University of Toronto facts for kids

Coat of arms
|
|
| Latin: Universitas Torontonensis | |
|
Former name
|
King's College (1827–1849) |
|---|---|
| Motto |
Velut arbor ævo (Latin)
|
|
Motto in English
|
"As a tree through the ages" |
| Type | Public research university |
| Established | March 15, 1827 |
|
Academic affiliation
|
|
| Endowment | |
| Chancellor | Wes Hall |
| President | Melanie Woodin |
| Provost | L. Trevor Young |
|
Academic staff
|
3,246 |
|
Administrative staff
|
7,462 |
| Students | 69,976 (St. George) |
| Undergraduates | 49,425 |
| Postgraduates | 20,551 |
| Location |
,
Ontario
,
Canada
43°39′42″N 79°23′42″W / 43.66167°N 79.39500°W |
| Campus | Large city, 138 acres (56 ha) (St. George) |
| Newspaper | The Varsity |
| Colours | UofT Blue and white |
| Nickname | Varsity Blues |
|
Sporting affiliations
|
U Sports – OUA, CUFLA |
| Mascot | True Blue the Beaver |
 |
|
The University of Toronto (often called U of T) is a large public research university. Its main campus is in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, near Queen's Park. It started in 1827 as King's College, the first place for higher learning in Upper Canada. In 1850, it became the University of Toronto and was no longer controlled by the Church of England.
U of T has three campuses: St. George, Mississauga, and Scarborough. The St. George campus in Downtown Toronto is the oldest. It works like a "collegiate university," meaning it has 11 different colleges. Each college has its own history and some freedom in how it runs.
The University of Toronto is the biggest university in Canada. It has over 100,000 students across its three campuses. It offers more than 700 programs for undergraduate students and 200 for graduate students. The university gets the most money for scientific research and has the largest financial fund of any Canadian university. It is also known for important ideas in how we understand communication and literature.
Many amazing discoveries happened at U of T. These include insulin, stem cell research, the first artificial cardiac pacemaker, and the first successful lung and nerve transplants. The first electron microscope was also developed here. Researchers at U of T also helped develop deep learning and multi-touch technology. The university received the largest donation in Canadian history in 2020, a $250 million gift. It also received the largest research grant in Canada in 2023, for $200 million.
The university's sports teams are called the Varsity Blues. They play in many intercollegiate games. The first recorded game of gridiron football happened at U of T in 1861. The university's Hart House is a special building for students. It offers cultural, intellectual, and fun activities.
As of 2024, 13 Nobel laureates (people who won Nobel Prizes), 6 Turing Award winners, and 1 Fields Medalist have been connected to the university. Many famous people have studied at U of T. These include five prime ministers of Canada and many other leaders.
Contents
University History
How the University Started

The idea for a college in Upper Canada came from John Graves Simcoe. He was the first Lieutenant-Governor. He wanted a college to help stop American ideas from spreading. In 1798, it was suggested that a college be built in York.
On March 15, 1827, King George IV officially created "King's College." It was meant to educate young people in Christian values and science. John Strachan, an important Anglican Bishop, helped make this happen. He became the college's first president. The first building was built where Queen's Park is today.
Under Strachan, King's College was a religious school. It was closely linked to the Church of England. But politicians wanted the college to be non-religious. In 1849, King's College was renamed the University of Toronto. It became a secular (non-religious) school. University College was then created as the teaching part of the University of Toronto.

The School of Practical Science started in 1878. This later became the Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering, also known as Skule. The Faculty of Medicine opened in 1843. The Faculty of Law opened in 1887. The Faculty of Dentistry opened in 1888. Women were first allowed to attend the university in 1884.
In 1890, a big fire damaged University College. But the university rebuilt it and refilled its library in just two years. Over time, more colleges joined the university. The university also ran the Royal Conservatory of Music and the Royal Ontario Museum for many years. The University of Toronto Press started in 1901. It was Canada's first academic publishing house.
University in the 20th Century

