Guyana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Co-operative Republic of Guyana
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Motto: "One People, One Nation, One Destiny"
|
|
|
Anthem: "Dear Land of Guyana, of Rivers and Plains"
|
|
Location of Guyana (green)
in South America (grey) |
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Georgetown 6°48′21″N 58°9′3″W / 6.80583°N 58.15083°W |
| Official languages | English |
| Recognised regional languages |
10 indigenous languages
|
| Vernacular language | Guyanese Creole |
| Other languages |
5 languages
|
| Ethnic groups
(2012)
|
|
| Religion
(2020)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Guyanese |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary republic with an executive presidency |
| Irfaan Ali | |
| Mark Phillips | |
| Bharrat Jagdeo | |
| Legislature | National Assembly |
| Establishment | |
|
• Dutch control
|
1667–1815 |
|
• British Guiana
|
1831–1966 |
| 26 May 1966 | |
|
• Republic
|
23 February 1970 |
|
• Joined CARICOM at the Treaty of Chaguaramas
|
1 August 1973 |
|
• Current constitution
|
6 October 1980 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
214,969 km2 (83,000 sq mi) (83rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
8.4 |
| Population | |
|
• 2024 estimate
|
817,607 (166th) |
|
• Density
|
3.502/km2 (9.1/sq mi) (239th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2007) | ▼ 44.6 medium |
| HDI (2022) | high · 95th |
| Currency | Guyanese dollar (GYD) |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
| Date format | dd-mm-yyyy |
| Driving side | left |
| Calling code | +592 |
| ISO 3166 code | GY |
| Internet TLD | .gy |
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country located on the northern mainland of South America. Its capital city is Georgetown. The name "Guyana" likely comes from an old word meaning "Land of Many Waters."
Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. It is the third-smallest country by land area in mainland South America. It is also one of the least populated countries on Earth. Guyana is known for its many natural habitats and amazing biodiversity.
The area called "the Guianas" is a large landmass north of the Amazon River. Nine indigenous tribes live in Guyana. These include the Wai Wai, Macushi, and Patamona. The country was first settled by the Dutch. Later, it came under British control in the late 1700s. It was known as British Guiana until it gained independence in 1966. In 1970, it became a republic.
Guyana is the only country in South America where English is the official language. However, most people speak Guyanese Creole, which is a mix of English and other languages. Guyana is part of the Anglophone Caribbean. It has strong cultural and historical ties with other Caribbean countries. It is also the main office for the Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
Since 2015, Guyana's economy has been changing a lot. This is because large amounts of crude oil were found. Commercial oil drilling started in 2019. Guyana's economy grew by 49% in 2020, even during the pandemic. This makes it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world. With its small population and large oil reserves, Guyana is set to become one of the biggest oil producers per person by 2030.
Contents
What Does the Name Guyana Mean?
The name "Guyana" comes from an older name, Guiana. This larger region included parts of what are now Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana, and parts of Venezuela and Brazil. The word "Guyana" comes from an indigenous language. It means "land of many waters." The word Co‑operative in the official name points to a type of socialism.
Guyana's History
Early Inhabitants of Guyana
Before Europeans arrived, nine indigenous tribes lived in Guyana. These tribes included the Wai Wai, Macushi, and Patamona. Historically, the Lokono and Kalina tribes were the most powerful in the area.
Colonial Times in Guyana
Christopher Columbus saw Guyana in 1498. However, the Dutch were the first Europeans to set up colonies. They started settlements like Pomeroon in 1581. The British took control in 1796. The Dutch officially gave up the area in 1814.
In 1831, different Dutch colonies joined together. They formed a single British colony called British Guiana.
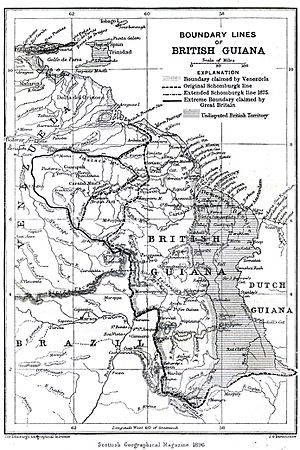
Since 1824, Venezuela has claimed land west of the Essequibo River. In 1899, an international court decided the land belonged to Great Britain. This claim was based on the Dutch presence in the area.
Becoming an Independent Nation
Guyana became independent from the United Kingdom on May 26, 1966. It became a republic on February 23, 1970. Guyana remained a member of the Commonwealth. After independence, Venezuela continued to claim land in Guyana.
Guyana was chosen twice to be a member of the United Nations Security Council. This happened in 1975–76 and again in 1982–83. In 2008, Guyana joined the Union of South American Nations.
