Electromagnetic induction facts for kids
Electromagnetic induction is a cool way to make electricity! It happens when you create a voltage (which is like an electrical push) or an electric current (a flow of electricity) in a wire. This happens just by changing the magnetic field around that wire.
Imagine you have a coil of wire. If you move a magnet near this coil, or if the magnetic field around the coil changes, it can make electricity flow in the wire. This idea is super important for how many things work, like generators and transformers.
Contents
What is Magnetic Flux?
Think of a magnet as having invisible lines of force all around it. These are called magnetic field lines. When you have a coil of wire, and these magnetic field lines pass through the coil, we call that "magnetic flux."
If you change how many of these lines pass through the coil, or how strongly they pass through, you are changing the magnetic flux. For example, if you push a magnet into a coil, more lines pass through. If you pull it out, fewer lines pass through. This change is what creates electricity!
When the magnetic flux changes, it creates something called an electromotive force (EMF). Don't let the big name scare you! EMF is simply the "push" that gets the tiny electrons in the wire moving. When electrons move in a certain direction, that's an electric current.
Faraday's Law: Making Electricity
A brilliant scientist named Michael Faraday discovered the main rules of electromagnetic induction. His discoveries are known as Faraday's Law.
He found that if you change the magnetic flux through a wire, you will create an electromotive force (EMF). The faster you change the magnetic flux, the stronger the EMF will be, and the more electricity you can make!
So, if you want to make a lot of electricity, you need to change the magnetic field around your wire very quickly.
If you have a coil with many loops of wire (like a solenoid), the EMF created will be even stronger. This is because the changing magnetic flux affects each loop, adding up to a bigger total push for the electrons.
Lenz's Law: Opposing the Change
Another scientist, Heinrich Lenz, added an important detail to Faraday's work. His discovery is called Lenz's law.
Lenz's Law tells us that the electric current created by induction always tries to work against the change that caused it.
Imagine you push a magnet into a coil. The current that forms in the coil will create its own magnetic field that tries to push the magnet back out. If you pull the magnet out, the current will create a magnetic field that tries to pull the magnet back in. It's like the coil is saying, "Hey, stop changing things!" This "opposition" is why there's a negative sign in the advanced equations for these laws.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
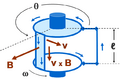
Alternating electric current flows through the solenoid on the left, producing a changing magnetic field. This field causes, by electromagnetic induction, an electric current to flow in the wire loop on the right.
-
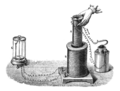
Faraday's experiment showing induction between coils of wire: The liquid battery (right) provides a current that flows through the small coil (A), creating a magnetic field. When the coils are stationary, no current is induced. But when the small coil is moved in or out of the large coil (B), the magnetic flux through the large coil changes, inducing a current which is detected by the galvanometer (G).
See also
 In Spanish: Inducción electromagnética para niños
In Spanish: Inducción electromagnética para niños