Bengal Subah facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Subah of Bengal
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision of Mughal Empire | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1576–1757 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
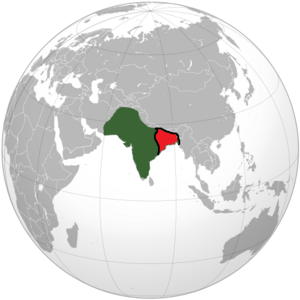 Mughal Bengal including present day Bihar, Jharkhand and Odisha. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Type | Viceregal | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Battle of Raj Mahal
|
1576 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Nawabs of Bengal
|
1717 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1757 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Bengal Subah, also known as Mughal Bengal, was a very important part of the Mughal Empire. It existed from 1576 to 1757. This area included parts of what is now Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal.
During its time, Bengal Subah was one of the richest places in the world. It was famous for its trade and farming. Many different goods were produced here.
Contents
A Rich and Important Region
Bengal Subah was known for its amazing wealth. It was like a powerhouse of trade and farming. The land was very fertile, meaning it was great for growing crops.
Farmers grew a lot of rice, which was a main food source. They also grew cash crops like cotton and silk. These were used to make beautiful fabrics.
Trade and Economy
Bengal was a hub for international trade. Merchants came from all over the world to buy goods. They traded spices, textiles, and other valuable items.
The region produced high-quality muslin, a very fine cotton fabric. This muslin was famous and sold across Asia and Europe.
The Dutch East India Company and other European companies set up trading posts here. They wanted to buy Bengal's goods. This trade made Bengal even richer.
Capital Cities
Bengal Subah had different capital cities over time. Each city played a key role in its history.
Dhaka was an early capital from 1608 to 1704 (with a break). It was a busy city with many important buildings. Dhaka was even named Jahangir Nagar for a while, after the Mughal Emperor Jahangir.
Later, the capital moved to Murshidabad in 1704. This city also became a major center for trade and government.
How Bengal Became Part of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire slowly took control of Bengal. This happened through several battles and agreements.
Early Mughal Influence
The first Mughal emperors, Babur and Humayun, began to expand their control into Bengal. This was a slow process.
Later, Emperor Akbar fully brought Bengal into the Mughal Empire. This happened after the Battle of Raj Mahal in 1576. Akbar also helped develop the modern Bengali calendar.
Governors and Rulers
Bengal was ruled by a Viceroy or governor called a Subahdar. These governors were appointed by the Mughal Emperor. They managed the region and collected taxes.
Important Viceroys included Munim Khan and Shaista Khan. Shaista Khan was known for his strong rule and for expanding trade.
Over time, the governors of Bengal became more independent. They were known as the Nawabs of Bengal. The first Nawab was appointed in 1717.
The End of Mughal Rule
The power of the Mughal Empire started to weaken. This led to changes in Bengal.
Rise of European Powers
European trading companies, especially the British East India Company, grew very powerful. They built forts and had their own armies.
These companies started to get involved in local politics. They wanted more control over trade and resources.
Battle of Plassey
The end of Bengal Subah came with the Battle of Plassey in 1757. This battle was fought between the Nawab of Bengal and the British East India Company.
The British, led by Robert Clive, won the battle. This victory marked the beginning of British rule in Bengal. Bengal then became part of the Bengal Presidency.
Legacy of Mughal Bengal
Mughal Bengal left a lasting impact on the region. Its culture, art, and economy were greatly influenced.
Architecture and Art
Mughal architects copied Bengali styles. For example, the curved roofs of Bengali buildings were used in other parts of the empire. The Naulakha Pavilion in Lahore is an example.
The region was also known for its beautiful Jamdani muslin. This special fabric is still made today.
Cultural Mix
Bengal Subah was a place where different cultures met. There were people from various parts of the Mughal Empire and beyond. This mix created a rich and diverse society.





See also
 In Spanish: Subá de Bengala para niños
In Spanish: Subá de Bengala para niños