Great Western Railway facts for kids
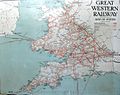
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a famous railway company in Britain. It connected London with the southwest, west, and West Midlands of England. It also served most of Wales.
The GWR started in 1833. It got official permission to build its railway on August 31, 1835. The first trains ran in 1838. The main line between London and Bristol was finished in 1841.
A brilliant engineer named Isambard Kingdom Brunel designed the railway. He chose a special wide track size called a broad gauge. It was 7 ft (2,134 mm) wide, which is much wider than most railways today. Later, it was made a tiny bit wider to 7 ft 1⁄4 in (2,140 mm).
Over time, the GWR also started using the more common 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) standard-gauge tracks. This happened after 1854 when it joined with other railway companies. The last broad-gauge trains ran in 1892.
The GWR was special because it was the only big railway company that kept its name after the Railways Act 1921. This law combined many smaller railways into bigger groups. The GWR finally became part of a national railway system at the end of 1947. It was then called the Western Region of British Railways.
Contents
Nicknames and Famous Journeys
People had different names for the GWR. Some called it "God's Wonderful Railway." Others jokingly called it the "Great Way Round." But it was most famous as the "Holiday Line."
The GWR took many people on holidays. It carried them to popular places along the English Channel and Bristol Channel. These included seaside towns like Torquay in Devon, Minehead in Somerset, and Newquay and St Ives in Cornwall.
Trains, Colors, and Other Services
The GWR's locomotives were often built at the company's own workshops in Swindon. They were painted a lovely Brunswick green color.
For most of its history, the passenger coaches were painted in a two-tone "chocolate and cream" color. This made them very recognizable. The goods wagons (freight cars) were first painted red, but later changed to a mid-grey color.
The Great Western Railway ran many different types of trains. These included long-distance express services. Some famous ones were the Flying Dutchman, the Cornish Riviera Express, and the Cheltenham Spa Express.
The company also ran shorter trips. These included suburban and rural services. Some of these were operated by special steam rail motors or autotrains.
The GWR was a leader in using larger, more efficient goods wagons. This was unusual for Britain at the time.
Beyond trains, the GWR offered other ways to travel. It ran ferry services to Ireland and the Channel Islands. It also had a network of road motor (bus) routes. The company was even part of the Railway Air Services. It owned ships, canals, docks, and hotels.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The Sonning Cutting in 1846
-
One of the first road motors working a service from Helston to The Lizard
-
Rain, Steam and Speed - The Great Western Railway, by Turner.
-
The nameplate on First Great Western power car 43185
-
Isambard Kingdom Brunel's statue at Paddington station
-
A display commemorating Daniel Gooch at the National Railway Museum
See also
 In Spanish: Great Western Railway para niños
In Spanish: Great Western Railway para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |