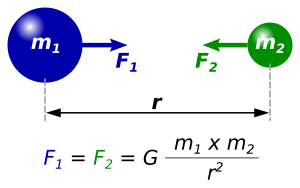Newton's law of universal gravitation facts for kids
Newton's universal law of gravitation is a very important physical law that explains how any two objects with mass (or "stuff" in them) are pulled towards each other. Think about how an apple falls to the ground, or how the Moon stays in orbit around Earth. This law helps us understand those pulls!
The famous scientist Isaac Newton wrote about this law in his book, Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica. It's a key part of what we call classical mechanics, which is the study of how things move.
What is the Gravity Formula?
Newton's law can be written as a mathematical formula. This formula helps scientists calculate exactly how strong the pull of gravity is between two objects.
The formula looks like this: 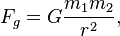
Let's break down what each part of the formula means:
- Fg is the total gravitational force. This is the strength of the pull between the two objects.
- G is something called the gravitational constant. It's a special number that makes the formula work correctly.
- m1 is the mass (how much "stuff" is in) of the first object.
- m2 is the mass of the second object.
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects.
How Do We Measure Gravity?
When we use the formula, we need to use specific units of measurement. These are part of the SI units, which scientists around the world use.
- The force of gravity (Fg) is measured in newtons (N).
- The masses (m1 and m2) are measured in kilograms (kg).
- The distance (r) is measured in metres (m).
- The gravitational constant (G) is approximately 6.674×10−11 N m2 kg−2. This number is very small, which means gravity is a weak force unless objects are very massive, like planets!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de gravitación universal para niños
In Spanish: Ley de gravitación universal para niños