Immigration facts for kids
Immigration is when people move from their home country to live permanently in a different country. These people are called immigrants. It's different from just visiting as a tourist or going for a short trip. Sometimes, people who move for seasonal jobs are also considered immigrants.
Many studies suggest that moving to a new country can be good for both the country people leave and the country they move to. People who move often adapt well over time, especially the first and second generations. However, people who move sometimes face unfair treatment because of where they come from.
Contents
Understanding Immigration
A Look at History
The word immigration became common in the 1600s. It described people moving peacefully between countries. When people cross borders to live in a new country, they are called immigrants by the new country. When they leave their home country, they are called emigrants.
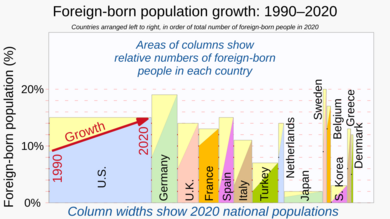
Global Movement: Facts and Figures
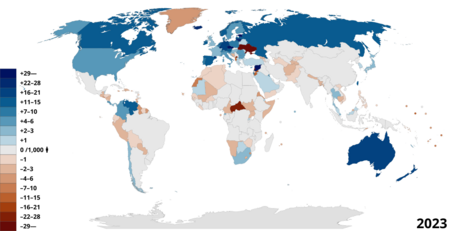
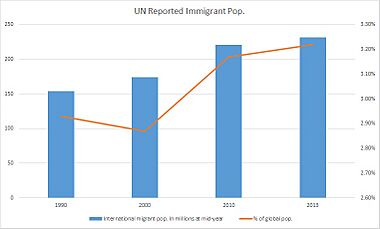
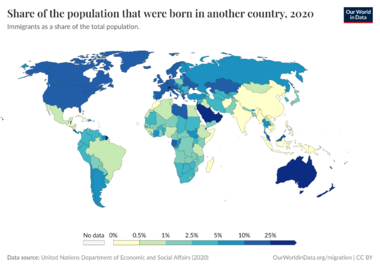
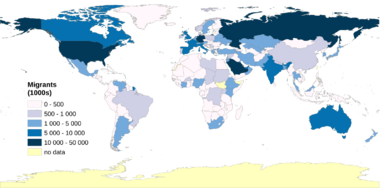
In 2015, about 244 million people were living outside their home countries. This was a big increase since the year 2000. The United States has the most international immigrants, with 19% of the world's total. Germany and Russia each host about 12 million immigrants. Other countries with many immigrants include Saudi Arabia, the United Kingdom, and the United Arab Emirates.
Most people move between countries that are close to each other. Between 2000 and 2015, Asia saw the biggest increase in immigrants, adding 26 million. Europe added about 20 million.
Many young people also move. In 2015, about 37 million international immigrants were under 20 years old. Most immigrants, about 177 million, were between 20 and 64 years old. Immigrants in Africa were the youngest, with an average age of 29. Those in Europe and Oceania were older, with average ages of 43 and 44.
Almost half of all international immigrants come from Asia. Europe is the birthplace of the second largest group, followed by Latin America. India has the largest group of people living outside their home country, with 16 million. Mexico has 12 million, and Russia has 11 million.
A 2012 survey found that many adults would like to move to another country if they could. The United States was the top choice for many, followed by the United Kingdom. Other popular countries included Canada, France, Saudi Arabia, and Australia.
Economic Migrants
An economic migrant is someone who moves to another region or country to find work. They hope to improve their quality of life and access better resources. This is different from a refugee, who flees danger or persecution.
Many countries have rules about who can enter to work. People usually need a special work visa. If someone tries to enter without the right documents to work, they might be refused entry.
Environmental Migration
Sometimes, people move because of changes in their environment. This can include natural disasters or climate changes that make it hard to live where they are.
Why People Move: Push and Pull Factors


People move for many reasons, which are often called push or pull factors. Push factors are reasons that make people want to leave their home country. Pull factors are reasons that attract people to a new country.
Seeking Better Opportunities
One common reason is to find better jobs and earn more money. If wages are higher in a new country, people might choose to move there. This was especially true in the 1800s when the United States grew quickly and needed many workers.
Moving became easier and cheaper over time. In the 1700s, crossing the Atlantic Ocean could take five weeks. By the 1900s, it took only about eight days. When travel is easier, more people tend to move. Escaping poverty and finding available jobs are strong reasons for people to move. Natural disasters can also make people leave their homes to find safety and work.
Safety and Personal Reasons
People also move to escape danger or unfair treatment. This can include persecution, conflict, or social exclusion. Some people move to escape difficult situations in their home country.
Sometimes, people move for personal reasons, like joining family members or a partner in a new country. They might also seek a place where they feel safer and more accepted. However, moving means leaving behind family, friends, and everything familiar. It also involves new laws, cultures, and sometimes facing unfair treatment.

How Immigration Affects Countries
Economic Benefits and Challenges
Studies show that immigration can help both the countries people leave and the countries they move to. It can boost the economy and help reduce poverty. However, there can also be challenges, like how it affects wages for some workers.
Some experts believe that making it easier for people to move between developing and developed countries could greatly reduce poverty worldwide.
Impact on Education and Health
Research in the United States suggests that immigration can help native-born students finish high school. Other studies in Europe found that immigrant students generally do not negatively affect the test scores of other students.
Immigration can also have positive effects on the health of workers already living in a country. As more immigrants join the workforce, native workers might move into less physically demanding jobs, which can improve their health. Studies in the United Kingdom found that immigration did not significantly increase waiting times for emergency healthcare. In fact, migrants often have better health than the general population.
Adapting to New Homes: Integration
When immigrants move to a new country, they often adapt to the new culture and way of life. This process is called integration. Studies in the United States and Europe show that immigrants, especially the second generation, often become very similar to the people already living there in terms of jobs, social life, and beliefs.
For example, studies in Europe found that immigrant families often adopt similar values to the local population over time. This includes views on gender roles, with children of immigrants often having similar attitudes to their native-born peers. Learning the local language and having the chance to become a citizen can also help immigrants integrate better into society and find good jobs.
Rules and Laws for Immigration
Every country has its own laws about immigration. International laws exist to protect immigrants' rights, like fair treatment and safe conditions. However, countries are independent and can decide how they handle immigration. Some organizations criticize countries for their immigration policies.
Many international agreements protect the rights of migrant workers. However, some major countries that receive many immigrants have not signed these agreements. While many documents say people have the freedom to move, this usually means within their own country or returning home. Some people believe that everyone should have the right to move freely between countries.
Immigration is often selective. Countries might give priority to people who are wealthy, highly educated, or have special skills. This can sometimes lead to a "brain drain," where a poorer country loses its skilled workers to richer countries. However, it can also encourage people in developing countries to get more education, hoping for better opportunities.
Discussing Immigration Policies
Different groups have different ideas about immigration. Businesses often support more immigration, while labor groups sometimes have concerns. Studies show that politicians' views on immigration can depend on the types of workers in their areas.
Immigration discussions can sometimes become linked to other important topics, like national security. This can make immigration a very emotional topic in many countries. Some research suggests that as the number of immigrants increases, public support for certain government programs might change. However, other studies question this idea, showing that diverse societies can still have strong public services.
See also
 In Spanish: Inmigración para niños
In Spanish: Inmigración para niños
- Immigration country
- Immigration reform
- Multiculturalism
- People smuggling
- Repatriation
- Non-citizen suffrage
- Non-resident citizen voting
- Skilled worker#Migration
- Xenophobia