Fanconi anemia facts for kids
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare genetic disorder. This means it is caused by changes in a person's genes. It is a type of anemia, a condition where your blood does not have enough healthy red blood cells. People with Fanconi anemia produce fewer red and white blood cells than they should. Red blood cells carry oxygen, and white blood cells fight infections.
The disease is named after Guido Fanconi. He was a doctor who first described it in 1929. It is important not to confuse Fanconi anemia with Fanconi syndrome. Fanconi syndrome is a different problem that affects the kidneys.
Contents
What is Fanconi Anemia?
Fanconi anemia is a serious blood disorder. It mainly affects the bone marrow. The bone marrow is the soft tissue inside your bones that makes blood cells. In people with FA, the bone marrow does not make enough new blood cells. This leads to low levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Why Does It Happen?
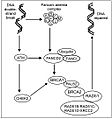
Fanconi anemia is a hereditary condition. This means it is passed down through families. It happens when a child inherits two changed genes, one from each parent. These genes are important for repairing damaged DNA in cells. When these genes don't work right, cells can't fix their DNA properly. This makes them more likely to be damaged or die.
Signs and Symptoms
People with Fanconi anemia can have many different signs. These can include:
- Tiredness: Low red blood cells can make you feel very tired.
- Infections: Low white blood cells make it harder to fight off sickness.
- Bleeding: Low platelets can cause easy bruising or bleeding.
- Physical differences: Some people are shorter than average. They might have problems with their thumbs or arms.
- Skin changes: They might have light brown spots on their skin.
- Kidney problems: Some people have kidneys that are not shaped normally.
These signs can be different for each person. Some people have mild symptoms, while others have more severe ones.
How is Fanconi Anemia Treated?
Treatments for Fanconi anemia focus on managing the symptoms. They also try to improve the number of blood cells.
- Blood transfusions: Sometimes, people need to receive blood from a donor. This helps to increase their red blood cells or platelets.
- Medications: Certain medicines can help the bone marrow make more blood cells.
- Bone marrow transplant: For some people, a bone marrow transplant is the best option. This replaces the unhealthy bone marrow with healthy bone marrow from a donor. This can be a very effective treatment.
Living with Fanconi Anemia
Living with Fanconi anemia requires ongoing medical care. Regular check-ups are important to monitor blood counts and overall health. Researchers are always working to find new and better treatments for FA. Support groups and medical teams help families manage the condition.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Anemia de Fanconi para niños
In Spanish: Anemia de Fanconi para niños