Biotechnology facts for kids
Biotechnology is an exciting field that mixes natural sciences, like biology, with engineering. It's all about using living things, or parts of them, to create useful products and services. People who work in this field are called biotechnologists.
The word "biotechnology" was first used in 1919 by Károly Ereky. He used it to describe making products from raw materials with the help of living organisms. The main idea is to use biological systems, like tiny bacteria, yeast, or plants, to do specific jobs or make valuable things.
Biotechnology has changed many parts of our lives, from medicine and agriculture to helping the environment. One important tool in biotechnology is genetic engineering. This lets scientists change the instructions (DNA) inside organisms. They can add genes from one organism to another to create new features or improve existing ones.
Other cool techniques include tissue culture, where scientists grow cells and tissues in a lab for research. There's also fermentation, which uses tiny organisms to make things like beer, wine, and cheese.
Biotechnology has given us many amazing things. These include important medicines, biofuels, special crops, and new materials. It also helps solve environmental problems, like making plastics that break down naturally. It also uses tiny organisms to clean up polluted areas.
This field is always growing and has a lot of potential to solve big global problems. It can also make life better for people everywhere. However, it also brings up important questions about how we use genetic changes and who owns new inventions. Because of this, there are ongoing discussions and rules about how biotechnology is used.
Contents
What is Biotechnology?
Biotechnology is all about using living things, like tiny cells or even whole plants and animals, to make useful products or solve problems. This idea isn't new! For thousands of years, people have used biotechnology without even knowing the word.
Think about how early humans started taming animals or growing plants. They picked the best ones to breed, making them stronger or more useful. This was an early form of biotechnology.
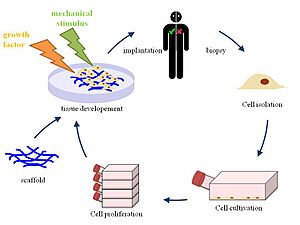
Today, biotechnology also includes advanced tools like genetic engineering. This is where scientists can carefully change the DNA of an organism. It also includes growing cells and tissues in a lab.
Scientists use biotechnology in labs for research and development. They use computers to help understand biological information, a field called bioinformatics. The goal is to find, use, and produce valuable things from living organisms. This can lead to new medicines, better crops, or ways to clean up the environment. Before new products are sold, they go through careful testing to make sure they are safe and work well.
How Did Biotechnology Start?
Biotechnology has a long and interesting history, going back thousands of years!
- Ancient Times: The earliest farmers were actually using biotechnology. They learned to pick the best seeds from plants and breed the strongest animals. This selective breeding helped them grow more food and raise healthier livestock.
- Fermentation: People in ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and India discovered how to use tiny organisms called yeast to make beer and leavened bread. This process, called fermentation, changes ingredients into new products. They also made foods like soy sauce using similar methods.
- Understanding Microbes: In 1857, Louis Pasteur helped us understand fermentation better. Later, in 1917, Chaim Weizmann used bacteria to make acetone, which was important for making explosives during World War I.
- Antibiotics: A huge step came in 1928 when Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin, a powerful medicine from mold. By 1940, penicillin was helping to treat bacterial infections and save lives.
- Modern Biotechnology Begins: The field of modern biotechnology really took off in the 1970s. In 1971, Paul Berg successfully combined DNA from different sources. Then, in 1972, Herbert Boyer and Stanley Norman Cohen found a way to put genetic material into bacteria, making the bacteria copy it. This was a big step for genetic engineering.
- New Inventions: In 1980, a court decision in the United States made it possible to get patents for genetically modified organisms. This encouraged more companies to invest in biotechnology. For example, Ananda Chakrabarty created a bacterium that could help clean up oil spills.
- Biofuels and Crops: Today, biotechnology helps create biofuels like ethanol and develops special crops. These crops can resist pests and drought, helping farmers grow more food and materials for fuel.
Different Kinds of Biotechnology
Biotechnology is used in many different areas to help us in various ways. Here are some of the main ones:
Biotechnology in Medicine
This is often called Red Biotechnology. It focuses on improving human health.
- New Medicines: Biotechnology helps discover and make important medicines. For example, in 1978, scientists used genetic engineering to create human insulin. This medicine, used by people with diabetes, was previously taken from animals. Now, bacteria can produce large amounts of it cheaply.
- Vaccines and Treatments: It helps create vaccines to protect us from diseases and antibiotics to fight infections. It also works on new ways to repair damaged tissues and even create artificial organs.
- Genetic Testing: Biotechnology allows for genetic tests. These tests can find out if someone might be at risk for certain inherited diseases. They can also help understand a person's family history.
- Personalized Medicine: A field called pharmacogenomics studies how a person's genes affect how they react to medicines. This helps doctors choose the best medicine and dose for each individual.
Biotechnology in Farming
This is known as Green Biotechnology. It applies biotechnology to agriculture.
- Better Crops: Scientists use genetic engineering to create GM crops. These plants have new traits that don't naturally occur. For example, some crops are made to resist pests, diseases, or harsh weather. Others are designed to need less water or have more nutrients.
- Examples of GM Crops: Farmers widely use GM crops like soybean, corn, and canola. These crops help produce more food and materials for things like biofuels.
- Environmental Benefits: Some insect-resistant GM crops can reduce the need for chemical pesticides. This can be better for the environment.
- Food Security: Biotechnology helps make food more secure. Crops like Golden rice are engineered to have more vitamins. It also helps speed up plant breeding, so we can grow more food faster.
Biotechnology in Industry
This is called White Biotechnology. It uses living things for industrial processes.
- Eco-Friendly Production: Industrial biotechnology uses cells or enzymes to make useful chemicals, foods, and fuels. It often uses renewable materials instead of fossil fuels. This helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and is better for the planet.
- Making Chemicals: Scientists can design organisms to produce valuable chemicals. They also use enzymes as natural helpers (catalysts) to make or break down chemicals.
- Synthetic Biology: This advanced area helps create new biological parts or redesign existing ones. It's used to make microorganisms, like Escherichia coli, better at producing things like medicines or biofuels.
Biotechnology for the Environment
This is known as Gray Biotechnology or Environmental Biotechnology. It focuses on protecting our planet.
- Cleaning Up Pollution: Biotechnology helps clean up waste and pollution. For example, bioremediation uses microorganisms to break down oil spills or hazardous chemicals.
- Waste Treatment: It's used in many cities to filter pollutants from the air, like with CityTrees. It also helps recycle materials and treat wastewater.
- Protecting Nature: This field also works on maintaining biodiversity and removing pollutants from the environment.
- Blue Biotechnology: This specific area uses resources from the ocean to create products. For example, it can use tiny algae to produce bio-oils.
- Brown Biotechnology: This branch focuses on managing dry lands and deserts. It helps create seeds that can grow in very tough, dry conditions.
Rules and Safety in Biotechnology
Because biotechnology uses powerful tools like genetic engineering, governments have rules to make sure it's used safely. These rules help manage any possible risks that come with creating and using genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Rules can be different in various countries. For example, the United States and Europe have some different rules for GMOs. The rules also depend on what the genetically engineered product is for. A crop used for fuel might have different rules than a crop grown for food. These rules help ensure that biotechnology benefits everyone safely.
Learning About Biotechnology
If you are interested in biotechnology, there are many ways to learn more!
- School and College: Many schools and colleges offer courses in biotechnology. You can study subjects like biology, chemistry, and engineering.
- Training Programs: Universities often have special programs to train students in biotechnology. These programs help students learn the skills needed for research and development in this field.
- Future Careers: Learning about biotechnology can open doors to exciting careers. You could become a biotechnologist, a researcher, or work in medicine, agriculture, or environmental science.
See also
 In Spanish: Biotecnología para niños
In Spanish: Biotecnología para niños