In March 2020, there was an election. Irfaan Ali became the new president.
Geography of Guyana

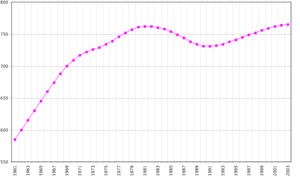
Guyana is located between 1° and 9°N latitude and 56° and 62°W longitude. It is one of the world's most sparsely populated countries.
The country has five main natural regions:
- A flat, wet plain along the Atlantic coast. Most people live here.
- A white sand area further inland. This area has many of Guyana's minerals.
- Thick rain forests in the south.
- Dry savannah areas in the southwest.
- Small interior lowlands with mountains. These mountains rise towards the Brazilian border.
Some of Guyana's highest mountains are Mount Ayanganna and Monte Caburaí. Mount Roraima is the highest mountain in Guyana. It is located where Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela meet. These flat-topped mountains are called tepuis. They are said to have inspired the novel The Lost World. There are also many waterfalls, like Kaieteur Falls. This is thought to be the largest single-drop waterfall by water volume in the world.
The four longest rivers are the Essequibo, Courentyne, Berbice, and Demerara. The Courentyne River forms the border with Suriname. Near the mouth of the Essequibo River is Shell Beach. This beach is a major breeding area for sea turtles.
Guyana has a tropical climate. It is generally hot and humid. However, cool winds from the northeast help to moderate the coast. There are two rainy seasons each year.
Guyana has one of the largest unspoiled rainforests in South America. Some parts are very hard to reach. The country's rich natural history has been studied by many naturalists. In 2008, the BBC showed a program about Guyana's amazing wildlife. It featured rare animals like the giant otter and harpy eagle.
In 2012, Norway gave Guyana $45 million. This was a reward for its efforts to protect its rainforests.
Amazing Plants and Animals
Guyana is home to over 900 types of birds. It also has 225 types of mammals and 880 types of reptiles. More than 6,500 different plant species grow here. Some famous animals include the Arapaima, the world's largest scaled freshwater fish. There is also the giant anteater and the giant otter. The cock-of-the-rock (Rupicola rupicola) is another unique bird.


More than 80% of Guyana is still covered by forests. These forests have some of the world's rarest orchids. They are home to over a thousand types of trees. Guyana's tropical climate and unique landforms support these rich forests. Many species found here live nowhere else in the world.
Guyana has one of the highest levels of biodiversity globally. It has 1,168 types of vertebrate animals and 814 bird species. This makes it one of the richest places for mammals. Over 70% of Guyana's natural habitat is still untouched.
The southern part of Guyana has some of the most untouched evergreen forests in South America. Most of these forests are tall and full of trees. They also have large areas of flooded forest along the rivers. Because there are very few people living here, most of these forests are still in their natural state.
The clean waters of the Essequibo watershed support many types of fish. They are also home to giant otters and capybaras. On land, large mammals like jaguars, tapirs, and giant anteaters are still common. Over 800 bird species have been seen in this region.
In 2004, the Government of Guyana set aside over 1 million acres of land. This area is called the Kanashen Community-Owned Conservation Area. It is managed by the Wai Wai people. The Iwokrama International Centre for Rain Forest Conservation and Development was also created. It helps protect and use the Iwokrama forest in a sustainable way.
Guyana's Economy
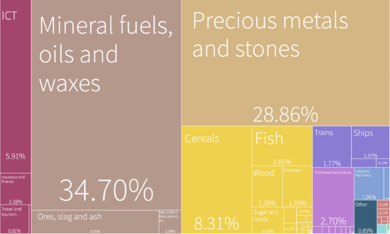
The main economic activities in Guyana include farming. They grow rice and Demerara sugar. Mining for bauxite and gold is also important. Other key industries are timber, seafood, and minerals.
A big change came with the discovery of large crude oil reserves. These were found off the Atlantic coast in 2015. Oil drilling started in 2019. This has greatly boosted Guyana's economy. The country's economy grew by 43% in 2020. It is expected to keep growing at a high rate. This growth is mostly due to the oil sector.
Protecting Guyana's forests has helped the country receive international aid.
Economic Snapshot
- Main Products: Sugar, rice, vegetable oils, beef, pork, poultry, fish, shrimp.
- Industries: Bauxite, sugar, rice milling, timber, textiles, gold mining, crude oil.
- Key Exports: Oil, gold, rice, sugar, bauxite, shrimp.
- Key Imports: Machinery, fuel, food, manufactured goods.
People of Guyana
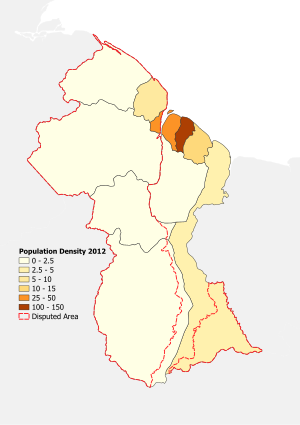
About 90% of Guyana's population lives along a narrow strip of coast. This coastal area is only about 10% of the country's total land.
Guyana's population is made up of many different ethnic groups. These groups come from India, Africa, Europe, and China. There are also the original indigenous peoples. Even with different backgrounds, most people speak English or Guyanese English Creole.
The largest group is the Indo-Guyanese. These are descendants of workers from India. They make up about 43.5% of the population. The next largest group is the Afro-Guyanese. They are descendants of enslaved people from Africa. They make up about 30.2% of the population. People of mixed heritage are 16.7%. Indigenous peoples, also called Amerindians, are 9.1%.
Major Cities and Towns
| Rank | Name | Region | Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Georgetown | Demerara-Mahaica | 118,363 |
| 2 | Linden | Upper Demerara-Berbice | 27,277 |
| 3 | New Amsterdam | East Berbice-Corentyne | 17,329 |
| 4 | Corriverton | East Berbice-Corentyne | 11,386 |
| 5 | Bartica | Cuyuni-Mazaruni | 8,004 |
| 6 | Mahaica | Demerara-Mahaica | 4,867 |
| 7 | Rose Hall | East Berbice-Corentyne | 4,413 |
| 8 | Parika | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 4,385 |
| 9 | Triumph | Demerara-Mahaica | 3,788 |
| 10 | Uitvlugt | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | 2,980 |
Languages Spoken in Guyana
English is the official language in Guyana. It is used in schools, government, and media. Most people speak Guyanese Creole as their first language. This creole is based on English, with some African, Indian, and Amerindian influences.
A small number of indigenous people speak Cariban languages. These include Akawaio, Wai-Wai, and Macushi. Older Indo-Guyanese people might speak Guyanese Hindustani. However, younger Guyanese usually speak English or Guyanese Creole.
Religions in Guyana
Religion in Guyana (2012 census) Christianity (62%) Hinduism (25%) Islam (7%) Other religious groups (3%) Irreligious (3%)
Religion in Guyana (2012 census) Hinduism (25%) Pentecostalism (23%) Other forms of Christianity (21%) Roman Catholicism (7%) Islam (7%) Anglicanism (5%) Seventh-day Adventism (5%) Methodism (1%) Other religious groups (3%) Irreligious (3%)
In 2012, about 63% of the population was Christian. About 25% were Hindu, and 7% were Muslim.
Religion is an important part of identity in Guyana. It shows the different influences from colonial times and immigrant groups. Christianity was seen as a high-status religion. It brought European culture and offered ways to improve one's social standing. Missionaries and churches built schools. Until the 1970s, most schools were run by religious groups. When Indian workers came to the country, Hinduism and Islam became more common.
Some traditional African and Amerindian folk beliefs still exist alongside the main religions.
Education System in Guyana
Education in Guyana was first started by Christian groups. Wealthy families often sent their children to England for school. As schools in Guyana got better, they followed the British education system. Primary education became required in 1876. However, many children still had to help with farm work. In the 1960s, the government took control of all schools. School fees were removed. New schools opened in rural areas. The University of Guyana was also started. This meant students no longer had to go abroad for college.
Guyana has one of the highest literacy rates in the Caribbean. In 2014, about 96.7% of people aged 15–24 could read and write.
Students take the NGSA (National Grade Six Assessment) to get into high school. They take the CXC exams at the end of high school. Many schools have also started using the CAPE exams.
Getting to school can be hard in some areas, especially in the interior. Many teachers may not have full training. They also might not have enough teaching materials.
How Guyana is Governed
Guyana is a parliamentary representative democratic republic. This means the people elect representatives to make decisions. The President of Guyana is both the country's leader and the head of the government. Guyana has a multi-party system. This means there are many political parties.
The President and the Government have executive power. This means they carry out the laws. The President and the National Assembly of Guyana share legislative power. This means they make the laws.
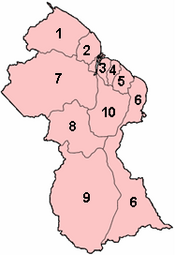
Regions of Guyana
Administrative Divisions
Guyana is divided into 10 regions. Each region has its own capital city.
| No | Region | Regional Capital | Area km2 | Pop. (2012 Census) |
Pop. Density per km2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Barima-Waini | Mabaruma | 20,339 | 26,941 | 1.32 |
| 2 | Pomeroon-Supenaam | Anna Regina | 6,195 | 46,810 | 7.56 |
| 3 | Essequibo Islands-West Demerara | Vreed-en-Hoop | 3,755 | 107,416 | 28.61 |
| 4 | Demerara-Mahaica | Triumph | 2,232 | 313,429 | 140.43 |
| 5 | Mahaica-Berbice | Fort Wellington | 4,190 | 49,723 | 11.87 |
| 6 | East Berbice-Corentyne | New Amsterdam | 36,234 | 109,431 | 3.02 |
| 7 | Cuyuni-Mazaruni | Bartica | 47,213 | 20,280 | 0.43 |
| 8 | Potaro-Siparuni | Mahdia | 20,051 | 10,190 | 0.51 |
| 9 | Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo | Lethem | 57,750 | 24,212 | 0.42 |
| 10 | Upper Demerara-Berbice | Linden | 17,040 | 39,452 | 2.32 |
| Total | 214,999 | 747,884 | 3.48 |
These regions are further divided into 27 smaller areas called neighbourhood councils.
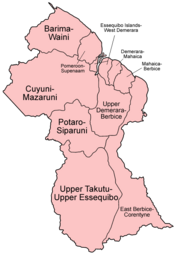
Natural Regions of Guyana
Guyana also has four main natural regions:
- Low Coastal Plain
- Hilly Sand and Clay
- Highland Region
- Interior Savannahs
Culture in Guyana
| 1 January | New Year's Day |
| Spring | Youman Nabi (Mawlid) |
| 23 February | Republic Day / Mashramani |
| March | Phagwah (Holi) |
| March / April | Good Friday |
| March / April | Easter Sunday |
| March / April | Easter Monday |
| 1 May | Labour Day |
| 5 May | Indian Arrival Day |
| 26 May | Independence Day |
| First Monday in July | CARICOM Day |
| 1 August | Emancipation Day |
| October / November | Diwali |
| 25 December | Christmas |
| 26 or 27 December | Boxing Day |
| Varies | Eid al-Fitr |
| Varies | Eid al-Adha |
Guyana's culture is very similar to other English-speaking Caribbean countries. This is because it was part of the British Empire for a long time.
Guyanese culture began to form as immigrants adapted to the main British culture. Enslavement removed many differences between African cultures. Instead, British culture became dominant. This led to the Afro-Guyanese culture we see today. Indian immigrants arrived later. They were able to keep more of their traditions. These include their religion, food, music, and festivals.
Guyana's location, its vast rainforests, and its large Amerindian population make it unique. Its mix of Indo-Guyanese and Afro-Guyanese cultures makes it similar to Trinidad and Tobago and Suriname. Guyana shares many interests with the West Indies islands. These include food, festivals, music, and sports.
Important events include Mashramani (Mash), Phagwah (Holi), and Deepavali (Diwali).
Famous Landmarks
- St George's Anglican Cathedral: A historic Anglican church made of wood.
- Demerara Harbour Bridge: One of the world's longest floating bridges.
- Berbice Bridge: Another one of the world's longest floating bridges.
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM) Building: This building is the main office for CARICOM. It is a powerful economic group in the Caribbean.
- Providence Stadium: This is the largest sports stadium in Guyana. It was built for the 2007 Cricket World Cup. It is near the Providence Mall.
- Arthur Chung Conference Centre: This center was a gift from China. It is the only one of its kind in the country.
- Stabroek Market: A large old market building made of cast-iron.
- Georgetown City Hall: A beautiful wooden building from the colonial era.
- Takutu River Bridge: A bridge connecting Guyana to Brazil.
- Umana Yana: An Amerindian benab (a traditional hut). It is a national monument.
- Shell Beach: A long beach with high biodiversity. It is an important nesting site for sea turtles.
- Parliament Building of Guyana: This building houses Guyana's National Assembly.
Popular Sports
The main sports in Guyana are cricket, basketball, football, and volleyball. Cricket is very popular. Guyana is part of the West Indies cricket team for international matches.
Guyana hosted international cricket matches for the 2007 Cricket World Cup. The new 15,000-seat Providence Stadium was built for this event.
Guyana's national basketball team has often been a top team in the CaribeBasket tournament. This is the main international basketball event for Caribbean countries.
For international football, Guyana is part of CONCACAF. Their national football team has never played in the FIFA World Cup. However, they qualified for the Caribbean Cup in 1991 and 2007. In 2019, they qualified for the CONCACAF Gold Cup for the first time.
Guyana also has five horse racing courses.
See also
 In Spanish: Guyana para niños
In Spanish: Guyana para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |