Caribbean Community facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
|
|
|---|---|
|
Flag
|
|
|
Anthem: "Celebrating CARICOM"
|
|
Full members
Associate members Observers |
|
| Seat of Secretariat | Georgetown, Guyana |
| Largest city | Port-au-Prince, Haiti |
| Official languages | English |
| Working language | |
| Other languages |
34 languages
Anguillian English Creole
Antillean French Creole Arabic Bajan English Bajan English Creole Bahamian English Creole Belizean English Creole Belizean Spanish Caribbean Hindustani Caribbean Spanish Cayman Islands English Chinese Dominican French Creole Grenadian English Creole Guyanese English Creole Jamaican English Jamaican Patois Montserrat English Creole Ndyuka Papiamento Plautdietsch German Saint Kitts Creole Saint Lucian French Creole Saramaccan Sranan Tongo (Taki Taki) Surinamese Dutch Tobagonian English Creole Trinidadian English Creole Trinidadian and Tobagonian English Turks and Caicos English Creole Venezuelan Spanish Vincentian English Creole Virgin Islands English Creole Arawak (Lokono)
Carib (Kari'nja) Garifuna (Karif) Kapóng Macushi Mawayana (Mapidian) Mopan Pemon (Arekuna) Qʼeqchiʼ (Kʼekchi) Sikiana (Kashuyana) Tiriyó Yucatec Waiwai Wapishana Warao (Guarauno) Wayana |
| Ethnic groups | In full member states:
|
| Demonym(s) | Caribbean people |
| Type | Supranational union |
| Member states |
15 full members
8 observers
|
| Government | Intergovernmental |
|
• Secretary-General
|
Carla Barnett |
|
• Chairman
|
Irfaan Ali |
| Establishment | |
|
• Treaty of Chaguaramas
|
4 July 1973 |
|
• Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas
|
2001 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
458,480 km2 (177,020 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2019 estimate
|
18,482,141 (in full member states) 239,251,864 (in all states) |
|
• Density
|
40.3/km2 (104.4/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2020 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$145.3 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$18,289 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$81.987 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$12,608 |
| HDI (2018) | high |
| Currency |
|
|
Website
https://caricom.org/ |
|
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM) is a group of 15 countries and 5 associated areas in the Caribbean. It works like a team to help its members grow stronger together. CARICOM aims to boost trade and cooperation among its members. It also makes sure that everyone shares the benefits fairly. Plus, it helps coordinate how these countries deal with other nations.
CARICOM was started in 1973 when four countries signed a special agreement called the Treaty of Chaguaramas. Its main office, called the Secretariat, is in Georgetown, Guyana.
Here are some of the things CARICOM does:
- It helps plan economic policies and development for the region.
- It creates special projects for smaller or less developed countries.
- It acts as a single market for many of its members, making trade easier.
- It helps solve trade disagreements between member countries.
CARICOM was first formed by English-speaking countries. Now, it includes countries where Dutch and French are spoken too. In 2001, a new version of the Treaty of Chaguaramas was signed. This led to the idea of a CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME). The CSME helps create a bigger, stronger economy for the Caribbean. It also set up the Caribbean Court of Justice to handle legal matters.
Contents
History of CARICOM
CARICOM, which used to be called The Caribbean Community and Common Market, officially began on August 1, 1973. The first countries to join were Barbados, Jamaica, Guyana, and Trinidad and Tobago.
Before CARICOM, there was another group called the Caribbean Free Trade Association (CARIFTA). It existed from 1965 to 1972. CARIFTA was created to keep Caribbean countries connected economically. This happened after the West Indies Federation ended in 1962.
In 2001, a new agreement called the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas was signed. This treaty helped turn CARICOM into the CARICOM Single Market and Economy (CSME). The CSME aims to make it easier for people, goods, and services to move freely between member countries.
For a few years, from 2004 to 2006, Haiti's membership in CARICOM was paused. This happened after a change in Haiti's government. CARICOM believes that leaders of democratically elected governments should not be removed from power. After new elections, Haiti was welcomed back into the group.
Since 2013, CARICOM countries and the Dominican Republic have had a special trade agreement with the European Union. This agreement is called CARIFORUM. It ensures fair trade and investment rights for all members.
Who are the Members of CARICOM?
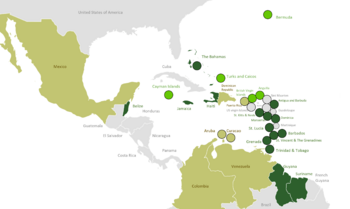
As of 2016, CARICOM has 15 full members, 5 associate members, and 8 observer states. The associate members are all British Overseas Territories. This means they are territories that are part of the United Kingdom but have their own governments. Observer states are countries that work with CARICOM on specific projects.
| Status | Name | Join date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full member | 4 July 1974 | ||
| 4 July 1983 | Not part of the customs union | ||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 2 July 2002 | Provisional membership on 4 July 1998 | ||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| 1 May 1974 | British overseas territory | ||
| 26 July 1974 | Joined as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla | ||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 1 May 1974 | |||
| 4 July 1995 | |||
| 1 August 1973 | One of the four founding members | ||
| Associate | July 1999 | British overseas territory | |
| 2 July 2003 | |||
| July 1991 | |||
| 16 May 2002 | |||
| July 1991 | |||
| Observer | Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | ||
| Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | |||
| Unincorporated territory of the United States | |||
| Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | |||
CARICOM's Relationship with Cuba
In 2017, Cuba and CARICOM signed an agreement to improve trade. In December 2022, Cuba's President, Miguel Díaz-Canel, met with CARICOM leaders. They celebrated 50 years of diplomatic ties and 20 years of CARICOM-Cuba Day. Cuba also agreed to work more closely with CARICOM. This includes joining discussions on food production and security.
How CARICOM is Organized
CARICOM divides its 15 full member states into two groups:
- Less Developed Countries (LDCs): These are smaller countries that need more support for their development.
- Antigua and Barbuda, Belize, Dominica, Grenada, Haiti, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
- More Developed Countries (MDCs): These are larger countries with stronger economies.
- The Bahamas, Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago.
Leadership of CARICOM
The role of Chairman, who is the main leader of CARICOM, rotates among the heads of government of the 15 member states. This means different leaders take turns leading the organization.
The Secretariat
The Secretariat of the Caribbean Community is like the main office for CARICOM. It handles all the day-to-day work. The Secretary-General of the Caribbean Community is the chief executive. They are in charge of foreign relations and community matters. The Secretary-General serves for five years and can be re-elected.
The Secretariat's main goal is to help improve the lives of people in the Caribbean. It also works to build a strong, innovative, and competitive community.
Main Groups and Committees
CARICOM has several important groups that help it run smoothly:
| Organ | Description |
|---|---|
| CARICOM Heads of Government | This group includes the leaders (Presidents or Prime Ministers) from each member country. |
Community Council
The Community Council is made up of ministers who handle community affairs. It is one of the two main parts of CARICOM, along with the Conference of the Heads of Government.
| Group | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| Council for Finance and Planning | COFAP |
| Council for Foreign and Community Relations | COFCOR |
| Council for Human and Social Development | COHSOD |
| Council for Trade and Economic Development | COTED |
| Committee | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Affairs Committee | Gives legal advice to CARICOM. |
| Budget Committee | Checks the budget and work plans of the Secretariat and makes suggestions. |
| Committee of the Central Bank Governors | Gives advice on money and financial matters. |
Important CARICOM Institutions
CARICOM has many important institutions that help with different areas. These include:
| Institution | Abbreviation | Location | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caribbean Centre for Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency | CCREEE | Bridgetown | Barbados |
| Caricom Development Fund | CDF | Bridgetown | Barbados |
| Caribbean Telecommunications Union | CTU | Port of Spain | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre | CCCCC | Belmopan | Belize |
| Caricom Regional Organisation for Standards and Quality | CROSQ | Bridgetown | Barbados |
| Caribbean Meteorological Organisation | CMO | Port of Spain | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism | CRFM | Belize City | Belize |
| Caricom Implementation Agency for Crime and Security | IMPACS | Port of Spain | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caribbean Institute for Meteorology and Hydrology | CIMH | Bridgetown | Barbados |
| Caribbean Examinations Council | CXC | Bridgetown | Barbados |
| Caribbean Court of Justice | CCtJ/CCJ | Port of Spain | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caricom Competition Commission | CCC | Paramaribo | Suriname |
| Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency | CDEMA | Saint Michael | Barbados |
| Caribbean Agricultural Health and Food Safety Agency | CAHFSA | Paramaribo | Suriname |
| Caribbean Aviation Safety and Security Oversight System | CASSOS | Kingston | Jamaica |
| Caribbean Public Health Agency | CARPHA | Port of Spain | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caribbean Centre for Development Administration | CARICAD | Saint Michael | Barbados |
| Caribbean Agriculture Research and Development Institute | CARDI | Saint Augustine | Trinidad and Tobago |
| Caribbean Organisation of Tax Administrators | COTA | Georgetown | Guyana |
Symbols of CARICOM
The CARICOM Flag
The flag of the Caribbean Community was chosen in November 1983. It was first flown on July 4, 1984, in The Bahamas.
The flag has a blue background. The top part is light blue, like the sky. The bottom part is darker blue, representing the Caribbean Sea. In the middle, there is a yellow circle, which stands for the sun. Inside the sun, there is a black logo of two interlocking "Cs." These "Cs" look like broken links in a chain. This symbolizes both unity and breaking away from the past. A thin green ring around the sun represents the lush plants of the region.
The CARICOM Song
For CARICOM's 40th anniversary in 2013, a competition was held to find an official song. The goal was to find a song that promoted unity and pride in CARICOM. In March 2014, Celebrating CARICOM by Michele Henderson of Dominica was chosen as the winner.
The song was first performed officially on July 1, 2014. This happened at a meeting of the Heads of Government in Antigua and Barbuda.
CARICOM Celebrations
CARICOM Day
CARICOM Day is a special day when some CARICOM countries remember the signing of the Treaty of Chaguaramas. This treaty created CARICOM on July 4, 1973. The treaty was signed in Trinidad and Tobago by the leaders of Barbados, Guyana, Jamaica, and Trinidad and Tobago.
CARICOM Day is a public holiday in Guyana, where the main office is located. It is celebrated on the first Monday of July. Antigua and Barbuda also celebrates CARICOM Day as a holiday. On this day, governments organize events like parades and campaigns to teach people about CARICOM.
Caribbean Festival of Arts – CARIFESTA
The Caribbean Festival of Arts, or CARIFESTA, is an annual festival that celebrates Caribbean arts. A different country hosts the event each year. It started in 1972 in Guyana. The festival aims to show the life, heroes, and traditions of the Caribbean people. It also helps unite the Caribbean and inspire artists.
Statistics about CARICOM Members
| Member | Membership | Land area (km2) | Population (2019) | GDP (PPP) Millions USD (2017) | GDP Per Capita (PPP) USD (2017) | Human Development Index (2022) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| associate | 91 | 15,174 | 175.4 | 12,200 | – | |
| full member | 442.6 | 104,084 | 2,390 | 26,300 | 0.826 | |
| full member | 10,010 | 385,340 | 9,339 | 25,100 | 0.820 | |
| full member | 430 | 287,010 | 4,919 | 17,500 | 0.809 | |
| full member | 22,806 | 398,050 | 3,230 | 8,300 | 0.700 | |
| associate | 54 | 63,779 | 5,198 | 85,700 | – | |
| associate | 151 | 32,206 | 500 | 42,300 | – | |
| associate | 264 | 64,420 | 2,507 | 43,800 | – | |
| full member | 751 | 74,679 | 851 | 12,000 | 0.740 | |
| full member | 344 | 108,825 | 1,590 | 14,700 | 0.793 | |
| full member | 214,970 | 786,508 | 6,367 | 8,300 | 0.742 | |
| full member | 27,560 | 11,242,856 | 19,880 | 1,800 | 0.552 | |
| full member | 10,831 | 2,728,864 | 26,200 | 9,200 | 0.706 | |
| full member | 102 | 5,220 | 43.8 | 8,500 | – | |
| full member | 261 | 56,345 | 1,528 | 26,800 | 0.838 | |
| full member | 606 | 180,454 | 2,384 | 13,500 | 0.725 | |
| full member | 389 | 109,803 | 1,281 | 11,600 | 0.772 | |
| full member | 156,000 | 573,085 | 7,928 | 13,900 | 0.690 | |
| full member | 5,128 | 1,359,193 | 42,780 | 31,200 | 0.814 | |
| associate | 948 | 37,910 | 632 | 29,100 | – | |
| Full members | members only | 432,510 | 18,400,316 | 130,711 | 15,247 | 0.751 |
Thousands of people from CARICOM countries live in other member states. For example, many Jamaicans live in The Bahamas, Antigua & Barbuda, Barbados, and Trinidad & Tobago. Also, many Guyanese live in Barbados and Suriname. This movement of people shows how connected the CARICOM nations are.
CARICOM's Relationships with Other Caribbean Groups
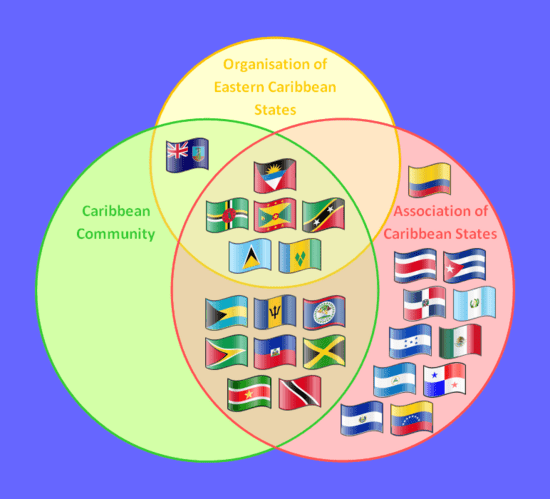
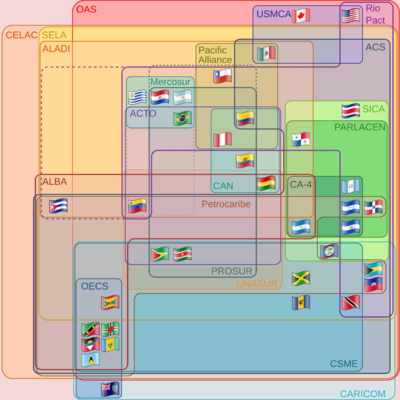
Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
CARICOM played a big part in creating the Association of Caribbean States (ACS) in 1994. The idea was to bring together all the countries in the Caribbean basin. This includes Central American and Latin American nations that border the Caribbean. The ACS aims to deepen cooperation across the wider Caribbean region.
Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
CARICOM also helped form the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC) in 2010. CELAC works to integrate the Americas. It complements other existing organizations like the Organization of American States.
Trade Agreements with the European Union
Since 2013, CARICOM countries and the Dominican Republic have a trade agreement with the European Union. This is called CARIFORUM. It gives equal trade and investment rights to all members. This agreement helps resolve trade disputes between CARIFORUM and EU states.
OHADAC Project for Business Law
In 2016, CARICOM's court, the CCJ, supported the OHADAC Project. This project aims to create common business laws across the Caribbean. It helps make trade and investment easier by having clear, shared rules.
See also
 In Spanish: Comunidad del Caribe para niños
In Spanish: Comunidad del Caribe para niños
- Association of Caribbean States
- EU/UK–CARIFORUM
- CSME
- Caribbean Financial Action Task Force
- Caribbean Initiative
- Caribbean Agricultural Research and Development Institute (CARDI)
- Caribbean Accreditation Authority for Education in Medicine and other Health Professions
- Caribbean Knowledge and Learning Network
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States
- Commonwealth of Nations
- Languages of the Caribbean
- List of regional organizations by population
- North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA)
- North American Union (NAU)
- Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States
- Organization of American States
- Petrocaribe
- Projects of the Caribbean Community
- Small Island Developing States
- Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- West Indies
Images for kids
-
Exclusive Economic Zones of the member states of the CARICOM.