Ptolemy's world map facts for kids
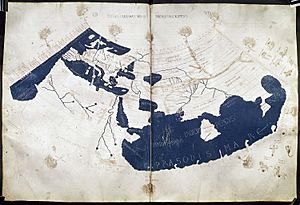
The Ptolemy world map is a famous map that shows what the world looked like to people in ancient Greece and Rome around the year 150 AD. It's based on a book called Geography, written by a smart person named Ptolemy. Some old copies of the map say it was drawn by Agathodaemon of Alexandria.
This map was very important because it was one of the first to use lines of longitude and latitude. These are like invisible grid lines that help you find exact spots on Earth, using observations of the sky. Ptolemy's ideas about mapping the world with a coordinate system changed how people thought about geography in Europe. It made mapmaking much more mathematical.
Ptolemy's original book probably came with maps, but none of them have been found. The maps we see today were put together much later, around 1295. Byzantine monks, led by Maximus Planudes, used Ptolemy's coordinates to draw them.
Continents and Oceans
Ptolemy's map shows three main continents: Europe, Asia, and Libya (which is Africa). The big World Ocean is only shown on the western side of the map.
The map also shows two large seas that are almost completely surrounded by land. One is the Mediterranean, which you might know. The other is the Indian Sea (called Indicum Pelagus). Because of some mistakes in measuring the Earth's size, the Mediterranean Sea looks much too long on the map. Also, the Indian Sea is shown as being completely enclosed by unknown lands to the east and south. This means the map doesn't show the western coast of the World Ocean.
Asia on the Map
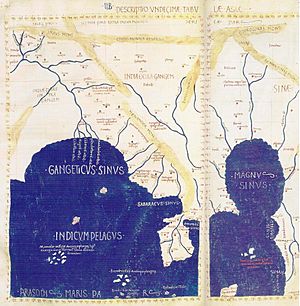
India on the map is bordered by the Indus River and Ganges River. However, the Indian peninsula looks much shorter than it is in real life. Sri Lanka (called Taprobane) is shown as being much bigger than its actual size.
The Malay Peninsula is called the Golden Chersonese. This name came from old Indian stories about gold mines on Sumatra. Beyond the Golden Chersonese, there's a huge gulf called the Great Gulf (Magnus Sinus). This gulf combines what we now call the Gulf of Thailand and the South China Sea. It's also shown as being surrounded by the unknown lands that were thought to enclose the Indian Sea.
China is divided into two parts on the map. One part is called the Qin (Sinae), and the other is the Land of Silk (Serica). This is because the Romans got different information about China from traders who traveled by land and those who traveled by sea on the Silk Road.
Roman Trade and the Map
The Geography book and the map that came from it were probably very important for the Roman Empire as it expanded eastward. There was a lot of trade happening across the Indian Ocean starting in the 100s AD. Many Roman trading ports have been found in India. From these ports, Roman messengers even traveled to China. Chinese history books record these visits starting around 166 AD.
Images for kids
-
Detail of East and Southeast Asia in Ptolemy's world map. Gulf of the Ganges (Bay of Bengal) left, Southeast Asian peninsula in the center, South China Sea right, with "Sinae" (China).
 | Madam C. J. Walker |
 | Janet Emerson Bashen |
 | Annie Turnbo Malone |
 | Maggie L. Walker |