Province of Quebec (1763–1791) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Province of Quebec
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1763–1791 | |||||||||||||
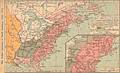
A portion of eastern North America in 1774 after the Quebec Act; Quebec extends all the way to the Mississippi River.
|
|||||||||||||
| Status | British colony | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Quebec | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | French, English | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism, Protestantism | ||||||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||||
| Governor | |||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||
| 7 October 1763 | |||||||||||||
| 1774 | |||||||||||||
| 1763 | |||||||||||||
| 26 December 1791 | |||||||||||||
| Currency | Canadian pound | ||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | CA | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||
The Province of Quebec was a British colony in North America. It was created by Great Britain in 1763. This happened after the Seven Years' War, a big conflict between European powers.
During the war, British forces took control of French Canada. As part of the peace treaty in 1763, France gave up its claim to Canada. Instead, France chose to keep the valuable sugar island of Guadeloupe.
Britain then renamed this area the Province of Quebec. This was done through the Royal Proclamation of 1763. The new British province was very large. It stretched from Labrador on the Atlantic coast. It went southwest through the Saint Lawrence River Valley to the Great Lakes. It even extended beyond to where the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers meet.
Some parts of its southwest area were later given to the United States. This happened in the Treaty of Paris (1783) after the American Revolution. However, the British army stayed there until 1796. In 1791, the land north of the Great Lakes was split. It became Lower Canada and Upper Canada.
Contents
How the Province of Quebec Began
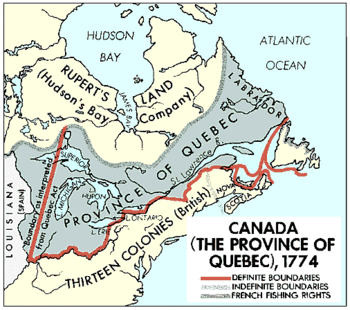
Under the Royal Proclamation, Quebec included the cities of Quebec and Montreal. It also covered the area around them. However, it did not reach as far west as the Great Lakes. It also did not go as far north as Rupert's Land. Rupert's Land was a huge territory owned by the Hudson's Bay Company.
Changes with the Quebec Act of 1774
In 1774, the British Parliament passed the Quebec Act. This act made some important changes. It allowed Quebec to use French law for private matters. This was called Coutume de Paris. It was used alongside the English common law system.
The act also let the Catholic Church collect tithes. Tithes were like taxes, usually a tenth of someone's income, paid to the church. The Quebec Act also made Quebec much larger. It added the Ohio Country and parts of the Illinois Country. These lands stretched from the Appalachian Mountains in the east. They went south to the Ohio River, west to the Mississippi River, and north to the southern border of Rupert's Land.
British Control and Trade Routes
Even after the Treaty of Paris (1783) gave control of the Ohio and Illinois Countries to the United States, Britain kept access to them through Quebec. The British used well-known trade and military routes across the Great Lakes. They continued to supply their own troops. They also supplied a large group of Native American nations. This was done through places like Detroit, Fort Niagara, and Fort Michilimackinac. These posts were finally given to the United States after the Jay Treaty in 1794.
Shift in Population and Division
Quebec kept its seigneurial system. This was a way of organizing land and farming that came from France. After the American Revolutionary War, many Loyalist refugees moved to Quebec. Loyalists were people who stayed loyal to Britain during the American Revolution.
This caused a big change in Quebec's population. It now included many English-speaking Protestants. These United Empire Loyalists settled in areas like the Eastern Townships, Montreal, and the Pays d'en Haut. The Pays d'en Haut was the land west of the Ottawa River.
Because of this new population, the colony was divided. The Constitutional Act of 1791 split Quebec into two parts at the Ottawa River. The western part became Upper Canada. It was mainly for English speakers and used the English legal system. The eastern part was named Lower Canada.
Geography and Districts
Around 1763 to 1764, the Province of Quebec was divided into two main judicial districts. These were areas for legal and administrative purposes.
- Montreal District: This covered the western parts of Quebec along the St. Lawrence River. It included the city of Montreal and much of what is now Eastern and Southern Ontario.
- Quebec District: This covered the eastern parts of Quebec along the St. Lawrence River and Labrador.
In 1790, the Trois-Rivières District was created. It was formed from a part of the Quebec District.
After 1791, when Lower Canada was formed, the Trois-Rivières and Quebec districts continued to exist within it. The Montreal District west of the Ottawa River became Upper Canada. The part of Montreal District east of the Ottawa River was divided into many smaller electoral areas.
Images for kids
-
Map of British America showing the original boundaries of the Province of Quebec and its Quebec Act of 1774 post-annexation boundaries
See also
 In Spanish: Provincia de Quebec (1763-1791) para niños
In Spanish: Provincia de Quebec (1763-1791) para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |