Western Canada facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Western Canada
Ouest canadien (French)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Region
|
|
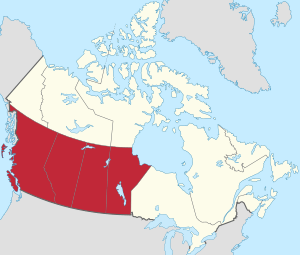
Western Canada, defined geographically
|
|
| Country | Canada |
| Composition |
|
| Capitals and largest cities | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,703,159 km2 (1,043,696 sq mi) |
| Population
(2021)
|
|
| • Total | 11,738,172 |
| • Density | 4.3423905/km2 (11.2467398/sq mi) |
Western Canada is a large region in Canada. It includes four provinces: British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provinces are located just north of the Canada–United States border. People from this area are often called "Western Canadians."
This region makes up about 32% of Canada's total population. Western Canada can be divided into two main parts. British Columbia is mostly west of the Canadian Rockies. It is often called the "west coast." The other three provinces, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, are east of the Rockies. They are known as the "Prairie Provinces."
Alberta and British Columbia are sometimes grouped together. This is because they both have large parts of the Rocky Mountains. They also share similar features like many people living in cities. Three of Canada's five largest cities are in this area: Calgary, Edmonton, and Vancouver. Alberta and Saskatchewan also have close ties. They were once a single territory. They share similar histories and have seen similar migration patterns.
Contents
Capital Cities of Western Canada
Each of the four western provinces has its own capital city. These cities are important centers for government and culture. From west to east, they are:
Winnipeg is the largest city in Manitoba. However, the other capital cities are the second-largest metropolitan areas in their provinces.
How Western Canada Became Part of Canada
Long before Europeans arrived, Western Canada was the home of Indigenous and First Nations peoples. As Britain started to colonize the West, they made agreements called treaties with many First Nations. Some areas were taken without conflict. In other places, Britain fought with First Nations for control. Not all lands were given up by the First Nations. Discussions about land claims are still happening today.
In 1858, the British government created the Colony of British Columbia. This colony covered the area we now call British Columbia. The British government also set up the Hudson's Bay Company. This company controlled most of what is now Western Canada. It also controlled parts of northern Ontario and Quebec. This large area was known as Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory.
In 1870, the British government gave these lands to Canada. The part of Western Canada not in British Columbia became the Northwest Territories. Over time, new provinces were created from these territories:
- Manitoba became a province in 1870. This happened after the Manitoba Act was passed.
- British Columbia joined Canada in 1871. Canada agreed to take on the colony's debt. It also promised to help with public works. Most importantly, Canada agreed to build a railway connecting British Columbia to Ontario.
- Saskatchewan became a province in 1905. This was thanks to the Saskatchewan Act.
- Alberta also became a province in 1905. It joined Canada in the same year as Saskatchewan. Alberta had its own law, called the Alberta Act.
Population and Major Cities
In 2016, Western Canada had almost 11.1 million people. British Columbia had about 4.65 million people. Alberta had 4.07 million. Saskatchewan had 1.1 million, and Manitoba had 1.28 million. This means about 31.5% of all Canadians live in the West.
Vancouver is the largest metropolitan area in Western Canada. It has nearly 2.5 million people. Calgary is the largest city itself, with over 1.2 million people.
Major City Areas in Western Canada

In 2016, Statistics Canada listed ten major city areas in Western Canada. British Columbia has four, Alberta has three, Saskatchewan has two, and Manitoba has one. Here are these areas and their populations from 2016:
| City | Population (2016) |
National rank |
|---|---|---|
| Vancouver | 2,463,431 | 3 |
| Calgary | 1,392,609 | 4 |
| Edmonton | 1,321,426 | 6 |
| Winnipeg | 778,489 | 8 |
| Victoria | 367,770 | 15 |
| Saskatoon | 295,095 | 17 |
| Regina | 236,481 | 18 |
| Kelowna | 194,882 | 22 |
| Abbotsford–Mission | 180,518 | 23 |
| Lethbridge | 117,394 | 34 |
Between 2011 and 2016, the fastest-growing cities in Canada were in Alberta and Saskatchewan. These included Calgary, Edmonton, Saskatoon, Regina, and Lethbridge. They were the only major cities in the country to grow by more than 10%.
Geography of Western Canada
Western Canada includes British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. It covers about 2.9 million square kilometers. This is almost 29% of all of Canada's land. British Columbia is on the Pacific Ocean to the west. Manitoba has a coastline on Hudson Bay in its northeast. Alberta and Saskatchewan are landlocked. This means they do not touch an ocean. They are located between British Columbia and Manitoba.
The Canadian Prairies are a huge flat area. They cover much of Alberta, southern Saskatchewan, and southwestern Manitoba. This flat land is great for farming grains. However, some areas like the Cypress Hills and Alberta Badlands are quite hilly. The prairie provinces also have large forests.
In Alberta and British Columbia, you will find the Canadian Cordillera. This is a large mountain system. It is bordered by the Rocky Mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
The Canadian Rockies are part of a major mountain range. This range stretches north and south through North and South America. The continental divide, which separates rivers flowing to different oceans, forms much of the border between Alberta and British Columbia. The Columbia and Fraser Rivers start in the Canadian Rockies. They are two of the largest rivers flowing to the west coast of North America. West of the Rockies, you'll find another group of mountains. These are the Columbia Mountains. They include the Selkirk, Purcell, Monashee, and Cariboo ranges.
Climate in Western Canada
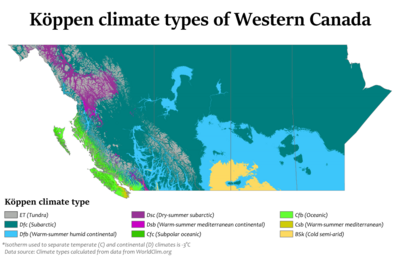
The coast of British Columbia has a mild oceanic climate. This is because of the Pacific Ocean. Winters are usually wet, and summers are fairly dry. These areas have the mildest winters in Canada. Temperatures rarely drop far below freezing.
The mountainous interior of British Columbia is drier. It has colder winters but hotter summers than the coast. Lytton, British Columbia holds the record for Canada's hottest temperature. It reached 49.6 °C (121.3 °F) (121.3°F) on June 29, 2021. It is often called Canada's hot spot in summer. Temperatures can easily reach the mid to high 30s °C (90s to 100s °F) in July and August. They sometimes even go above 40 °C (104 °F) (104°F).
Alberta has a dry continental climate. It has warm summers and cold winters. Cold Arctic air from the north can bring very cold conditions in winter. Sometimes, a warm wind called the "Chinook wind" can temporarily raise winter temperatures. Summers can be cool or hot and are generally wetter.
Saskatchewan and Manitoba have a continental climate. This means they have extreme weather. Winters in both provinces can be very harsh. Arctic winds can bring temperatures as low as −40 °C (−40 °F) (−40 °F (−40 °C)). Winter temperatures usually average between −10 and −15 °C (14 and 5 °F) (14 and 5 °F). In contrast, summers can be hot. Temperatures often go above 35 °C (95 °F) (95°F) at least once a year in most places.
| City | July (°C) | July (°F) | January (°C) | January (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calgary | 23/9 | 73/48 | −1/−13 | 27/5 |
| Edmonton | 23/12 | 73/54 | −6/−14 | 21/5 |
| Regina | 26/11 | 79/52 | -10/-22 | 14/-8 |
| Saskatoon | 25/11 | 77/52 | -12/-22 | 10/-8 |
| Winnipeg | 26/13 | 79/55 | −13/−20 | 9/−4 |
| Vancouver | 22/13 | 71/54 | 6/1 | 43/33 |
| Victoria | 22/11 | 71/51 | 7/1 | 44/33 |
Economy and Industries
Energy and agriculture are the most important industries in Western Canada. Even though only about 11 million people live here, this region is one of the world's largest exporters of both energy and farm products.
Here's a look at what Western Canada produces:
Energy:
- Oil: The region has about 13% of the world's oil reserves. It produces about 4% of the world's oil.
- Uranium: Western Canada holds 8% of the world's uranium reserves. It produces 20% of the world's uranium.
Agriculture:
- Potash: This region has 60% of the world's potash reserves. It produces 30% of the world's potash. Potash is used in fertilizers.
- Grains: Western Canada is a major exporter of wheat, coarse grains, and oilseeds. It accounts for 21% of the world's wheat export market and 10% for oilseeds.
- Farmland: About 80% of all Canadian farmland is located in Western Canada.
See also
 In Spanish: Oeste de Canadá para niños
In Spanish: Oeste de Canadá para niños