Central bank facts for kids
A central bank is like the main bank for a country. It helps manage a country's money, including its currency, how much money is available, and interest rates.
Central banks usually watch over the other banks in their country, called commercial banks. They are the only ones who can print or create the national money. They control the total amount of money in the country. Unlike a regular bank where you keep your savings, a central bank can actually increase or decrease the amount of money flowing in the nation's economy.
The oldest central bank is the Bank of England. Today, some of the biggest central banks include the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Federal Reserve in the United States.
Central banks also have special powers to make sure banks are safe. These powers help prevent "bank runs," which is when too many people try to take all their money out of a bank at once. They also stop commercial banks from doing risky or dishonest things. How much power a central bank has compared to its government can be different in each country.
The main leader of a central bank is often called the Governor, President, or Chairman.
Contents
What Does a Central Bank Do?

Central banks have many important jobs. Here are some of them:
- Setting Money Rules: They create and carry out rules about money, known as monetary policies.
- Controlling Interest Rates: They set the official interest rate. This rate affects how much it costs to borrow money. It helps manage how fast prices go up (inflation) and the value of the country's money compared to other currencies (exchange rate).
- Managing Money Supply: They control the total amount of money available in the country.
- Government's Banker: They act as the bank for the government, handling its money. They are also the "bankers' bank," meaning they lend money to other banks if those banks need help. This is why they are called the "lender of last resort."
- Handling National Wealth: They manage the country's foreign money and gold reserves. They also keep track of the government's financial records.
- Watching Over Banks: They regulate and supervise the banking industry to make sure banks follow the rules and stay safe.
How Central Banks Manage Money
Central banks are responsible for putting a country's chosen monetary policy into action. This means they decide how much money should be in circulation and what the interest rates should be to keep the economy stable and growing.
Where Do Central Banks Keep Their Money?
As of 2016, most of the world's central bank money (about 75%) was held by central banks in four main places: China, the United States, Japan, and the eurozone (countries that use the Euro). Other countries like Brazil, Switzerland, Saudi Arabia, the U.K., India, and Russia each held a smaller but still significant amount. The remaining 107 central banks around the world held less than 13% of the total.
Images for kids
-
The European Central Bank building in Frankfurt.
-
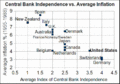
This chart shows that when a central bank is more independent (meaning it's less controlled by politicians), the country often has lower inflation (prices don't go up as fast). This research suggests that politicians might be tempted to create too much money if they had full control, which can lead to higher inflation.
-
The Bank of England, which was started in 1694.
-
The Bank of Finland in Helsinki.
-
The main office of the People's Bank of China (started in 1948) in Beijing.
See also
 In Spanish: Banco central para niños
In Spanish: Banco central para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |