2003 invasion of Iraq facts for kids
Quick facts for kids 2003 invasion of Iraq |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Iraq War | |||||||
|
From left to right: Marines of the U.S. 1st Marine Regiment escort Iraqi prisoners of war; a convoy of U.S. military vehicles in a sandstorm; U.S. soldiers watch an enemy building in Baghdad burn; Iraqi civilians cheer as a statue of Saddam Hussein is toppled. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Coalition forces: With military support from:
|
|
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Ahmed Chalabi |
|||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
|
Shia Al Mahdi Army: 1600–2800 |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Coalition: 214 killed 238 dead, 1,000+ wounded |
Estimated Iraqi combatant fatalities: 30,000 (figure attributed to General Tommy Franks) 7,600–11,000 (4,895–6,370 observed and reported) (Project on Defense Alternatives study) 13,500–45,000 (extrapolated from fatality rates in units serving around Baghdad) Total: 7,600–8,000 killed |
||||||
|
Estimated Iraqi civilian fatalities: |
|||||||
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a war that took place from March 20 to May 1, 2003. It involved countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland. Their goal was to end the rule of Saddam Hussein in Iraq.
A main reason for the war was the belief that Iraq had dangerous weapons of mass destruction. These included chemical or nuclear weapons. However, after the invasion, it was found that Iraq did not have these weapons.
Another reason was the idea that Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, an al-Qaeda leader, was hiding in Iraq. This was after the September 11, 2001 attacks. Even though Saddam Hussein was not involved in those attacks, some people thought he was helping al-Qaeda hide. The war was very controversial. It led to many negative feelings towards British Prime Minister Tony Blair and American President George W. Bush.
During the war, 4,734 soldiers from the Coalition forces were killed. This included 4,416 U.S. soldiers and 179 UK soldiers. More than 31,882 U.S. soldiers and over 3,600 UK soldiers were wounded. Sadly, over 100,000 Iraqi civilians, who were not soldiers, also lost their lives.
Contents
Why the Invasion Happened
The main reason given for the invasion was that Iraq had not followed U.N. Security Council rules. These rules asked Iraq to get rid of its weapons of mass destruction. Iraq had also made U.N. weapons inspectors leave the country.
Concerns About Weapons
Before the war, leaders in the U.S. and UK believed Iraq had hidden dangerous weapons. These were called weapons of mass destruction (WMDs). They were worried these weapons could be used against other countries.
Links to Terrorism
Some people also believed that Saddam Hussein was connected to terrorist groups. They thought he might be helping al-Qaeda, a group responsible for the September 11 attacks. This idea added to the reasons for the invasion.
Who Was Involved
Many countries and groups took part in the invasion. They were divided into two main sides.
Coalition Forces
The main group invading Iraq was called the Coalition forces.
- The United States provided the largest number of troops.
- The United Kingdom also sent many soldiers.
- Australia and Poland were part of this group too.
- They also had help from Iraqi groups like the Iraqi National Congress.
- The Peshmerga, a military force from Iraqi Kurdistan, also supported the Coalition.
Iraqi Forces
On the other side were the forces loyal to Saddam Hussein.
- These included the regular Iraqi Armed Forces.
- There were also special groups like the Iraqi Republican Guard.
- Some volunteers from other Arab countries joined the fight.
Key Leaders of the War
Many important leaders were involved in the decision-making and fighting.
Coalition Leaders
- George W. Bush was the President of the United States.
- Tony Blair was the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
- John Howard was the Prime Minister of Australia.
- Aleksander Kwaśniewski was the President of Poland.
- Military commanders like Tommy Franks led the troops on the ground.
Iraqi Leaders
- Saddam Hussein was the President of Iraq.
- His sons, Qusay Hussein and Uday Hussein, also held important positions.
- Other top Iraqi officials and generals were involved in leading their forces.
What Happened During the Invasion
The invasion began with air strikes and then ground forces moved into Iraq. The goal was to quickly take control and remove Saddam Hussein from power.
The Start of the Invasion
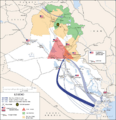
The invasion officially began on March 20, 2003. Air attacks targeted key locations in Iraq. Ground troops then crossed the borders from Kuwait and other areas.
Moving Towards Baghdad
Coalition forces moved quickly through Iraq. They faced some resistance but generally advanced well. Their main target was the capital city, Baghdad.
The Fall of Baghdad
Baghdad was captured by Coalition forces in early April 2003. A famous moment was when a statue of Saddam Hussein in Baghdad's Firdos Square was pulled down. This event showed the end of Saddam Hussein's rule.
After the Invasion
The main fighting of the invasion ended on May 1, 2003. However, the war in Iraq continued for many years after this.
Changes in Government
After Saddam Hussein's government was removed, a new Iraqi government was set up. This marked the start of a new period for Iraq.
Ongoing Challenges
Even after the invasion, there were still many challenges. The country faced a long period of occupation and continued conflict.
Images for kids
-
Gen. Anthony C. Zinni briefs reporters at The Pentagon following Operation Desert Fox, 21 December 1998
-
Two US F-16 Fighting Falcons prepare to depart Prince Sultan Air Base in Saudi Arabia for a patrol as part of Operation Southern Watch, 2000.
-
George W. Bush addressed the General Assembly of the United Nations on 12 September 2002 to outline the complaints of the United States government against the Iraqi government.
-
From left: French President Jacques Chirac, US President George W. Bush, British Prime Minister Tony Blair and Italian Prime minister Silvio Berlusconi at the G8 Summit at Evian, France. Chirac opposed the invasion; the other three leaders supported it.
-
60,000–200,000 protesters of various ages demonstrated in San Francisco, 15 February 2003
-
José Manuel Durão Barroso, Tony Blair, George W. Bush and José María Aznar on 16 March 2003
-
Colin Powell holding a model vial of anthrax while giving presentation to the United Nations Security Council on 5 February 2003 (still photograph captured from video clip, The White House/CNN)
-
Tony Blair (left) and George W. Bush at Camp David in March 2003, during the build-up to the invasion of Iraq
-
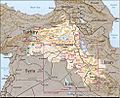
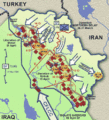
Kurdish areas in Northern Iraq
-
Carrier Air Wing Two (CVW-2) mission briefing aboard Constellation (CV-64), 21 March 2003.
-
Wingtip vortices are visible trailing from an F-15E as it disengages from midair refueling with a KC-10 during Operation Iraqi Freedom
-
Destroyed Iraqi T-72 tank on Highway 9 outside Najaf
-
British soldiers engage Iraqi Army positions with their 81mm Mortars south of Basra, 26 March 2003.
-
U.S. Army M1A1 Abrams tanks and their crews pose for a photo in front of the "Victory Arch" monument at Baghdad's Ceremony Square in November 2003.
-
Members of the RAN Clearance Diving Team Three and an Australian Army LCM-8 inspecting camouflaged mines, 21 March 2003.
-
Aircraft of the USAF 379th Air Expeditionary Wing and UK and Australian counterparts stationed together at Al Udeid Air Base, Qatar, in southwest Asia, fly over the desert on 14 April 2003. Aircraft include KC-135 Stratotanker, F-15E Strike Eagle, F-117 Nighthawk, F-16CJ Falcon, British GR-4 Tornado, and Australian F/A-18 Hornet
-
The famous statue of Saddam Hussein being knocked down by US forces
See also
 In Spanish: Invasión de Irak de 2003 para niños
In Spanish: Invasión de Irak de 2003 para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |