Santiago, Chile facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Santiago
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

A collage of Santiago, showing places like Santa Lucía Hill, La Moneda Palace, and the National Museum of Fine Arts.
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Nickname(s):
"The City of the Island Hills"
|
|||||
| Country | Chile | ||||
| Region | Santiago Metropolitan Region | ||||
| Province | Santiago Province | ||||
| Foundation | 12 February 1541 | ||||
| Founded by | Pedro de Valdivia | ||||
| Named for | Saint James | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • City | 641 km2 (247.6 sq mi) | ||||
| Elevation | 570 m (1,870 ft) | ||||
| Population
(2017)
|
|||||
| • Density | 9,821/km2 (25,436/sq mi) | ||||
| • Metro | 6,310,000 | ||||
| Demonym(s) | Santiaguinos (-as) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−4 (CLT) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−3 (CLST) | ||||
| Postal code |
8320000
|
||||
| Area code(s) | +56 2 | ||||
| HDI (2017) | 0.874 – very high | ||||
Santiago de Chile, often called Santiago, is the capital and largest city of Chile. It is also one of the biggest cities in the Americas. Santiago is the heart of Chile's most populated area, the Santiago Metropolitan Region, which has over 7 million people.
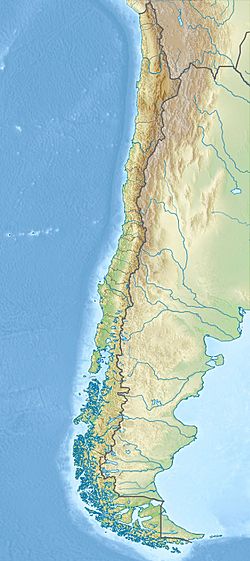
The city is located in Chile's central valley, mostly between 500 and 650 meters (about 1,640 to 2,130 feet) above sea level. Pedro de Valdivia, a Spanish conqueror, founded Santiago in 1541. It has been the capital of Chile ever since.
Santiago's downtown has many buildings from the 1800s with a classic style. You can also find other styles like Art Deco. The city's look is shaped by several hills and the Mapocho River, which has parks along its banks. The amazing Andes Mountains can be seen from almost anywhere in Santiago. These mountains can sometimes trap air pollution, especially in winter. Outside the city, there are vineyards, and you can reach both the mountains and the Pacific Ocean in about an hour.
Santiago is very important for Chile's culture, politics, and money. Many big international companies have their main offices here. The Chilean government's executive and judicial branches are in Santiago. However, the country's Congress usually meets in Valparaíso, a city nearby. Santiago is named after Saint James from the Bible. Santiago will host the 2023 Pan American Games, a big sports event.
Contents
Geography: Where is Santiago Located?
Santiago sits in the middle of the Santiago Basin. This is a large, bowl-shaped valley with rich, flat land surrounded by mountains. The city's height above sea level changes. It starts at about 400 meters (1,312 feet) in the west and goes up to over 700 meters (2,296 feet) in the east. For example, Santiago's international airport is at 460 meters (1,509 feet). Plaza Baquedano, near the city center, is at 570 meters (1,870 feet).
The Santiago Basin is very flat, except for a few "island hills." These include Cerro Renca, Cerro Blanco, and Cerro Santa Lucía. The basin is about 80 kilometers (50 miles) long from north to south and 35 kilometers (22 miles) wide from east to west. The Mapocho River flows right through the city.
Mountains Around Santiago
The city is surrounded by mountains. To the east, you'll find the main chain of the Andes Mountains. To the west, there's the Chilean Coast Range. To the north, the Cordón de Chacabuco, an Andes mountain range, forms a border. In the south, the Angostura de Paine is a long part of the Andes that almost reaches the coast.
The mountain range right next to the city on the east is called the Sierra de Ramón. It was formed by movements of the San Ramón Fault in the Earth. This range reaches 3,296 meters (10,813 feet) at Cerro de Ramón. About 20 kilometers (12 miles) further east is the even larger Andes mountain range. It has huge mountains and volcanoes that are over 6,000 meters (19,685 feet) tall, some with glaciers. The tallest is Tupungato mountain at 6,570 meters (21,555 feet). Other big mountains include Tupungatito, San José, and Maipo. Cerro El Plomo is the highest mountain you can see from Santiago.
In recent years, Santiago has grown beyond its original borders. It has expanded eastward, climbing up the slopes of the Andes mountains. In areas like La Dehesa, Lo Curro, and El Arrayan, buildings are now found at over 1,000 meters (3,280 feet) high.
Plants and Trees in Santiago
The natural plants in Santiago are mostly thorny woodlands. In the west, you'll find Vachellia caven (also known as espinillo) and Prosopis chilensis. In the east, near the Andes foothills, Vachellia caven grows with Baccharis paniculata.
Climate: What's the Weather Like in Santiago?
Santiago has a cool semi-arid climate with Mediterranean weather patterns. This means it has warm, dry summers from October to March, where temperatures can reach 35°C (95°F) on the hottest days. Winters, from April to September, are cool and humid. Mornings are often chilly, with temperatures sometimes near 0°C (32°F). During winter, the highest daily temperatures are usually around 14°C (57°F).
The average rainfall in Santiago is about 341.8 mm (13.46 inches) near downtown and 367.8 mm (14.48 inches) in higher areas closer to the Andes.
Images for kids
-
Municipality of Santiago Commune
-
The founding of Santiago in 1541. A painting by Pedro Lira.
-
The Battle of Maipú in 1818.
-
The Neptune Terrace on Santa Lucía Hill.
-
The Santiago metro expanded to areas like Maipú and Puente Alto.
-
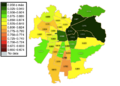
Santiago by Human Development Index in 2017.
-
The front of the Santiago Stock Exchange.
See also
 In Spanish: Santiago de Chile para niños
In Spanish: Santiago de Chile para niños