Eurasian plate facts for kids
The Eurasian Plate is a huge piece of the Earth's outer shell. It is one of the major tectonic plates that make up our planet's surface. This plate includes most of the landmass known as Eurasia. Eurasia is a very large area that combines the traditional continents of Europe and the northern part of Asia.
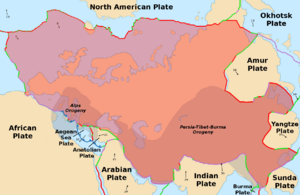
The Eurasian Plate stretches across a vast region. It does not include the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian Peninsula, or the area east of the Chersky Range in East Siberia. However, it does include the oceanic crust that extends west to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and north to the Gakkel Ridge.
Contents
What is a Tectonic Plate?
The Earth's surface is not one solid piece. Instead, it is broken into several large and small sections. These sections are called tectonic plates. Think of them like giant puzzle pieces that fit together. These plates are always moving, though very slowly. They float on a softer, hotter layer of rock deep inside the Earth.
How Plates Move
Tectonic plates move because of heat from the Earth's core. This heat creates slow currents in the molten rock beneath the plates. These currents act like a conveyor belt, gently pushing the plates around. This movement can cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and the formation of mountains over millions of years.
Where is the Eurasian Plate Located?
The Eurasian Plate covers a massive part of the Northern Hemisphere. It includes almost all of Europe and a large part of Asia. It also extends into the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the Arctic Ocean to the north.
Borders of the Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate shares borders with several other major plates:
- To the south, it meets the African Plate, the Arabian Plate, and the Indian Plate.
- To the east, it borders the North American Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate.
- To the west, it meets the North American Plate along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This is where new oceanic crust is formed.
Geological Features of the Eurasian Plate
The movement of the Eurasian Plate has created many interesting geological features. For example, the Alps and the Himalayas mountain ranges were formed by the collision of the Eurasian Plate with other plates.
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
Along the edges where the Eurasian Plate meets other plates, there is often a lot of geological activity. This includes earthquakes and volcanoes. For instance, Iceland sits right on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, where the Eurasian Plate is pulling away from the North American Plate. This causes a lot of volcanic activity and hot springs.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Placa euroasiática para niños
In Spanish: Placa euroasiática para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |