Weimar Republic facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
German Reich
Deutsches Reich
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1933 | |||||||||
|
Motto: "Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit"
"Unity and Justice and Freedom" |
|||||||||
|
Anthem:
|
|||||||||
Germany in 1930
|
|||||||||
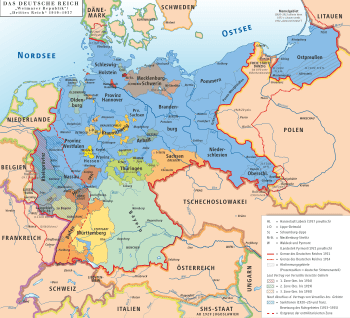
German states in 1920s (Free State of Prussia with its provinces shown in blue)
|
|||||||||
| Capital | Berlin Weimar (de facto) | ||||||||
| Common languages | Official: German Unofficial:
Danish, French, Polish, Czech, Dutch, Sorbian, Low German, Frisian, Lithuanian, Yiddish |
||||||||
| Religion | 1925 census 64.1% Protestant (Lutheran, Reformed, United) 32.4% Roman Catholic 0.9% Jewish 2.6% Other |
||||||||
| Government | 1919–30 Federal semi-presidential constitutional republic 1930–33 De facto authoritarian presidential republic |
||||||||
| President | |||||||||
|
• 1919–25
|
Friedrich Ebert | ||||||||
|
• 1925–33
|
Paul von Hindenburg | ||||||||
| Chancellor | |||||||||
|
• 1919 (first)
|
Philipp Scheidemann | ||||||||
|
• 1933 (last)
|
Adolf Hitler | ||||||||
| Legislature | Reichstag | ||||||||
|
• State Council
|
Reichsrat | ||||||||
| Historical era | Interwar period | ||||||||
|
• Established
|
9 November 1918 | ||||||||
|
• Government by decree begins
|
29 March 1930 | ||||||||
|
• Hitler appointed Chancellor
|
30 January 1933 | ||||||||
| 27 February 1933 | |||||||||
| 23 March 1933 | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1925 | 468,787 km2 (181,000 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
|
• 1925
|
62,411,000 | ||||||||
| Currency |
|
||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Weimar Republic (German: Weimarer Republik) was the name for the government of Germany from 1919 to 1933. It was a republic, meaning the people had a say in who governed. Even though it was a republic, its official name was still the German Reich (German: Deutsches Reich).
Contents
The Start of the Weimar Republic
After Germany lost World War I, the country changed from an empire ruled by an emperor to a republic. This new government was called the Weimar Republic. It got its name because its new constitution was written in the city of Weimar.
How the Republic Began
On November 9, 1918, a new republic was announced in Berlin. Philipp Scheidemann made the announcement at the Reichstag building. Just two hours later, Karl Liebknecht announced a socialist republic nearby.
The German Emperor, Wilhelm II, left the country and went to the Netherlands. The new Republic was declared even before World War I officially ended.
Challenges Faced by the Republic
The Weimar Republic faced many difficulties. The Treaty of Versailles, signed after World War I, put a heavy burden on Germany's economy. This led to extreme inflation, where money lost its value very quickly. For example, a loaf of bread could cost millions of marks!
Politically, the government was unstable. Leaders often stayed in power for only short periods, making it hard to solve big problems. There were also many groups with extreme views. Some wanted the monarchy back, while others were communists who believed all property and wealth should be shared. These groups sometimes had their own armed groups that fought each other.
One group that formed after World War I was called the Stahlhelm, Bund der Frontsoldaten. This means "Steel Helmet, League of Front Soldiers." They were like a security force for a conservative political party. Later, in 1935, they became part of the Nazi Party.
Positive Changes and Culture
Despite its problems, the Weimar period was also known for its exciting culture. Artists explored new ideas and used modern things like film in their work. The famous Bauhaus art and design school also started in the 1920s, bringing new styles to architecture and art.
The End of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic ended on March 23, 1933. On this day, Adolf Hitler, who had become Chancellor, put the Enabling Act into law. This act gave him special powers and marked the beginning of Nazi Germany, also known as the Third Reich.
Images for kids
-
Philipp Scheidemann speaks to a crowd from a window, 9 November 1918
-
Wilhelm Marx's Christmas broadcast, December 1923
-
The SA had nearly two million members by late 1932.
See also
 In Spanish: República de Weimar para niños
In Spanish: República de Weimar para niños