Newtonian telescope facts for kids
The Newtonian telescope, also known as the Newtonian reflector, is a special type of reflecting telescope. It was invented by the famous English scientist Sir Isaac Newton. This telescope uses a curved primary mirror and a flat secondary mirror to gather and focus light. Newton finished his first reflecting telescope in 1668. It was the first working reflecting telescope ever made. Because it's fairly simple to build, the Newtonian telescope is very popular with people who like to make their own telescopes.
Contents
How a Newtonian Telescope Works
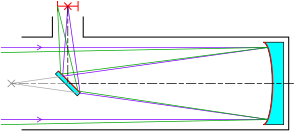
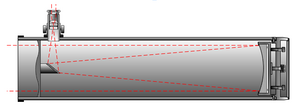
A Newtonian telescope has two main parts: a large primary mirror and a smaller flat secondary mirror. The primary mirror is usually shaped like a parabola. Its job is to collect light from the sky. The secondary mirror then bounces this light at a right angle out of the side of the telescope. This way, you can look through an eyepiece to see the image.
Good Things About Newtonian Telescopes
- They don't have a problem called chromatic aberration. This is a color distortion that happens in telescopes that use lenses (refracting telescopes).
- Newtonian telescopes are often cheaper to make than other types of telescopes. This is true for telescopes of the same size.
- Making a Newtonian telescope is simpler. Only one main mirror needs to be shaped and polished. Other telescope designs often need two or more complex surfaces to be made.
- They can easily have a short focal ratio. This means they can show a wider area of the sky at once.
- The eyepiece is located at the top side of the telescope tube. This design can make the telescope easier to set up and carry around.
Challenges with Newtonian Telescopes
- Newtonian telescopes can have an issue called coma. This makes stars at the edges of the view look like small comets. It's not a problem in the center, but it gets worse towards the edges. This is more noticeable in telescopes with a low focal ratio.
- The secondary mirror sits in the middle of the light path. This can slightly reduce the image contrast. Also, the supports for the secondary mirror can create "diffraction spikes" around bright stars. These look like faint cross shapes.
- If you move a portable Newtonian telescope, its mirrors can get out of alignment. This is called collimation. You might need to re-align the mirrors each time you set up the telescope. Other types of telescopes, like refractors, usually stay aligned.
- The eyepiece is at the top of the telescope tube. For very large telescopes, you might need a ladder to reach the eyepiece. This can make observing a bit tricky.
Different Kinds of Newtonian Telescopes
Some variations of the Newtonian design add a special lens. These are called catadioptric telescopes. They help fix some image problems or make the telescope cheaper.
Schmidt–Newtonian
A Schmidt–Newtonian telescope combines the Newtonian design with a Schmidt corrector plate. This plate is placed at the front of the telescope. It helps correct image problems like spherical aberration and can also hold the secondary mirror. This design results in less coma and fewer diffraction effects from the mirror supports.
Maksutov–Newtonian
Similar to the Schmidt–Newtonian, a Maksutov telescope can also be made into a Newtonian. It uses a special curved lens called a meniscus corrector. This gives it a very clear view over a wide area. It also has much less coma than a standard Newtonian.
Jones–Bird
A Jones–Bird Newtonian uses a simpler, spherical primary mirror instead of a parabolic one. A special lens, called a sub-aperture corrector, fixes the image problems caused by the spherical mirror. This lens is usually placed near the eyepiece. This design helps make the telescope smaller and cheaper. However, some commercially made versions might not have the best image quality.
History of the Newtonian Telescope
The idea of using a mirror in a telescope wasn't new when Newton came along. Scientists like Galileo Galilei had already talked about it. Others, like Niccolò Zucchi, even claimed to have tried it in 1616. Newton might have even read a book by James Gregory from 1663. This book described telescope designs that used curved mirrors.
Newton built his reflecting telescope because he had a theory about light. He believed that white light was made up of many different colors. Old refracting telescopes had a problem called chromatic aberration. This made bright objects look blurry with rainbow colors around them. Newton thought this happened because the telescope's lens acted like a prism. It would split white light into its different colors. If this was true, then a telescope without a lens – a reflecting telescope – would not have this problem.
In late 1668, Isaac Newton built his first reflecting telescope. He used a special alloy of tin and copper for his main mirror. He also figured out how to shape and polish the mirror. He chose a simple spherical shape for his mirror. This made it easier to build, even though it would cause a slight image problem. The most important part of his design was the small, flat secondary mirror. This mirror bounced the light to the side of the telescope, where the eyepiece was. This way, the image could be seen without blocking the main mirror too much.
Newton's first telescope had a main mirror that was about 1.3 inches (33 mm) wide. He found that it worked without color distortion. He could even see the four largest moons of Jupiter and the crescent shape of Venus with it. Newton's friend, Isaac Barrow, showed a second telescope to the Royal Society of London in 1671. They were very impressed and showed it to King Charles II in 1672. Newton became a member of the Royal Society that same year.
Building an effective reflecting telescope was hard, even for Newton. The special metal mirrors would tarnish quickly. This made the view through the telescope very dim compared to other telescopes of the time. Because of these difficulties, the Newtonian telescope was not widely used at first. But in 1721, John Hadley showed a much better model to the Royal Society. Hadley had solved many of the problems of making a good curved mirror. His Newtonian telescope, with a 6-inch (150 mm) mirror, worked just as well as the large refracting telescopes of that era.
See also
 In Spanish: Telescopio newtoniano para niños
In Spanish: Telescopio newtoniano para niños