Matter facts for kids
    |
|
| Matter is usually classified into three classical states, with plasma sometimes added as a fourth state. From top to bottom: quartz (solid), water (liquid), nitrogen dioxide (gas), and a plasma globe (plasma). |
Matter is what everything around us is made of. It's the stuff that makes up all objects that have mass. Think of mass as how much "stuff" is in something. Even when matter isn't moving or is very cold, it still has this special kind of energy called rest mass.
Most of the matter we see every day is made of tiny bits called atoms. These atoms are always moving or vibrating. There are small spaces between them. When matter gets hotter, these tiny particles move faster and spread out more. When it gets colder, they slow down and get closer.
Contents
What is Matter Made Of?
Almost all the matter you can touch and feel is called baryonic matter. This includes all kinds of atoms. Atoms are what give things their mass.
There's also non-baryonic matter. This is matter that isn't mostly made of baryons. Examples include tiny particles called neutrinos and electrons. Scientists also think there's something called dark matter. We can't see or touch dark matter, but it seems to be a big part of the universe.
How Can We Describe Matter?
We can learn about matter using our senses. Matter has properties we can measure, like its mass (how much stuff it has), volume (how much space it takes up), and density (how much mass is in a certain space).
Matter also has qualities we can describe, like its taste, smell, or colour. For example, a lemon tastes sour, a flower smells sweet, and a sky is blue.
Where Do We Find Matter?
Everything physical in the universe is made of matter. This includes huge galaxies, bright stars, and our own planets. Even everyday things like rocks, water, and air are matter.
Living things like plants, animals, and humans are also made of matter.
In physics, some things are not considered matter. For example, photons, which are tiny packets of light, don't have rest mass. So, light is a form of energy, but it's not matter.
Matter can also hold other forms of energy. This energy lets matter interact with other things. Examples include kinetic energy (energy of motion), heat, light, and sound waves.
Outside of science, many things aren't matter or energy. For instance, emotions like happiness or ideas you have are not physical things.
Inside Matter: From Big to Small
Scientists study matter by breaking it down into smaller and smaller pieces. For example, living things are made of cells. Cells are made of molecules.
A molecule is formed when two or more atoms join together chemically. Each atom, in turn, is made of even smaller elementary particles. So, everything is built up from these tiny, tiny parts!
Different Forms of Matter
Scientists also group matter into different forms called states. These states have very different properties:
Solids
Solids are objects where molecules and atoms are strongly connected. They tend to keep their own shape, even when you move them. They can change shape if you push or pull them hard enough.
Fluids
Fluids are types of matter where the molecules and atoms are only weakly connected. They don't have their own fixed shape. There are two main types of fluids:
Liquids
Liquids are like solids because their particles are still close together. But the connections between these particles are loose. This lets them slide past each other while staying together. Liquids always have a clear surface. They take the shape of whatever container they are in.
- Examples: water, oil, blood, lava, soft drinks.
Gases
Gases are forms of matter where the connections between molecules and atoms are very weak. This means the particles can move freely and independently. Gases don't have a fixed surface. They spread out to fill up all the space available to them.
- Examples: air, water vapor, helium.
Plasma
Plasmas are made of ionized matter. This means their atoms have lost or gained electrons, making them electrically charged. Plasmas are mostly studied by scientists.
- Examples: The Earth's ionosphere (a layer in the atmosphere), the Sun's corona (its outer atmosphere). You can also see plasma in lightning. The particles in plasma move freely, like a liquid, but their attraction is weak, like a gas.
Bose–Einstein Condensate
A Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a very special state of matter. It's made by cooling a very thin gas of particles called bosons to extremely cold temperatures, almost to absolute zero (the coldest possible temperature).
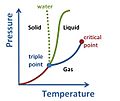
Matter can change from one state to another. This depends on its temperature and pressure. For example, on Earth, water can be solid (ice), liquid (water in lakes), and gas (vapor or steam) all at the same time!
Related pages
Images for kids
-
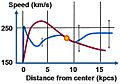
This graph shows how fast stars rotate in our Milky Way galaxy. The difference between the blue and red lines suggests the presence of dark matter.
See also
 In Spanish: Materia para niños
In Spanish: Materia para niños