During the First and Second World Wars, many students joined the military. Some university activities were paused. The David Dunlap Observatory opened in 1935. The University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies opened in 1949.
By 1961, the university had over 14,000 students. New campuses opened in Scarborough in 1964 and Mississauga in 1967. In the 1980s, the university started working harder to raise money. This was because government funding was reduced.
Recent Developments
The University of Toronto was the first Canadian university to have a financial fund of over one billion dollars in 2007. From 2011 to 2018, the university had a big fundraising campaign called Boundless. It raised over $2.6 billion, which was a new record for Canada.
In 2020, the university received the largest single donation in Canadian history. It was a $250 million gift from James and Louise Temerty for the Faculty of Medicine. The Faculty of Medicine was renamed the Temerty Faculty of Medicine in their honor. In 2021, the university started an even bigger fundraising campaign called Defy Gravity. Its goal is to raise $4 billion.
University Campuses
The University of Toronto calls itself "one university [with] three campuses." It started with one location in Downtown Toronto. Then it grew to the east and west. This helped meet the needs of the fast-growing Greater Toronto Area.
St. George Campus
The St. George campus (UTSG) is the university's main and oldest campus. It is in Downtown Toronto. It is home to the college system and many academic departments. The campus covers about 138 acres. It is known for its green spaces and many courtyards. This makes it feel like a park in the city center.
The buildings on campus are a mix of Romanesque and Gothic Revival styles. Many were built between 1858 and 1929. The main part of the university is called Front Campus. It is an oval lawn surrounded by King's College Circle. The most important building is University College. It was built in 1857. This building is a National Historic Site of Canada.
Convocation Hall was built in 1907. It has a domed roof and tall pillars. It is used for graduation ceremonies and other events. Knox College has a classic Gothic design with courtyards.

Hart House is a Gothic-style student center. It has many common rooms, including the Great Hall with stained-glass windows. The nearby Soldiers' Tower is 143 feet tall. It has the names of university members who died in the World Wars. The tower also has 51 bells that are played on special days. Trinity College has a Tudor-style main building. Its chapel is built in a unique Gothic style. Philosopher's Walk is a pretty path that connects different parts of the campus. Victoria College is on the east side of Queen's Park. It has a main building made of red sandstone and grey limestone.
The western part of the campus has more modern buildings. These include laboratories and offices. The Robarts Library is a very large concrete building. It was built in 1972. The Leslie L. Dan Pharmacy Building, finished in 2006, is a modern building made of glass and steel.
Mississauga Campus
The Mississauga campus (UTM) opened in 1967. It was first called Erindale College. It mainly served students who lived in Mississauga. Since the 2000s, it has become the second-largest part of U of T. It is an important university for the Peel Region. UTM is known for its beautiful forested area. It is located on the bank of the Credit River. Popular programs there include forensic science and biomedical communications.
Scarborough Campus
The Scarborough campus (UTSC) opened in 1964. At that time, Scarborough was a separate town. Now it is part of the City of Toronto. This campus offers many co-operative education programs. It serves students from the east side of Downtown Toronto.
Other Locations
Besides the three main campuses, U of T has other locations. The University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies (UTIAS) is in North York. Hart House also manages Hart House Farm. This is a 150-acre piece of land in Caledon, Ontario. It is used for student activities.
How the University is Organized
The University of Toronto is set up in a way that power is shared. The main administration, academic departments, and colleges all have a say. The Governing Council is the main group that makes decisions. It handles academic, business, and other university matters. Its offices are in Simcoe Hall on the St. George campus.
The chancellor is the ceremonial head of the university. This person is usually a former important leader. The president is the chief executive of the university. Both the chancellor and president are part of the Governing Council.
University Colleges
|
Constituent colleges
Theological colleges
|
Federated colleges
Postgraduate college
|
Unlike most universities in North America, U of T is a collegiate university. This means it has a system of colleges, similar to universities in Britain. These colleges have a lot of freedom. They handle admissions, scholarships, and some academic programs. They also provide housing and social activities for students. This system started in the 19th century. It allowed religious colleges to join the university while keeping their traditions.
Every undergraduate student in the Faculty of Arts & Science at the St. George campus belongs to one of the seven colleges.
University College was the first non-religious college. It was created in 1853. Other colleges like Knox College and Wycliffe College joined later. Victoria University and Trinity College also became part of the university. In 1910, St. Michael's College, a Roman Catholic college, joined too.
After World War II, new non-religious colleges were created. These include New College (1962), Innis College (1964), and Woodsworth College (1974). Massey College was created in 1963 just for graduate students. Regis College joined in 1979.
Some colleges, like Knox, Massey, Regis, St. Michael's, Trinity, Victoria, and Wycliffe, are still separate legal entities. They have their own money. While some still have religious ties, they now have non-religious policies for students and teaching.
Academics
|
|
|

The Faculty of Arts & Science is the main faculty for undergraduate students at the St. George campus. It runs most of the courses in the college system. While colleges don't do all the teaching, many have special academic programs. For example, Trinity College is known for international relations. University College is known for Canadian studies.
U of T is famous for a way of thinking about communication and literature called the Toronto School. This idea explores how communication shapes human cultures and minds.
Many important works in arts and humanities are based at the university. These include the Dictionary of Canadian Biography and the Collected Works of Erasmus.
The Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy offers programs in international affairs and public policy. It is also home to the G20 Research Group. This group studies the Group of Twenty countries. The Citizen Lab at the Munk School researches Internet censorship.
The Dalla Lana School of Public Health is a faculty that focuses on public health. It started in 1927. After the 2003 SARS crisis, it grew a lot. It is now Canada's largest public health school. It does research on global health, air pollution, and other important health issues.
The Temerty Faculty of Medicine works with ten teaching hospitals. These hospitals provide medical care and do research. Doctors at these hospitals also teach at the university. The Rotman School of Management teaches a special way of thinking called integrative thinking. The Faculty of Law focuses on liberal arts and legal theory. The Ontario Institute for Studies in Education is the university's teachers college.
Library and Collections

The University of Toronto Libraries is the third-largest academic library system in North America. It has over 12 million print books and 1.9 million digital books. It also has many journals and historical documents. There are 40 libraries across the three campuses. The biggest is Robarts Library. It holds about five million books for humanities and social sciences.
The Thomas Fisher Rare Book Library has one of the largest collections of rare books and manuscripts. Its collections include ancient Egyptian papyri and early printed books. The Cheng Yu Tung East Asian Library has a rare collection of 40,000 Chinese books. The Richard Charles Lee Canada-Hong Kong Library has the largest collection for Hong Kong and Canada–Hong Kong studies outside of Hong Kong.
The University of Toronto Art Centre has three main art collections. The Malcove Collection has Early Christian and Byzantine art. It also has a painting called Adam and Eve from 1538. The University of Toronto Collection shows Canadian contemporary art. The University College Art Collection has works by the Group of Seven painters.
Rankings and Reputation
| University rankings | |
|---|---|
| Global rankings | |
| ARWU World | 26 |
| QS World | 25 |
| Times World | 21 |
| U.S News & World Report Global | 17 |
| Canadian rankings | |
| ARWU National | 1 |
| QS National | 1 |
| Times National | 1 |
| U.S News & World Report National | 1 |
| Maclean's Medical/Doctoral | 2 |
The University of Toronto is highly ranked around the world. In 2022, the Academic Ranking of World Universities ranked it 22nd globally and first in Canada. The 2023 QS World University Rankings placed it 21st in the world and first in Canada. In 2023, the Times Higher Education World University Rankings ranked it 18th globally and first in Canada. In the 2024–25 U.S. News & World Report Best Global University Ranking, it was 17th in the world and first in Canada.
Maclean's magazine ranked U of T second in its 2022–2023 Medical Doctoral university category. It also ranked U of T first in its 2023 reputation survey.
The university's research is also highly rated. In 2019, the Performance Ranking of Scientific Papers for World Universities ranked it fourth in the world. The University Ranking by Academic Performance 2019–2020 rankings placed it second in the world.
U of T graduates are also highly sought after for jobs. In 2022, the Times Higher Education ranked the university 11th globally for graduate employability. QS ranked it 21st in the world for graduate employability in 2022.
Since 2024, the University of Toronto has been named the most sustainable university in the world by QS World University Rankings.
Research and Discoveries
Since 1926, U of T has been part of the Association of American Universities. This group includes top research universities in North America. U of T has the largest annual research budget of any university in Canada. In 2021, it was named the top research university in Canada.
The first practical electron microscope was built by the physics department in 1938. During World War II, the university developed the G-suit. This suit saved the lives of fighter plane pilots. In 1963, the asteroid 2104 Toronto was discovered at the David Dunlap Observatory. It was named after the university. In 1972, studies at U of T helped prove that black holes exist. Toronto astronomers have also discovered moons of Uranus and dwarf galaxies.
U of T was a pioneer in computer technology. It designed UTEC, one of the world's first working computers. AlexNet, an important development in deep learning, was created at the university. Multi-touch technology, used in many devices today, was also developed here. The AeroVelo Atlas, a human-powered helicopter, was developed by U of T students and graduates. It won a major competition in 2013.
Biological Breakthroughs
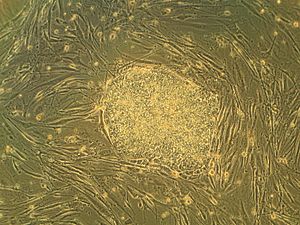
The discovery of insulin at U of T in 1921 is one of the most important events in medical history. Frederick Banting and Charles Best made this discovery. Stem cells were discovered at the university in 1963. This discovery led to bone marrow transplantation and all modern stem cell research. Researchers at U of T also found cancer stem cells in 1997.
Other medical inventions from Toronto include the glycaemic index and the infant cereal Pablum. The first successful single-lung transplant was done in Toronto in 1981. The first nerve transplant was in 1988. The first double-lung transplant was in 1989. Researchers here also found the genes that cause cystic fibrosis and early-onset Alzheimer's disease.
The University of Toronto is a key part of one of the world's largest groups of biotechnology companies. Over 5,000 researchers work near the university. They do $1 billion of medical research every year. MaRS Discovery District is a research park that helps businesses and university inventions. In 2008, the university had 159 inventions and 114 active start-up companies. Its SciNet Consortium runs Canada's most powerful supercomputer.
Student Life and Culture

Hart House is a special student activity center at U of T. It was opened in 1919. It helps create a strong student community. Hart House offers many services and facilities. These include a library, restaurants, an art gallery, a theater, and a swimming pool. It also hosts concerts, debates, and study spaces.
Hart House supports student clubs. It also has committees with many students. The main student unions are the University of Toronto Students' Union and the Graduate Students' Union. Each college and department also has its own student groups.
The Hart House Debating Club is known for its debating style. It combines American analysis with British wit. The club won the World Universities Debating Championship in 1981 and 2006. The Toronto chess team has won the top title six times at the Pan American Intercollegiate Team Chess Championship. The Formula SAE Racing Team won European championships in 2003, 2005, and 2006.
The University of Toronto also has a fun student tradition. It's called the University of Toronto Aphrodite Project. Students fill out a psychology survey. Then they are matched with their best algorithmic match for Valentine's Day.
Theatre and Music
Hart House Theatre is the university's student theater. It usually puts on four plays each season. It has helped many famous performers get their start. These include Donald Sutherland and Lorne Michaels. Three members of the Group of Seven painters designed sets for the theater. The theater also hosts annual shows by student groups from different colleges.
Hart House has many musical groups. These include an orchestra, chamber strings, and a chorus. The Jazz at Oscar's series plays jazz music on Friday nights. Open Stage is a monthly event for singers, comics, and poets. The Sunday Concert series has performed free classical music concerts since 1922.
Student Media
The Varsity is one of Canada's oldest student newspapers. It has been published since 1880. It comes out weekly during the school year. Hart House Review is a literary magazine. It publishes writing and art from new Canadian artists. The Newspaper is another student-run newspaper. CIUT-FM is the university's radio station. University of Toronto Television broadcasts student-made content.
Students at each college also have their own publications. The Gargoyle from University College helped start the careers of people like journalist Naomi Klein. Acta Victoriana from Victoria University is Canada's oldest active literary journal. It published early works by writers like Margaret Atwood.
Residences
The university has housing for about 6,400 students. It guarantees housing only for first-year undergraduate students. Most older students and graduate students live off-campus. The neighborhoods near the university, like The Annex and Harbord Village, are popular places for students to live.
Student Demographics
The University of Toronto has the most students of any post-secondary school in Canada. In 2024, the total number of students across all three campuses went over 100,000 for the first time. The university has many international students. In 2024–25, about 28.8 percent of students were from other countries.
| Undergraduate | Graduate | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 43.6% | 40.1% |
| Female | 53.5% | 58.8% |
| Canadian student | 70.1% | 73.0% |
| International student | 29.9% | 27.0% |
In 2024–25, about 54.8 percent of students were female and 42.7 percent were male. The average high school grade for first-year students in fall 2014 was about 86 percent. About 92.1 percent of students continued their studies after their first year.
In 2024–25, about 25.2 percent of students were in Social Science and Humanities. About 28.1 percent were in Biology, Engineering, and Mathematics & Physical Sciences.
Athletics
The Varsity Blues are the university's sports teams. They have 44 teams that compete against other universities. They play in national competitions through U Sports. They also play in provincial competitions in the Ontario University Athletics (OUA) conference. The nickname "Varsity Blues" became common in the 1930s.
North American football started at the University of Toronto. The first recorded game was played at University College on November 9, 1861. The Blues played their first game against the University of Michigan in 1877. The Blues have won four Grey Cup championships and two Vanier Cup championships. They also won 25 Yates Cup championships. Varsity Stadium has been the main field for football and soccer since 1898.

The Varsity Blues men's ice hockey team started in 1891. They have a rich history in hockey. Conn Smythe, a famous hockey figure, played and coached for the Blues. When he took over the Toronto Maple Leafs, his new team used the Blues' blue-and-white uniform design. The Blues hockey team won the gold medal for Canada at the 1928 Winter Olympics. They have won the national hockey title ten times. Varsity Arena has been their home since 1926.
In swimming, the men's team has won the national title 16 times since 1964. The women's team has won 14 times since 1970. The University of Toronto Rowing Club started in 1897. It is Canada's oldest college rowing club. They won a silver medal for Canada in rowing at the 1924 Summer Olympics in Paris.
Notable People
-
William Lyon Mackenzie King, the longest-serving Prime Minister in Canadian history with over 21 years in office, BA, MA
-
Lester B. Pearson, Canadian Prime Minister and winner of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1957, BA
-
Paul Martin, 21st Canadian Prime Minister, LLB
-
John Kenneth Galbraith, noted economist and a leading proponent of 20th-century American liberalism, B.Sc.(Agr.)
-
John Charles Fields, mathematician and the founder of the prestigious Fields Medal
-
Frederick Banting, Nobel Laureate in Medicine and the first person to use insulin on humans, MB, MD
-
Roberta Bondar, CSA astronaut and the first Canadian female in space, PhD
-
Julie Payette, CSA astronaut and the 29th Governor General of Canada, MASc
Many famous people have studied or taught at the University of Toronto. These include 13 Nobel laureates. As of 2006, U of T academics made up a large number of Canadian members in important academic groups.
Alumni from U of T have become leaders in many fields. In government, former Governors General Vincent Massey, Adrienne Clarkson, and Julie Payette are graduates. So are Prime Ministers William Lyon Mackenzie King, Arthur Meighen, Lester B. Pearson, Paul Martin, and Stephen Harper. Many justices of the Supreme Court also studied here. World leaders like President of Latvia Vaira Vīķe-Freiberga and President of Trinidad and Tobago Noor Hassanali are also alumni.
Famous academics from U of T include economist John Kenneth Galbraith, philosopher David Gauthier, and historian Margaret MacMillan. Doctors Norman Bethune and Charles Best also graduated from here. Astronauts Roberta Bondar and Julie Payette are also U of T alumni.
In business, U of T alumni include leaders from major companies. These include Rogers Communications' Ted Rogers and Toronto-Dominion Bank's W. Edmund Clark. BlackBerry's Jim Balsillie and eBay's Jeffrey Skoll also studied here.
In literature and media, the university has produced writers like Margaret Atwood and Michael Ondaatje. Film directors like David Cronenberg and actors like Donald Sutherland are also alumni. Musicians like Paul Shaffer and journalists like Malcolm Gladwell also attended U of T.
Companies started by University of Toronto alumni create about one-quarter of Canada's GDP. This was shown in a 2021 survey.
See also
 In Spanish: Universidad de Toronto para niños
In Spanish: Universidad de Toronto para niños
- Education in Toronto
- Higher education in Ontario
- List of universities in Canada
- University of Toronto Campus Safety
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |


























