Cooperative banking facts for kids
Cooperative banking is a way of doing banking where the bank is owned by its customers. These banks offer services like taking deposits and giving out loans, just like regular banks. But the big difference is who owns and controls them.
Cooperative banking includes different types of financial groups. These are credit unions, mutual savings banks, building societies, and other cooperatives. They also include bigger groups that help cooperative businesses.
Contents
What are Cooperative Banks?
Cooperative Banks
Cooperative banks are special because their customers own them. They follow a rule called "one person, one vote." This means every customer has a say in how the bank is run, no matter how much money they have there.
These banks offer savings and loans to everyone, not just their owners. Some even trade in big financial markets. Sometimes, people who are not customers can also own parts of these banks, which means the customers might have less control. This makes them "semi-cooperative."
Cooperative banks often work together more closely than credit unions. Local branches might have their own leaders, but big decisions usually need approval from a main office.
Credit Unions
Credit unions help their members save money and get loans at fair rates. Members usually have something in common, like living in the same area, working for the same company, or having the same job. Credit unions usually get all their money from their members' deposits.
They are often smaller than other cooperative banks. In some places, they only give out small personal loans. In other places, they can give loans to farmers or for buying homes.
Land Development Banks
Land Development Banks (LDBs) are special banks that give out long-term loans. The first one started in India in 1920. These banks are also based on the cooperative idea. Their main goal is to help develop land, support farming, and increase food production. They give long-term loans directly to their members.
Building Societies
Building societies are found in places like Britain and Ireland. They are similar to credit unions because their members own them. However, their main purpose is to help members get mortgages (loans to buy homes).
Both people who borrow money and people who save money with a building society are members. They help decide how the society is run and choose its leaders. Building societies also offer other banking services like checking accounts and credit cards. The biggest building society in the world is Britain's Nationwide Building Society.
Other Types
There used to be many Mutual savings banks and mutual savings and loan associations. They were common in the 1800s and 1900s but are less common now.
Trustee savings banks are similar to other savings banks, but they are not cooperatives. They are controlled by special leaders called trustees, not by their customers.
Working Together Globally
There are important groups that bring cooperative banks together from different countries. The European Association of Co-operative Banks is one, and the International Cooperative Banking Association (ICBA) is another. They help cooperative banks work together around the world.
Cooperative Banking Around the World
Canada
In Canada, credit unions are the main type of cooperative banking. In 2012, there were 357 credit unions with over 5 million members. They had a lot of money in assets, showing how big they are.
The first credit union in North America was started in Quebec, Canada, in 1900 by Alphonse Desjardins. He wanted to help working people get financial protection.
United Kingdom
British building societies grew into banks that offer many services, with members having "one person, one vote" control. Many of them later became regular banks.
The Co-operative Group used to own The Co-operative Bank. Even though it had "Co-operative" in its name, the bank itself was not directly owned by its members. It was owned by a larger cooperative group. The Co-operative Group still has an insurance company that supports ethical investments.
Europe
Europe has many important cooperative banking systems. Some big ones include Crédit Agricole in France, Rabobank in the Netherlands, and the German Cooperative Financial Group in Germany.
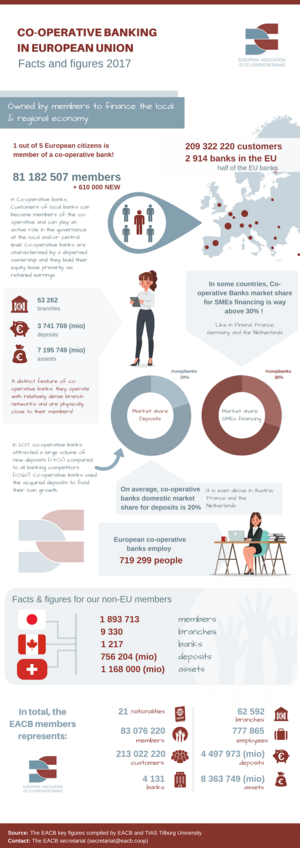
Cooperative banks that are part of the European Association of Co-operative Banks serve 130 million customers. They manage a lot of money and hold a big share of Europe's deposits.
In Italy, a rule in 2015 made some larger cooperative banks change into regular companies.
United States
Credit unions in the United States had over 96 million members in 2013. During the 2007–2008 financial crisis, credit unions failed much less often than other banks. They also helped small businesses a lot, increasing their loans while other banks decreased theirs.
People in the United States trust credit unions more than big banks. Small businesses are also much happier with credit unions.
India
Cooperative banks are very important in India, especially in rural areas. In cities, they mainly help small businesses and people who work for themselves. They are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India.
The first known cooperative credit union in India started in 1889. India's cooperative credit system has two main parts: short-term and long-term loans for farmers.
Israel
Ofek is a group that started in 2012. They wanted to create the first cooperative bank in Israel.
Microcredit and Microfinance
Microcredit and microfinance are newer ideas that often use a cooperative model. They focus on giving small loans to small businesses. In 2006, Muhammad Yunus, who started the Grameen Bank in Bangladesh, won the Nobel Peace Prize. He won it for his ideas about helping people by giving them very small loans when they can't get loans from regular banks.
However, cooperative banking is different from modern microfinance. In cooperative banking, members control the money. Modern microfinance often focuses on making a profit, which means the people who provide the loans have more control and can charge higher interest rates.
Cooperative banks are different because they get most of their money from local savings. Microfinance groups often rely on donations or loans from outside. This can lead to higher interest rates and short repayment times, which can make it hard for people with low incomes to save money or build wealth. Cooperative banking aims to help people earn, save, and grow their wealth.
List of Cooperative Banking Institutions
| Name | Country | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coop Bank Pertama | Malaysia | Islamic cooperative bank | First national cooperative bank in Malaysia, started in 1950. |
| Bank Rakyat | Malaysia | Islamic cooperative bank | Second national cooperative bank in Malaysia, founded in 1954. |
| Crédit agricole SA | France | Bank | Local banks are mostly owned by individuals. |
| Islami Co-operative Bank Ltd. | Bangladesh | Central Co-Operative Bank | First and largest Islamic cooperative bank in Bangladesh. |
| Crelan | Belgium | Bank | Independent since 2015. |
| DZ Bank | Germany | Bank | Owned by many German cooperative banks. |
| Caisse d'épargne | France | Bank | A group of savings banks. |
| Rabobank | Netherlands | Bank | A large credit union group. |
| Nationwide Building Society | UK | Building society | The world's largest building society. |
| Bangladesh Samabaya Bank LTD. | Bangladesh | Bank | The largest cooperative bank in Bangladesh. |
| Groupe Banque Populaire | France | Bank | A group of popular banks. |
| Desjardins Group | Canada | Credit union federation | A leading bank in Quebec. |
| Raiffeisen Bank International | Austria | Bank | Owned by regional Raiffeisen Banks. |
| Nonghyup | South Korea | Banking division of agricultural cooperative | A large agricultural cooperative bank. |
| ICCREA Banca | Italy | Bank | Owned by credit unions in Italy. |
| Cassa Centrale Banca – Credito Cooperativo del Nord Est | Italy | Bank | Owned by credit unions in Northern Italy. |
| Raiffeisen Landesbank Südtirol | Italy | Bank | Owned by credit unions in South Tyrol. |
| Raiffeisen (Switzerland) | Switzerland | Credit union federation | A group of credit unions. |
| Banco Cooperativo Español and Caja Rural | Spain | Bank | A group of cooperative banks. |
| OP Financial Group | Finland | Bank | A large financial group in Finland. |
| POP Pankki | Finland | Credit union federation | A group of credit unions. |
| S-Bank | Finland | Cooperative supermarket bank | Belongs to a retail cooperative group. |
| Bank Australia | Australia | Bank | Australia's first customer-owned bank. |
| Navy Federal Credit Union | US | Credit union | A large credit union. |
| Shared Interest | UK | Cooperative lending society | Provides money for fair trade. |
| GLS Bank | Germany | Bank | A cooperative bank. |
| The Cooperative Bank | New Zealand | Bank | A customer-owned bank. |
| Banco Credicoop | Argentina | Bank | A cooperative bank. |
| Laboral Kutxa | Spain | Credit union | Part of a larger cooperative group. |
How Cooperative Banks Help
During Tough Times
A report in 2013 found that cooperative banks did better than other banks during the 2007–2008 financial crisis. Even though they made up a big part of the European banking world, they had fewer problems and losses. They also lent more money to small and medium-sized businesses during this time.
In the US, credit unions failed much less often than other banks during the crisis. They also greatly increased their loans to small businesses when other banks were lending less.
See also
- Building society
- Credit union
- Mutual savings bank
- Rotating savings and credit association
- Savings and loan association