Golan Heights facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
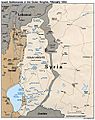
Golan Heights
هضبة الجولان
רמת הגולן |
|
|---|---|

Lake Ram near Mount Hermon (background), in the northeastern Golan Heights
|
|
 |
|
| Country | Syrian territory occupied by Israel. |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,800 km2 (700 sq mi) |
| • Occupied by Israel | 1,200 km2 (500 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 2,814 m (9,232 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
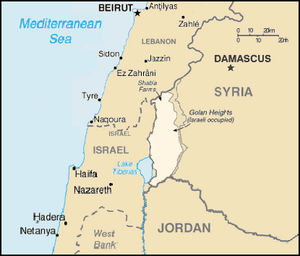
The Golan Heights is a hilly area of land in the Middle East. It was captured by Israel from Syria in 1967 during a war called the Six-Day War. The United Nations wants Israel to leave the Golan Heights.
Syria and Israel have not yet signed a peace agreement because of this land. They have tried to make peace, but they can't agree on who owns the land. On the western side of the Golan Heights, there are old, inactive volcanoes.
In 2013, the Israeli government said it planned to build a wall along the eastern edge of the Golan Heights. This wall would be on its border with Syria.
Contents
Maps
-
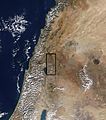
A map of the Golan Hights from a satellite.
Geography
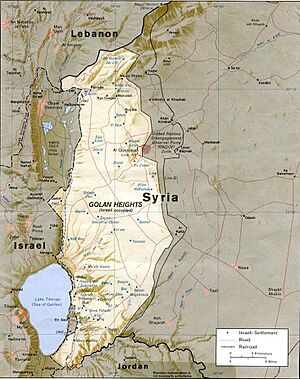
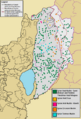
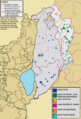
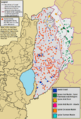
The Golan Heights shares borders with Israel, Lebanon, and Jordan. Different groups have slightly different ideas about how big the Golan Heights is. Israel says it controls about 1,150 square kilometers (440 sq mi). Syria says the whole area is 1,860 square kilometers (720 sq mi), with Israel occupying about 1,500 square kilometers (580 sq mi). The CIA says Israel holds about 1,300 square kilometers (500 sq mi).
This area is hilly and high up. It looks over the Jordan Rift Valley, which includes the Sea of Galilee and the Jordan River. The tallest point is Mount Hermon, which is about 2,814 meters (9,232 ft) high. The average height of the plateau is about 1,000 meters (3,300 ft).
The Golan Heights is part of a larger area of volcanic rock. This rock was formed by volcanoes that started erupting almost 4 million years ago. The area has clear natural borders. To the north, the Sa'ar valley separates the lighter limestone mountains from the dark volcanic rocks of the plateau.
The western edge of the plateau drops steeply into the Jordan Rift Valley. The southern border is the Yarmuk River, which separates it from Jordan. The eastern part of the Golan Heights is marked by the Raqqad river and areas still controlled by Syria.
The Golan Heights is about 65 kilometers (40 mi) long from north to south. Its width from east to west changes, from 12 kilometers (7.5 mi) to 25 kilometers (16 mi). The land is highest at Mount Hermon in the north. It gets lower towards the Yarmuk River in the south, where it's about 400 meters (1,300 ft) high. The Sea of Galilee, at the southwest corner, is about 200 meters (660 ft) below sea level. The northern part is steeper and rougher, while the southern part is flatter.
The wider Golan plateau is generally between 120 meters (390 ft) and 520 meters (1,710 ft) high. In Israel, the Golan plateau is split into three parts: northern, central, and southern. The western side of the Golan Heights has a steep rock wall that drops 500 meters (1,600 ft) down to the Jordan River valley and the Sea of Galilee.

The Golan plateau is part of a large area of volcanoes that also reaches northeast to Damascus. Many dormant volcanoes and cinder cones are scattered across the area, like near Majdal Shams. There is also a crater lake called Birkat Ram, which gets its water from rain and underground springs. These volcanic areas have dark soils from the breakdown of basalt rock.
The rock in the northern Golan Heights, near Mount Hermon, is different. It's lighter-colored limestone from the Jurassic period. This limestone has cracks and channels, forming a karst-like landscape where springs are common.
Besides its military importance, the Golan Heights is a very important source of water. The higher parts get a lot of snow in winter, which melts and feeds rivers and springs during the dry season. The Golan Heights gets much more rain than the lower areas around it. The part of the Golan Heights controlled by Israel provides a lot of water for the Jordan River watershed. This water then helps supply Israel's water needs. The Golan Heights provides about 15% of Israel's water.
Images for kids
-
Israeli children in a bomb shelter at Kibbutz Dan during the Six-Day War
-
Israeli soldiers of the Alpinist Unit are dispatched to Mount Hermon
-
View of Mount Hermon from the road to Masaade.
-
View of Beer Ajam (بئرعجم), a Syrian Circassian village in the province of Quneitra founded in 1872. -
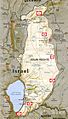
Demographic map of Quneintra Governorate (Golan Heights) today (excludes any permanent depopulation or repopulation that might have happened during the Syrian civil war
See also
 In Spanish: Altos del Golán para niños
In Spanish: Altos del Golán para niños