William Bourne (mathematician) facts for kids
William Bourne (born around 1535, died 1582) was a clever English mathematician. He also worked as an innkeeper and used to be a gunner in the Royal Navy. He is famous for creating one of the first designs for a submarine that could actually travel underwater. He also wrote important books that helped sailors navigate the seas. People often called him William Bourne of Gravesend, which is a town in England.
In 1574, he made a simpler version of a popular sailing book called Arte de Navegar. Bourne's version was called A Regiment for the Sea. He thought the original book could be better, so he made his own guide more useful for everyday sailors. His book taught sailors how to observe the sun and stars using a tool called a cross-staff. It also showed them how to map out coastal areas from their ship by taking measurements using a method called triangulation.
Contents
Life in Gravesend
Before he published his submarine design, William Bourne was an important local official in Gravesend, England. His name first appears in the official records of Gravesend on June 5, 1562. His name is also listed again on June 5, 1568.
During this time, the rules for trading in Gravesend were written in Bourne's own handwriting. This suggests he held an important job, perhaps like a clerk who managed the market. He also worked as an innkeeper, running one of the fourteen inns in the town of Gravesend.
Designing an Underwater Ship
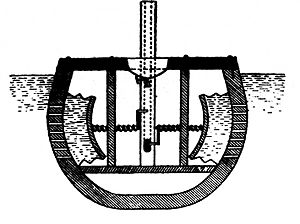
William Bourne's design for a submarine was one of the first ever recorded plans for a vehicle that could travel underwater. He described it in his book Inventions or Devises, published in 1578.
He imagined a sealed boat that could go underwater by changing its size. This was different from modern submarines that fill special tanks with water to sink. Bourne's idea was for a wooden frame covered in waterproof leather. It would be rowed underwater.
While his description was more of a general idea than a detailed blueprint, the concept of an underwater rowing boat was later built. A Dutch inventor named Cornelius Drebbel created one in 1620. Later, in 1729, Nathaniel Symons showed off a "sinking boat" that also used the idea of the boat expanding and shrinking to go underwater.
Bourne's submarine design was even recreated on a TV show called "The Re-Inventors". In one episode, they tried to build his submarine. It worked a little bit, but then it sank when water pressure broke some parts during a test dive.
Important Inventions and Ideas
Inventions or Devises, published in 1578, is one of William Bourne's most important books. This book offers many guides and tools for sailors. Most of these ideas help sailors communicate or interact with other ships.
One of the inventions described in the book is the earliest known description of a ship's log and line. This tool was used to measure a ship's speed. Bourne said that Humprey Cole, an officer at the Tower Mint, created it.
Another idea in the book is a night signal system, like an early semaphore. This system used a series of lights and ways of standing to send messages between ships far away. Sailors would have agreed on a secret code beforehand.
The book also describes what seems to be a type of telescope. This device was supposedly used by a mathematician named Leonard Digges. Queen Elizabeth I's chief advisor, Lord Burghley, asked Bourne to investigate it. Bourne's description is the best one we have. From his writing, it seems the device involved looking into a large curved mirror that reflected an image made by a big lens. Bourne noted that it worked but had a very narrow view, making it not very useful for military purposes. This "backwards" reflecting telescope was described 30 years before the first known working telescope. However, it was too difficult to use, so it wasn't developed further.
Books by William Bourne
- An Almanac and Prognostication for Three Years, 1571
- Treasure for Travellers, 1572/3
- Art of Shooting in Great Ordnance, 1572/3
- A Regiment for the Sea, 1574 (This book was very popular and had many editions.)
- Inventions or Devises. Very Necessary for all Generalles and Captaines, as wel by Sea as by Land, 1578
- The Arte of Shooting in Great Ordinance, 1578
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |


