Eastern European Time facts for kids
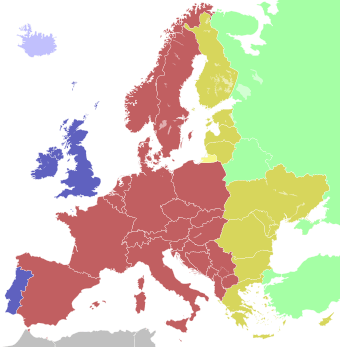
| blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) Western European Summer Time (UTC+1) |
| light blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) |
| red | Central European Time (UTC+1) Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) |
| yellow | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) |
| orange | Kaliningrad Time (UTC+3) |
| green | Further-eastern European Time (UTC+3), a.k.a. Moscow Time |
Eastern European Time (EET) is a way to measure time. It means the time is 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). Think of UTC as a main clock that helps everyone around the world know what time it is.
EET is used in some countries in Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. Many of these countries also use Eastern European Summer Time (which is UTC+3) during the summer. This is a special time change called daylight saving time, where clocks are moved forward to make evenings brighter.
Contents
Where Eastern European Time is Used
A few countries use Eastern European Time all year long, meaning they don't change their clocks for summer:
The following countries use Eastern European Time during the winter. They switch to a different time zone for summer:
- Bulgaria (since 1894)
- Cyprus (except for a period in Northern Cyprus)
- Estonia (used for many years, including since 1989)
- Finland (since 1921)
- Greece (since 1916)
- Israel (since 1948)
- Jordan
- Latvia (used for many years, including since 1989)
- Lebanon
- Lithuania (used for many years, including since 1989)
- Moldova (used for many years, including since 1991)
- Palestinian territories
- Romania (since 1931)
- Syria
- Ukraine (used for many years, including since 1990)
Moscow in Russia used EET for some years in the past. Poland also used this time zone between 1918 and 1922. Turkey used EET for a long time, from 1910 to 2016, but now uses a different time zone all year.
Big Cities Using Eastern European Time
Many large cities are in the Eastern European Time zone. Here are some of them:
- Ankara, Turkey
- Athens, Greece
- Beirut, Lebanon
- Brasov, Romania
- Bucharest, Romania
- Cluj Napoca, Romania
- Chişinău, Moldova
- Damascus, Syria
- Helsinki, Finland
- Istanbul, Turkey
- İzmir, Turkey
- Jerusalem, Israel
- Kiev, Ukraine
- Lviv, Ukraine
- Minsk, Belarus
- Nicosia, Cyprus
- Riga, Latvia
- Sofia, Bulgaria
- Tallinn, Estonia
- Tel Aviv, Israel
- Thessaloniki, Greece
- Timişoara, Romania
- Vilnius, Lithuania
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hora de Europa Oriental para niños
In Spanish: Hora de Europa Oriental para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |