Caliph facts for kids
A caliph was a very important leader in the Islamic world. In Arabic, the word "caliph" means "a successor to the prophet." This title was given to the leaders who followed the Prophet Muhammad. Their rule was called a caliphate.
Some of the early leaders of the Muslim community, after Muhammad's death (570–632 AD), called themselves "Khalifat Allah". This meant representative of God. But the more common title became "Khalifat rasul Allah", which means successor to the prophet of God.
Caliphs were often also called Amīr al-Mu'minīn (أمير المؤمنين). This title means leader of the Muslims. Today, this title has been shortened to "emir". It is also used as a personal name in some countries.
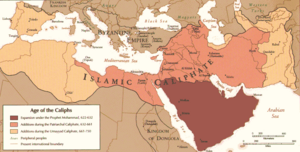
After the first four caliphs (Abu Bakr, Umar ibn al-Khattab, Uthman ibn Affan, and Ali ibn Abi Talib), many other powerful groups used the title. These included the Umayyads, the Abbasids, and the Ottomans. Other dynasties in places like Southern Pakistan, Spain, Northern Africa, and Egypt also used it.
Most historical Muslim rulers simply called themselves sultans or emirs. Often, the caliph himself had very little real power. The title was no longer used after the Republic of Turkey ended the Ottoman caliphate in 1924.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Mustansiriya Madrasah in Baghdad
-
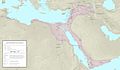
Ayyubid Sultanate (in pink) at the death of Saladin in 1193
-
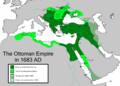
The Ottoman Empire at its greatest extent in 1683, under Sultan Mehmed IV
-
Abdulmejid II, the last caliph of Sunni Islam from the Ottoman dynasty, with his daughter Dürrüşehvar Sultan
-
Official portrait of Abdulmejid II as caliph
-
Hafiz Muhiuddin Aurangzeb, unlike his predecessors, was considered to be a Caliph of India
-
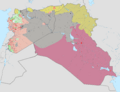
ISIL's territory, in grey, at the time of its greatest territorial extent in May 2015
See also
 In Spanish: Califato para niños
In Spanish: Califato para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |