Arctic Cordillera facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Arctic Cordillera |
|
|---|---|

The Baffin Mountains at the northern end of Auyuittuq National Park
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Barbeau Peak |
| Elevation | 2,616 m (8,583 ft) |
| Geography | |
| Country | Canada |
| Territories and Provinces | Nunavut, Quebec and Labrador |
| Regions | Arctic Archipelago and Ungava Peninsula |
| Geology | |
| Type of rock | Igneous, Metamorphic and Sedimentary |
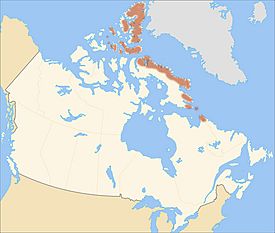
The Arctic Cordillera is a huge mountain range found in the northeastern part of North America. It stretches all the way from Ellesmere Island down to the northern tip of Labrador. This mountain range is special because it's the only major one in Canada located east of the famous Rocky Mountains.
The Arctic Cordillera covers a massive area of about 218,225 square kilometers (which is about 84,257 square miles). Its highest point is a peak called Barbeau Peak, which stands tall at 2,616 meters (or 8,583 feet) above sea level.
Contents
What is the Arctic Cordillera?
The Arctic Cordillera is a long chain of mountains. It runs along the coast of Canada's Arctic Archipelago. This area is known for its cold climate and rugged beauty.
Where is this Mountain Range Located?
The Arctic Cordillera is mainly in Nunavut, a territory in northern Canada. Parts of it also reach into Quebec and Labrador. These mountains are a big part of the landscape in the Canadian Arctic.
What Kind of Rocks Make Up the Mountains?
The mountains in the Arctic Cordillera are made of different types of rocks. You can find igneous rocks, which form from cooled lava. There are also metamorphic rocks, which have changed due to heat and pressure. Finally, sedimentary rocks are also present, formed from layers of sediment.
Exploring the Arctic Cordillera's Features
This mountain range is home to many interesting natural features. It has tall peaks, deep valleys, and large glaciers. The landscape is often harsh but very beautiful.
What are the Highest Peaks?
Barbeau Peak is the highest point in the Arctic Cordillera. It is located on Ellesmere Island. Other notable peaks include Mount Asgard and Mount Thor in Auyuittuq National Park. These mountains are popular for climbing and exploring.
Are There Glaciers in the Arctic Cordillera?
Yes, many parts of the Arctic Cordillera are covered by glaciers and ice caps. These are large sheets of ice that stay frozen all year round. They are a key feature of the Arctic landscape.
What is the Climate Like?
The climate in the Arctic Cordillera is very cold. It has long, dark winters and short, cool summers. This harsh weather makes it a challenging place for plants and animals to live. However, some species are specially adapted to survive here.
Wildlife and Nature in the Arctic Cordillera
Despite the cold, the Arctic Cordillera supports unique wildlife. Animals like polar bears, Arctic foxes, and caribou roam these lands. Birds also visit during the warmer months.
What Animals Live Here?
- Polar Bears: These large predators hunt seals on the sea ice.
- Arctic Foxes: Small and quick, they are well-adapted to the cold.
- Caribou: Herds of caribou migrate across the tundra.
- Arctic Hares: These large hares blend in with the snow.
- Muskoxen: Large, shaggy animals that can withstand extreme cold.
What About Plants?
The plant life in the Arctic Cordillera is mostly low-growing. You'll find mosses, lichens, and small shrubs. Taller trees cannot grow here because of the cold temperatures and thin soil.
Images for kids
-
Tanquary Fiord, showing confluence of Air Force River, Rollrock River and Macdonald River
-
Gull Glacier in Tanquary Fjord
-
Folded rock in the Torngat Mountains
-
Dragon Cliff, including the flood basalt lava layers
-
Mount Asgard in July 2001
-
Mount Thor in 1997
-
The Conger Range and Ad Astra Icecap
-
The Osborn Range seen from a Twin Otter
-
Qijuttaaqanngittuq Valley in the southern Baffin Mountains
-
Nachvak Fjord, Torngat Mountains
See also
 In Spanish: Cordillera Ártica para niños
In Spanish: Cordillera Ártica para niños