Age of Discovery facts for kids
The Age of Discovery or Age of Exploration was a time from the early 1400s to the early 1600s. During this period, European ships sailed all over the world. They were looking for new trading routes and partners.
Explorers wanted to find valuable goods like gold, silver, and spices. As they traveled, Europeans met new people and mapped lands they had not known before. Some of the most famous explorers were Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, Ferdinand Magellan, and Captain James Cook.

Contents
Portugal's Explorations
Prince Henry the Navigator helped start the Age of Discovery. He paid Portuguese sailors to explore the west coast of Africa. In 1419, João Gonçalves Zarco found the Madeira Islands. Later, in the 1400s, Vasco da Gama reached the southern tip of Africa. He helped set up the city of Cape Town, which became a Portuguese colony. This opened a sea path to the Indian Ocean.
Over the next two centuries, Portugal built a large trading empire. They had trading posts along the coasts of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and India. However, the Portuguese Empire became weaker later on. The Dutch East India Company grew stronger and took over much of the trade in the Indian Ocean.
Spain's Explorations
Spain wanted to compete with Portugal to build its own empire. So, Spain sent Christopher Columbus in a different direction. Instead of sailing south along Africa, Columbus sailed west across the Atlantic Ocean. When his ships landed, he thought he had reached Asia.
Later, other Spanish sailors realized this land was a new continent. Today, we call it the Americas. In the 1500s, Spanish conquistadores took control of most of what is now Latin America. Brazil belonged to Portugal, and some parts were British or French. The Spanish focused on conquest, unlike the Portuguese who focused more on trading.
Spain built a huge colonial empire. Portugal mostly ruled islands and coastal cities. When Spain and Portugal were united under King Philip II of Spain, their combined empire was the biggest in the world.
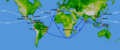
In 1522, the ships of Ferdinand Magellan returned to Spain. The sailors who survived were the first people to sail all the way around the world.
Britain, France, and the Netherlands
In the 1600s, wars in Europe weakened Spain and Portugal. These wars involved Britain, France, and the Netherlands. These three nations became new major powers. For the next two centuries, the world became a place where these three countries often fought.
Britain and France gained land in North America, India, and other distant places. The Dutch took over smaller parts of the Americas. They also captured former Portuguese trading centers around the Indian Ocean. The Dutch also conquered Indonesia. These three new great powers had influence all over the world.
Many wars were fought both in Europe and overseas. Britain usually won these wars. In the 1700s, Britain took Canada and India from France. They also became the strongest naval power in the Indian Ocean. By 1763, the British Empire was the second largest global empire after Spain. However, in 1776, thirteen colonies in British America declared independence. With help from France, the Netherlands, and Spain, they defeated Britain in the American Revolution.
Exploring the Southern Pacific Ocean
In 1778, Captain James Cook of Britain sailed across the South Pacific Ocean. He was looking for a mysterious continent in the Southern Hemisphere. He landed on two large islands, which are now New Zealand. Then he sailed west and found a much bigger piece of land, which is now Australia. Captain Cook claimed these lands for Britain. He explored the Pacific for another year and died in a fight with the Hawaiians.
Effects of the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery had a huge impact on the world. Many people were brought from Africa to the Americas against their will. Spain gained control of almost all of Latin America and found a massive amount of silver. This silver made Spain very rich.
When Christopher Columbus tried to find a new trade route to Asia, he thought he could sail around the world. Instead, he found a New World. Vikings had briefly visited Vinland around 1000 A.D., long before Columbus.
Interesting Facts About the Age of Discovery
- Niccolò de' Conti traveled for 25 years (1414-1439). He suggested that it was possible to reach Asia by sailing around Africa.
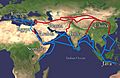
- The Ottoman Empire helped start the Age of Discovery. When they conquered Constantinople, they made Europeans look for other trade routes to Asia.
- Forests in Poland were cut down to build the ships needed to sail to the East Indies.
- It is thought that Columbus's ship captain, Rodrigo de Triana, was the first to see the New World.
- Sailors' meals were made from food that would not spoil. These meals were prepared months in advance.
- Abel Tasman, often credited with discovering New Zealand, missed Australia the first time he sailed in the area.
- Sir Walter Raleigh is credited with bringing potatoes to Ireland. The Spanish found them in Peru.
- The Pilgrims at Plymouth Colony were greeted in English by a Native Wampanoag person.
- European explorers brought diseases to the New World. The native people there had never experienced these diseases before.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The Portuguese caravel ship was very important for ocean travel. This image shows the "Caravela Vera Cruz" on the Tagus river in Lisbon.
-
The Nao Victoria was the Spanish ship that completed the first trip around the world. This is a replica of Victoria visiting Nagoya, Japan.
-
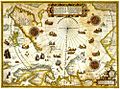
Ptolemy's world map from the 2nd century, recreated in the 15th century.
-
The Silk Road and spice trade routes. These were later blocked by the Ottoman Empire in 1453, leading to the search for new sea routes.
-
The travels of Marco Polo (1271–1295).
-
"Mao Kun map," believed to be based on Zheng He's travels. It shows sailing directions in Southeast Asia and as far as Malindi.
-
Saharan trade routes around 1400.
-
A map of Africa from 1482, showing what Europeans knew at the time.
-
A replica of a caravel ship. These ships were used for ocean exploration starting in the mid-15th century.
-
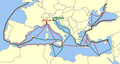
The 1494 Tordesilhas Treaty line (purple) and the later Maluku Islands line (green) from the Treaty of Zaragoza (1529).
-
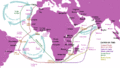
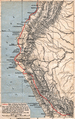
Vasco da Gama's journey to India (1497–1499) shown in black.
-
Vasco Núñez de Balboa's journey to the "South Sea" in 1513.
-
Victoria, the only ship to complete the first trip around the world.
-
A map of the island city Tenochtitlan and the Gulf of Mexico, made in 1524.
-
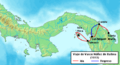
Francisco Pizarro's exploration route during the conquest of Peru (1531–1533).
-
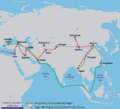
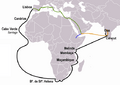
Portuguese trade routes (blue) and the rival Manila-Acapulco galleons trade routes (white).
-
A Portuguese carrack ship in Nagasaki, Japan. This is from Nanban art.
-
A world map from Abraham Ortelius's Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (1570), considered the "first modern atlas."
-
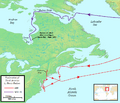
A map of Henry Hudson's voyages to North America (1609–1611) for the Dutch East India Company.
-
Henry Hudson's ship Halve Maen in the Hudson River.
-
A 1599 map of Arctic exploration by Willem Barentsz during his third voyage.
-
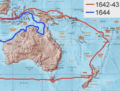
The route of Abel Tasman's voyages in New Holland (Australia) in 1642 and 1644.
-
A replica of the Duyfken ship in Swan River, Australia.
-
Yermak Timofeyevich and his group crossing the Ural Mountains into Asia from Europe.
-
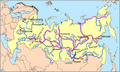
A map of Irkutsk and Lake Baikal from the late 17th century.
-
A 17th-century koch boat in a museum in Krasnoyarsk. These boats were used by Russians in the Arctic and on Siberian rivers.
-
Jesuit scholars worked with Chinese astronomers. Top: Matteo Ricci, Adam Schaal, and Ferdinand Verbiest. Bottom: Paul Siu (Xu Guangqi) and his granddaughter.
-
A world map from Johannes Kepler's Rudolphine Tables (1627), showing many new discoveries.
-
A detail of silverware from a painting by Jan Davidsz. de Heem.
See also
 In Spanish: Era de los Descubrimientos para niños
In Spanish: Era de los Descubrimientos para niños