Disease facts for kids
A disease or medical condition is when your body or mind isn't working right. Diseases can make you feel pain, stop parts of your body from working properly, or even cause death. The word disease can mean many things, including:
- Injuries to parts of the body
- Losing normal abilities
- Certain health problems or syndromes
- Infections from tiny microorganisms
- Feeling sick, like having pain or a fever (these are called symptoms)
- Unusual shapes of body parts
Contents
What Causes Diseases?
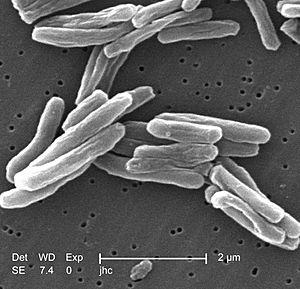
Many things can cause a disease. Sometimes, germs get into our bodies through food, water, or even the air we breathe. You can get infected by tiny living things like bacteria, viruses, or fungus.
Eating bad or old foods can also make you sick because they might have small germs that cause diseases. Sometimes these germs make chemicals or toxins (poisons) that cause the illness.
How Germs Spread
One common cause of disease is poor sanitation and not having clean water. Some serious diseases, like malaria in tropical parts of the world, are spread by mosquitoes. Animals that spread diseases are called vectors. Other vectors include snails, ticks, and fleas.
Genetic and Environmental Causes
Some people are born with 'genetic diseases'. These happen because of a small change or mutation in a person's DNA (the instructions for your body). Cancer is an example of a disease that can be caused by a mutation.
Living or working in an unhealthy environment can also cause diseases. Diseases are also more common as people get older.
How Doctors Treat Diseases
Some diseases can be helped with medicine. For example, Infections can often be cured by antibiotics. However, antibiotics sometimes stop working against certain germs, which is a problem.
Some diseases might need surgery to fix them. But not every disease can be helped with medicine or surgery. Some diseases, called chronic (long-lasting) diseases, need to be treated throughout a person's whole life. An example of a chronic disease is diabetes mellitus. Diabetes can be managed and made better, but it cannot yet be totally cured.
People who usually treat diseases are called doctors or physicians.
How to Prevent Diseases
Some common or very serious diseases are tested for even in people who don't show any symptoms. If these diseases are found early, they can be treated before they cause big problems.
Early Detection
For example, doctors check women for cervical cancer with a test called a pap smear. If cervical cancer is found early, it can often be cured. If it's found later, it usually causes death.
Immunization and Vaccines
Another way to prevent diseases is through immunization. This means getting your body ready to fight a disease. Your body has its own defense system against diseases called the immune system.
A special thing about the immune system is that it can remember some diseases. If you get sick and then get better, your immune system will make special substances called antibodies. These antibodies fight the disease if it tries to come back.
Each antibody is specific to a particular disease or antigen (the part of the germ that triggers the immune system). For example, measles is caused by a virus. A child who has never had measles can be given a milder form of the virus (a vaccine). This causes their immune system to make antibodies against the virus. If this person is exposed to the real measles virus later, their immune system will remember it and fight it off.
General Prevention Tips
For general prevention to work well:
- The disease must be found and stopped early.
- The disease should be common or easy to recognize.
- The test for the disease should be easy, reliable, and safe.
- People in the community should be trained to recognize common symptoms of some diseases.
- The treatment for the disease should be safe and easy for people to get.
Studying Disease Causes (Epidemiology)

Epidemiology is the study of what causes diseases and how they spread. Some diseases are more common in groups of people who share certain things, like where they come from, their social background, their diet, or their nationality.
Without good epidemiological research, some diseases can be hard to track and identify correctly. Sometimes, one disease might even be mistaken for another. This is why epidemiology is a huge part of understanding how to protect ourselves from viruses, toxins, and bacteria.
Related Pages
See also
In Spanish: Enfermedad para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |