Seven Years' War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Seven Years' War 1756–1763 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Clockwise from top left: the Battle of Plassey (23 June 1757); the Battle of Carillon (6–8 July 1758); the Battle of Zorndorf (25 August 1758); the Battle of Kunersdorf (12 August 1759) |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
(from 1762)
|
||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Seven Years' War was a huge global conflict that lasted from 1756 to 1763. It involved most of the major countries in Europe and their colonies around the world. People sometimes call it the "first world war" because fighting happened in so many different places.
At its heart, the war was really two main conflicts happening at the same time. One was a big rivalry between Britain and France. They were fighting over land and trade in places like North America and India. The other conflict was in Europe, mainly between Prussia and its enemies: France, Austria, Russia, and Sweden.
A big reason for the war was an earlier conflict called the War of the Austrian Succession. This war had left some countries feeling like they had lost out, especially Austria, which wanted to get back a region called Silesia from Prussia.
Contents
What Was the Seven Years' War?
This war had different names depending on where you were. In the United States, it's known as the French and Indian War. This name highlights the fighting between the British and French, and their Native American allies. In French Canada, it's called the War of Conquest.
In Europe, the fight between Prussia and Austria over Silesia was known as the Third Silesian War. In India, the conflict was part of the Third Carnatic War.
Why Did Countries Fight?
During this time, many European countries had colonies around the world. These colonies were important for trade and power. Britain and France, led by the Bourbon family, were often rivals for control of these colonies. They wanted to control trade routes and resources.
In Europe, the Hohenzollern family, who ruled Prussia, and the Habsburg family, who ruled Austria, were fighting for power. Prussia wanted to keep Silesia, which it had taken from Austria. Austria wanted it back.
The Two Main Sides
The war saw a big shift in alliances, sometimes called a "diplomatic revolution."
- One side was the Anglo-Prussian camp. This included Great Britain, Prussia, and some smaller German states. Later, Portugal joined them.
- The other side was the Austro-French camp. This included Austria, France, Sweden, and Saxony. Later, Spain joined this side.
This war changed a lot of things around the world. It set the stage for Britain to become a very powerful country in the 1800s. It also helped Prussia become a leading German state, eventually taking Austria's place. The war also led to problems in British North America, which later contributed to the American Revolution. In Europe, the war was very harsh, with many battles, sieges, and towns being burned.
Major Battles of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War involved many important battles across different continents. Here are some of the key land battles that took place.
Battles in Europe
These battles were fought mainly between the armies of Prussia, Austria, France, and their allies.
| Battle | Anglo-Prussian coalition numbers | Franco-Austrian coalition numbers | Anglo-Prussian coalition casualties | Franco-Austrian coalition casualties | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lobositz | 28,500 | 34,000 | 3,300 | 2,984 | Austrian victory |
| Prague | 64,000 | 61,000 | 14,300 | 13,600 | Prussian victory |
| Kolín | 34,000 | 54,000 | 13,733 | 8,100 | Austrian victory |
| Hastenbeck | 36,000 | 63,000 | 1,200 | 1,200 | French victory |
| Gross-Jägersdorf | 25,000 | 55,000 | 4,520 | 5,250 | Russian victory |
| Rossbach | 21,000 | 40,900 | 541 | 8,000 | Prussian victory |
| Breslau | 28,000 | 60,000 | 10,150 | 5,857 | Austrian victory |
| Leuthen | 36,000 | 65,000 | 6,259 | 22,000 | Prussian victory |
| Krefeld | 32,000 | 50,000 | 1,800 | 8,200 | Prussian-allied victory |
| Zorndorf | 36,000 | 44,000 | 11,390 | 21,529 | Indecisive |
| Belle Île | 9,000 | 3,000 | 810 | 3,000 | British victory |
| Saint Cast | 1,400 | 10,000 | 1,400 | 495 | French victory |
| Hochkirch | 39,000 | 78,000 | 9,097 | 7,590 | Austrian victory |
| Kay | 28,000 | 40,500 | 8,000 | 4,700 | Russian victory |
| Minden | 43,000 | 60,000 | 2,762 | 7,086 | British-allied victory |
| Kunersdorf | 49,000 | 98,000 | 18,503 | 15,741 | Russo-Austrian victory |
| Maxen | 15,000 | 32,000 | 15,000 | 934 | Austrian victory |
| Landeshut | 13,000 | 35,000 | 10,052 | 3,000 | Austrian victory |
| Warburg | 30,000 | 35,000 | 1,200 | 3,000 | British-allied victory |
| Liegnitz | 14,000 | 24,000 | 3,100 | 8,300 | Prussian victory |
| Kloster Kampen | 26,000 | 45,000 | 3,228 | 2,036 | French victory |
| Torgau | 48,500 | 52,000 | 17,120 | 11,260 | Prussian victory |
| Villinghausen | 60,000 | 100,000 | 1,600 | 5,000 | British-allied victory |
| Schweidnitz | 25,000 | 10,000 | 3,033 | 10,000 | Prussian victory |
| Wilhelmsthal | 40,000 | 70,000 | 700 | 4,500 | British-allied victory |
| Freiberg | 22,000 | 40,000 | 2,500 | 8,000 | Prussian victory |
Battles in North America
In North America, the war was mainly between Britain and France, with their Native American allies.
| Battle | British-native numbers | French, Spanish and native numbers | British-native casualties | French, Spanish and native casualties | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monongahela | 1,300 | 891 | 906 | 96 | French-allied victory |
| Lake George | 1700 | 1500 | 331 | 339 | British-allied victory |
| Fort William Henry | 2,372 | 8,344 | 2,372 | Unknown | French-allied victory |
| Fort Ticonderoga I | 18,000 | 3,600 | 3,600 | 377 | French-allied victory |
| Louisbourg | 9,500 | 5,600 | 524 | 5,600 | British victory |
| Guadeloupe | 5,000 | 2,000 | 804 | 2,000 | British victory |
| Martinique | 8,000 | 8,200 | 500 | N/A | French victory |
| Fort Niagara | 3,200 | 1,786 | 100 | 486 | British-allied victory |
| Quebec I | 9,400 | 15,000 | 900 | N/A | British victory |
| Montmorency | 5,000 | 12,000 | 440 | 60 | French victory |
| Plains of Abraham | 4,828 | 4,500 | 664 | 644 | British-allied victory |
| Saint-Foy | 3,866 | 6,900 | 1,088 | 833 | French victory |
| Quebec II | 6,000 | 7,000 | 30 | 700 | British victory |
| Havana | 31,000 | 11,670 (Spanish) | 5,366 | 11,670 | British victory |
Battles in India
In India, the war was fought between the British East India Company and the French, often with local Indian rulers as allies.
| Battle | British-sepoy numbers | Mughal-French numbers | British-sepoy casualties | Mughal-French casualties | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcutta I | 514 | 50,000 (Mughals) | 218 | 7,000 | Mughal victory |
| Calcutta II | 1,870 | 40,000 (Mughals) | 194 | 1,300 | British victory |
| Plassey | 2,884 | 50,000 (Mughals) | 63 | 500 | British victory |
| Chandannagar | 2,300 | 900 (French-sepoy) | 200 | 200 | British victory |
| Madras | 4,050 | 7,300 (French-sepoy) | 1,341 | 1,200 | British victory |
| Masulipatam | 7,246 | 2,600 (French-sepoy) | 286 | 1,500 | British victory |
| Wandiwash | 5,330 | 4,550 (French-sepoy) | 387 | 1,000 | British victory |
How the War Ended
The Seven Years' War officially ended with two important agreements in 1763: the Treaty of Paris and the Treaty of Hubertusburg.
Key Outcomes of the War
- Great Britain gained a lot of new land overseas. They took most of New France (which is now Canada), Spanish Florida, some islands in the Caribbean, and parts of Senegal. They also became the main power over French areas in India.
- Prussia managed to keep Silesia. Even though Prussia faced many challenges, their leader Frederick II fought hard and didn't have to give up any land.
- France lost many of its colonies and its influence in India.
- Spain lost Florida to Britain but gained French Louisiana (west of the Mississippi River) from France. Britain also returned Cuba and the Philippines to Spain.
- The war was very costly in terms of lives. Around 900,000 to 1,400,000 people died during the conflict.
The British politician William Pitt famously said, "America was won in Germany." This meant that Prussia's fighting in Europe helped Britain focus its navy and resources on winning battles in its colonies, especially in North America. The British navy's strong presence stopped France from sending supplies to its colonies, which helped Britain win.
The war changed the balance of power in Europe and around the world. It helped set the stage for future events, like the American Revolution and the rise of the British Empire.
Images for kids
-
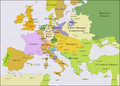
Europe in the years after the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748
-
British raid on French settlement of Miramichi (later called Burnt Church, New Brunswick), 1758
-
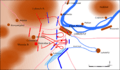
Battle of Lobositz. Austria: blue; Prussia: red
-
The Battle of Kolín in 1757 in Bohemia (the site is now in the Czech Republic)
-
The Battle of Rossbach in Saxony
-
The Battle of Leuthen in Silesia, by Carl Röchling
-
Frederick the Great and staff at Leuthen
-
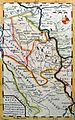
The Battle of Krefeld in Prussia – a map of the area in The Gentleman's Magazine
-
The Battle of Hochkirch in Saxony
-
The Battle of Maxen in Saxony
-
The Battle of Kunersdorf in Prussia
-
Battle of Liegnitz (1760) in what is now Poland
-
Under William Pitt the Elder's leadership, Britain's position as the leading colonial power was confirmed by the Seven Years' War.
-
August 2009 historical re-enactment of the Battle of Warburg fought on 31 July 1760
-
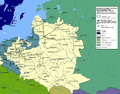
Map showing British territorial gains in North America following the Treaty of Paris in pink, and Spanish territorial gains after the Treaty of Fontainebleau in yellow
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de los Siete Años para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de los Siete Años para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |