. It has also become a big banking center. Monaco has no personal income tax for most residents, which attracts many people.
Monaco is not part of the European Union (EU), but it works closely with the EU on things like customs. It uses the euro as its money because of its connection with France. Monaco joined the Council of Europe in 2004. It hosts the famous Monaco Grand Prix car race every year. The country also has a successful football team, AS Monaco, and a basketball team. Monaco is also a leader in marine conservation and has an Oceanographic Museum.
Contents
History of Monaco
Monaco's name comes from an ancient Greek colony from the 6th century BC. The local people called it Monoikos, meaning "single house." This name came from a myth that Hercules built a temple there, and it was the only temple in the area. Later, the Holy Roman Empire gave Monaco to the people of Genoa.
The Grimaldi Family Arrives

In 1297, a branch of the Genoese House of Grimaldi family took control of Monaco. François Grimaldi, known as "The Cunning One," captured the fortress by dressing up as a Franciscan friar. The name monaco in Italian means "monk," which was a funny coincidence.
The Grimaldi family fought for control of Monaco for many years. Between 1346 and 1355, Monaco grew much larger by taking over the towns of Menton and Roquebrune.
Monaco from 1400 to 1800
In 1419, the Grimaldi family officially bought Monaco from the Crown of Aragon and became its undisputed rulers. In 1612, Honoré II started calling himself "Prince" of Monaco. He sought protection from France against Spain and became a special ally of the French kings.
The princes of Monaco lived mostly in Paris and married into French and Italian noble families. Monaco remained under France's protection until the French Revolution.
Monaco in the 19th Century
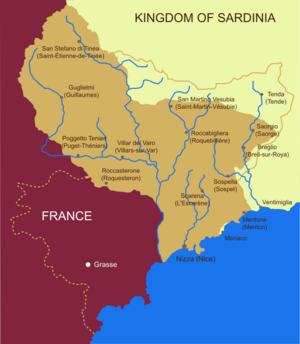
In 1793, French forces took over Monaco during the French Revolution. It was occupied by France until 1814. After Napoleon's defeat, Monaco was put under the care of the Kingdom of Sardinia.
In the 1800s, when Sardinia became part of Italy, Monaco came under French influence again but stayed independent. In 1860, the Treaty of Turin officially recognized Monaco's independence from Sardinia.
Before this, people in Menton and Roquebrune were unhappy with high taxes from the Grimaldi family. They declared independence. To solve this, Charles III of Monaco gave up his claim to these towns, which were about 95% of Monaco's land at the time. France paid Monaco 4,100,000 francs for them. This agreement was confirmed by the Franco-Monégasque Treaty of 1861.
In 1869, Monaco stopped collecting income tax from its residents. This was possible because the casino was so successful. This made Monaco a popular place for wealthy people to live.
Monaco in the 20th Century

Until 1910, the princes of Monaco were absolute rulers, meaning they had complete power. The Monégasque Revolution of 1910 led to the adoption of the 1911 Constitution of Monaco, which limited the prince's power.
In 1918, a new treaty with France stated that Monaco's international policies would be in line with France's interests.

During World War II, in 1943, the Italian Army occupied Monaco. Later, the German army took over. This led to the Jewish population being deported from Monaco.
Rainier III became prince in 1949 and ruled until 2005. In 1956, he married American actress Grace Kelly. Their wedding was a huge event that brought worldwide attention to Monaco.
In 1962, the constitution was changed to allow women's suffrage (women's right to vote) and create a Supreme Court of Monaco to protect people's rights. In 1963, there was some tension with France because Monaco was seen as a place where wealthy French citizens could avoid taxes.
In 1993, Monaco became a full member of the United Nations.
Monaco in the 21st Century
In 2002, a new treaty with France said that if the Grimaldi family had no heirs, Monaco would still remain an independent country. France continues to be responsible for Monaco's defense.
On March 31, 2005, Rainier III passed his duties to his son, Albert. Prince Rainier died six days later. Prince Albert II officially became the ruler on July 12, 2005.
In 2015, Prince Albert II apologized for Monaco's role during World War II in helping to deport 90 Jewish people and resistance fighters. He said, "We committed the irreparable in handing over to the neighboring authorities women, men and a child who had taken refuge with us."
Monaco has also been expanding its land by building into the sea. In 2015, a new project called Anse du Portier was approved to create more space for housing, parks, and shops.
In 2020, Monaco had its first case of COVID-19. Also in 2020, Monaco launched its first satellite, OSM-1 CICERO, into space. In July 2024, Monaco hosted the start of the final stage of the Tour de France bicycle race.
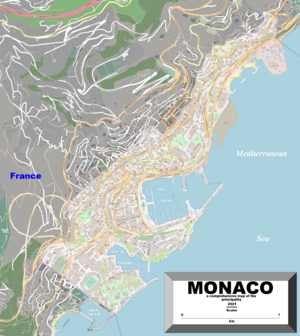
Geography of Monaco
Monaco is a city-state located on the French Riviera in Western Europe. It is bordered by France on three sides and the Mediterranean Sea on one side. Monaco is about 16 kilometers from Italy and 13 kilometers northeast of Nice.
It has an area of about 2.1 square kilometers and a population of 38,400. This makes Monaco the second-smallest and the most densely populated country in the world. Its land border is only 5.47 kilometers long, and its coastline is 3.83 kilometers.
The highest point in Monaco is 164.4 meters above sea level, near the Patio Palace building. The lowest point is the Mediterranean Sea. The longest stream is Saint-Jean brook, and the largest lake is Fontvieille. The most populated area is Monte Carlo.
Monaco has expanded its land by reclaiming it from the Mediterranean Sea. There are two main ports: Port Hercules and Port Fontvieille. Monaco's only natural resource is fishing, and because it is mostly an urban area, it does not have much agriculture. A new area called Le Portier is being built on reclaimed land.
Government
Monaco has been a constitutional monarchy since 1911. The Sovereign Prince of Monaco is the head of state. The government is led by a Prime Minister, who works with five other members of the Council of Government. Since 2002, the Prime Minister can be either French or Monégasque.
The prince shares his power with the National Council, which has 24 members elected for five-year terms. All new laws need the approval of the National Council.
Local city matters are handled by the Municipality of Monaco. This is managed by the Communal Council, which has 14 elected members and is led by a mayor.
Judges in Monaco are chosen by the Prince. Important legal positions are often held by French judges.
Relations with Other Countries
Monaco has a long history of relationships with many nations. Honoré II, Prince of Monaco gained recognition for Monaco's independence from Spain in 1633 and from France in 1641.
Monaco has a special agreement with France from 1963, which means French customs laws apply in Monaco. Monaco uses the euro but is not a member of the European Union. Monaco shares a 6-kilometer border with France. Two important agreements that support Monaco's independence are the Franco-Monégasque Treaty of 1861 and the French Treaty of 1918.
France and Italy have embassies in Monaco. Most other countries are represented through their offices in Paris. Monaco also has about 30 consulates around the world.
Many people living in Monaco are from other countries. In 2015, about 60% of the population were immigrants. It is difficult to become a citizen of Monaco. Monaco does not allow people to have dual citizenship.
Monaco has faced issues with people using it to avoid paying taxes in their home countries. However, Monaco does collect taxes, including a 20% VAT (value-added tax) and 33% on companies unless most of their income is earned within Monaco. French citizens who live in Monaco must still pay taxes to France unless they lived in Monaco before 1962 for at least five years.
There are no border checks when entering or leaving France from Monaco. Visitors can get a souvenir passport stamp at Monaco's tourist office.
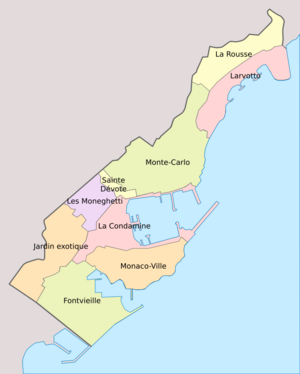
Administrative Divisions

Monaco is the second-smallest country in the world, after Vatican City. It is also the most densely populated country. Monaco has only one municipality (city government). The government and city responsibilities are separate.
Historically, Monaco was divided into three municipalities:
- Monaco-Ville: The old city and government center on a rocky hill called "The Rock."
- Monte Carlo: The main living and resort area with the Monte Carlo Casino.
- La Condamine: The southwestern area, including the port.
These areas were combined into one municipality in 1917 and became known as Wards or Quartiers.
New wards were added later:
- Fontvieille: A new area built on land reclaimed from the sea in the 1970s.
- Moneghetti: Created from part of La Condamine.
- Larvotto: Created from part of Monte Carlo.
- La Rousse/Saint Roman: Also created from part of Monte Carlo.
Some other wards were created but later combined. A new 6-hectare area called Le Portier is currently being built on the sea.
Traditional Quarters and Modern Areas
The four main traditional areas of Monaco are Monaco-Ville, La Condamine, Monte Carlo, and Fontvieille. Moneghetti is often seen as a fifth important area due to its unique feel and hilly landscape.
Wards
For city planning, Monaco is divided into "reserved sectors" and "wards." The current division, from 2013, includes two reserved sectors and seven wards.
| Wards | Area | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in m2 | in % | |||||
| Reserved Sectors | ||||||
| Ravin de Sainte-Dévote | Reserved Sectors | 23485 | 1.2 % | |||
| Wards | ||||||
| Monaco-Ville | Quartier ordonnancé | 196491 | 9.7 % | |||
| La Condamine | Quartier ordonnancé | 295843 | 14.6 % | |||
| Fontvieille | Quartier ordonnancé | 329516 | 16.3 % | |||
| Larvotto | Quartier ordonnancé | 217932 | 10.8 % | |||
| Jardin Exotique | Quartier ordonnancé | 234865 | 11.6 % | |||
| Les Moneghetti | Quartier ordonnancé | 115196 | 5.7 % | |||
| Monte-Carlo | Quartier ordonnancé | 436760 | 21.5 % | |||
| La Rousse | Quartier ordonnancé | 176888 | 8.7 % | |||
| Total | 2026976 | 100 % | ||||
Climate
Monaco has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate. This means it has warm, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. The summers are not usually too hot because of cool sea breezes. Winter temperatures rarely drop below freezing, and snow is very rare. Snow fell in Monaco in February 2018.
Economy

Monaco has one of the highest GDP per person in the world. It also has a very low unemployment rate of 2%. Over 48,000 workers travel from France and Italy to Monaco each day. Monaco has the lowest poverty rate and the highest number of millionaires and billionaires per person in the world. In 2012, Monaco had the most expensive real estate market, costing $58,300 per square meter.
One of Monaco's main sources of money is tourism. Many people visit its casinos and enjoy the pleasant weather. Monaco has also become a major banking center, holding over €100 billion in funds. Banks in Monaco offer special services for managing money and wealth.
Monaco has also worked to grow its economy in other areas, like services and small, high-tech industries that don't cause pollution, such as cosmetics.
The government controls some services, like tobacco sales and the postal service.
Monaco is not a member of the European Union, but it has a close customs agreement with France. Because of this, it uses the euro as its currency. Before 2002, Monaco had its own coins, called the Monegasque franc.
Monaco has never collected income tax from individuals. This has attracted many wealthy people from other European countries who want to live there and pay less tax.
Transport
The Monaco-Monte Carlo train station is part of the French national rail system (SNCF). The Monaco Heliport offers helicopter service to the nearest airport, Côte d'Azur Airport in Nice, France.
The Monaco bus company (CAM) has routes that cover all the main tourist spots, museums, the Exotic Garden, business centers, the Casino, and the Louis II Stadium.
Monaco has about 77 kilometers (48 miles) of roads. Many of these roads are also used for car races.
The main port is Port Hercules, which has a deep-water pier. There is also a smaller harbor between the Rock and Fontvieille.
Demographics
In 2015, Monaco's population was 38,400. What's interesting is that native Monégasques are a minority in their own country. The largest groups are French (28.4%), followed by Monégasque (21.6%), Italian (18.7%), and British (7.5%). In 2019, it was reported that 31% of Monaco's population were millionaires.
People who are citizens of Monaco, whether born there or naturalized, are called Monégasque. Monaco has the highest life expectancy in the world, almost 90 years.
Language

The main and official language of Monaco is French. Italian is also widely spoken by the large Italian community. French and Italian are actually spoken more than Monégasque, which is the traditional local language. Monégasque is not an official language, but it is taught in schools, and some street signs are in both French and Monégasque. English is also commonly used.
Italian was the official language until 1860, when French replaced it after the surrounding area became part of France.
The Grimaldi princes of Monaco have Italian roots. The traditional language, Monégasque, is a type of Ligurian. Only a small number of residents speak it, but many native residents know it as a second language.
Religion
The official religion in Monaco is Catholicism. However, the constitution guarantees freedom for other religions. Christians make up 86% of Monaco's population.
Sports
Two very important sports in Monaco are football and racing. Sports are a big part of Monaco's economy and culture.
Formula One
Since 1929, the Monaco Grand Prix has been held every year on the streets of Monaco. It is one of the most famous car races in the world. It takes six weeks to set up the Circuit de Monaco and three weeks to take it down after the race.
The track is narrow and has tight turns, tunnels, and many changes in elevation. This makes it one of the most challenging Formula One tracks. One driver, Nelson Piquet, said driving it was like "riding a bicycle around your living room."
Despite how difficult it is, only two drivers have died from injuries during the race: Luigi Fagioli in 1952 and Lorenzo Bandini in 1967. Two other drivers, Alberto Ascari in 1955 and Paul Hawkins in 1965, were lucky to survive after crashing into the harbor.
In 2020, the Monaco Grand Prix was canceled for the first time since 1954 because of the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Monégasque Formula 1 Drivers
There have been five Formula One drivers from Monaco:
- Charles Leclerc (2018–present) – He won the 2024 Monaco Grand Prix.
- Robert Doornbos (2005, a Dutch driver with a Monégasque license).
- Olivier Beretta (1994).
- André Testut (1958–1959).
- Louis Chiron (1950–1958) – He won the 1931 Monaco Grand Prix.
Formula E
Since 2015, Formula E races have been held in Monaco every two years, along with the Historic Grand Prix of Monaco. These races use a shorter version of the Formula 1 circuit around Port Hercules.
ROKiT Venturi Racing is a motor racing team based in Monaco. They compete in Formula E, which is a championship for electric cars.
Monte Carlo Rally
Since 1911, part of the Monte Carlo Rally has been held in Monaco. This rally is organized by the Automobile Club de Monaco. It is known as one of the toughest and most respected events in rallying. Because Monaco is so small, most of the rally takes place in France.
Football
Monaco has two main football teams: the men's club, AS Monaco FC, and the women's club, OS Monaco. AS Monaco plays at the Stade Louis II and competes in Ligue 1, the top French football league. The club has won Ligue 1 eight times and reached the 2004 UEFA Champions League Final. Famous players like Thierry Henry and Kylian Mbappe have played for AS Monaco. The Stade Louis II also hosted the annual UEFA Super Cup from 1998 to 2012.
The women's team, OS Monaco, plays in the French football league system.
The Monaco national football team represents the country in football. Monaco is one of only two countries in Europe (the other being Vatican City) that is not a member of UEFA. This means they do not compete in the UEFA European Football Championship or FIFA World Cup. They play their home matches at the Stade Louis II.
