Atomic theory facts for kids
The atomic theory helps us understand how our ideas about atoms have changed over time. Atoms were once thought to be the smallest pieces of everything around us. But now we know that atoms are actually made of even smaller parts! These tiny parts are called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Even these particles are made of something smaller called quarks.
The very first idea of the atom came from an ancient Greek thinker named Democritus. Later, many of the ideas in our modern atomic theory came from John Dalton, a British scientist. This theory helps us understand solids, liquids, and gases.
Contents
Democritus's Idea of Atoms
Democritus, an ancient Greek philosopher, had a big idea about matter. He thought that if you kept cutting something in half again and again, you would eventually reach a point where you couldn't cut it anymore. He called these tiny, uncuttable pieces "atoms," which means "indivisible."
Democritus believed that these atoms would last forever, never change, and could not be destroyed. He also thought there was empty space between atoms. He felt that if we understood how these atoms worked, we could explain everything around us. Other thinkers at the time either agreed or disagreed, but they had no way to do experiments to prove if his idea was true.
Boscovich's Early Atomic Idea
In 1758, a scientist named Roger Joseph Boscovich described an early version of the atomic theory.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
In 1803, an English scientist named John Dalton updated Democritus's ideas. Here are the main points of his theory:
- All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible, meaning they cannot be broken into smaller pieces, and they are invisible.
- Atoms of the same element are exactly alike in type and mass.
- When atoms combine to form chemical compounds, they do so in specific, fixed amounts.
- Chemical changes happen when atoms rearrange themselves during a chemical reaction.
Dalton said that an atom is the basic unit of an element that can take part in a chemical combination.
Thomson's Atomic Model
In 1850, Sir William Crookes created a special glass tube called a 'discharge tube'. This tube had most of the air removed and metal pieces (electrodes) at each end, connected to a high-voltage power source. When electricity was turned on, a glowing beam shot from the negative electrode (cathode) to the positive electrode (anode). Crookes called these 'cathode rays'.
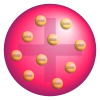
Later, Sir Joseph John Thomson studied these cathode rays. He found that the rays were made of tiny particles with a negative charge. He knew that atoms as a whole were neutral (had no overall charge). So, he figured that atoms must also have positive charges to balance out the negative ones. He called these negative particles "electrons."
Based on this, Thomson suggested the first atomic model. He imagined the atom as a positively-charged sphere with tiny, negatively-charged electrons stuck inside it, like plums in a pudding. This is why it's called the "plum pudding model."
In 1906, Robert Millikan figured out the exact charge of an electron. This helped scientists calculate that electrons are incredibly tiny, with very little mass.
Around the same time, experiments by Eugen Goldstein in 1886 showed that there were also positively charged particles. Lord Ernest Rutherford later named these positive particles "protons."
Rutherford's Atomic Model
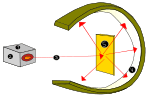
In 1910, a physicist from New Zealand named Ernest Rutherford proposed a new idea for the atom. He suggested that most of the atom's positive charge was concentrated in a tiny, central part called the nucleus. The electrons, he thought, orbited around this nucleus.
Rutherford proved this with his famous Gold Foil Experiment. He shot tiny, positively charged particles (called alpha particles) at a very thin sheet of gold. Most of the particles went straight through, but some bounced back or were deflected. This showed him that the atom was mostly empty space, with a small, dense, positively charged center.
By this time, scientists understood the main parts of the atom. They also discovered that atoms of the same element could have different numbers of neutrons in their nucleus. These are called isotopes. While this model was a big step forward, modern physics has developed even further!
Modern Atomic Physics
Atoms are not the most basic particles. They are made of subatomic particles like protons and neutrons. But even protons and neutrons aren't elementary! They are made of even smaller particles called quarks, which are held together by other particles called gluons. Quarks are considered elementary because, as far as we know, they cannot be broken down any further.
Images for kids
-
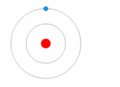
The Bohr model of the atom, which came after Rutherford's model.
See also
 In Spanish: Teoría atómica para niños
In Spanish: Teoría atómica para niños