Basketball
AS Monaco Basket is a basketball team founded in 1928. They play in the top European basketball league, the EuroLeague, and the top French league, the LNB Pro A. They play their games at Salle Gaston Médecin, which is part of Stade Louis II.
Other Sports and Events
The Monte-Carlo Masters is an annual professional tennis tournament held nearby in France. The Monte Carlo Open golf tournament was also held there from 1984 to 1992.
Monaco has a national Davis Cup team for tennis. Monaco has also competed in the Olympic Games, but no athlete from Monaco has won an Olympic medal yet.
The 2009 Tour de France, a famous bicycle race, started in Monaco.
The Monaco Marathon is the only marathon in the world that passes through three countries: Monaco, France, and Italy.
The Monaco Ironman 70.3 triathlon race is an annual event with over 1,000 athletes. It includes swimming, biking, and running.
The headquarters of the International Association of Athletics Federations, which governs athletics worldwide, is located in Monaco.
The Rainier III Nautical Stadium in Port Hercules has a heated saltwater Olympic-size swimming pool. In winter, the pool is turned into an ice rink.
Monaco also hosts the Solar1 Monte Carlo Cup, a series of races for solar-powered boats. The chess club CE Monte Carlo's women's team has won the European Chess Club Cup several times.
Culture
Cuisine
The food in Monaco is a type of Mediterranean cuisine. It is influenced by the cooking styles of nearby southern France and northern Italy, along with Monaco's own traditions.
Two famous restaurants in Monaco are Le Louis XV, which has three Michelin stars, and the Café de Paris. The Café de Paris, located next to the Casino, first opened in 1868.
Music

Monaco has an opera house, a symphony orchestra, and a classical ballet company. Monaco often participated in the Eurovision Song Contest and won in 1971.
Architecture
Monaco has many different styles of buildings. The most famous style, especially in Monte Carlo, is called Belle Époque. You can see this style in the Monte Carlo Casino and the Salle Garnier, built in 1878–79. These buildings have turrets, balconies, colorful tiles, and statues, creating a luxurious and beautiful look.
In the 1970s, Prince Rainier III stopped the building of tall skyscrapers. However, his son, Prince Albert II, later allowed them again. Recently, many old villas have been torn down, which has caused some concern because Monaco does not have laws to protect its old buildings.
Visual Arts
Monaco has a national museum for modern art called the New National Museum of Monaco. The Audiovisual Institute of Monaco was created in 1997 to save old films and show how Monaco is shown in movies. The country also has many public artworks, statues, and other museums.
Museums in Monaco
- Monaco Top Cars Collection
- Napoleon Museum (Monaco)
- Oceanographic Museum
Events, Festivals, and Shows
Monaco hosts many big international events, such as:
- International Circus Festival of Monte-Carlo
- Mondial du Théâtre (World Theatre Festival)
- Monte-Carlo Television Festival
Bread Festival
Monaco also has an annual bread festival on September 17th each year.
Parks and Gardens
Monaco has several beautiful gardens with different styles. These include the Exotic Garden, Saint Martin Gardens, African Plants Garden, Casino Gardens, Princess Grace Rose Garden, and a Japanese Garden.
Education
Primary and Secondary Schools
Monaco has ten state-run schools:
- Seven nursery and primary schools.
- One secondary school, Collège Charles III.
- One lycée (high school) for general and technical education, Lycée Albert 1er.
- One lycée for vocational and hotel training, Lycée technique et hôtelier de Monte-Carlo.
There are also two private religious schools and one international school, the International School of Monaco, which opened in 1994.
Colleges and Universities
Monaco has one university, the International University of Monaco (IUM). It is an English-language university that focuses on business education.
Flag

The flag of Monaco is one of the oldest national flag designs in the world. It was adopted on April 4, 1881, and is based on Monaco's royal colors from the 14th century.
The flag looks similar to the flags of Indonesia and Poland.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Mónaco para niños
In Spanish: Mónaco para niños