Antibiotic resistance facts for kids
Antibiotics are special medicines that can kill tiny living things called microorganisms, like bacteria, or stop them from growing. But over time, these tiny organisms can learn to fight back against the antibiotics. This is called antibiotic resistance. It's a really big problem for modern surgery and medicine, and it's also a great example of how evolution works in real life.
Antibiotic resistance is spreading much faster than scientists expected. For a long time, people thought it wouldn't be a problem as long as new medicines kept being discovered. However, no completely new types of antibiotics have been found since the 1980s! We now know that bacteria have a special way, called an integron, that helps them share resistance quickly.
Contents
How Bacteria Become Resistant
A clear example of natural selection happening is how bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. Since penicillin was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming, antibiotics have been used to fight diseases caused by bacteria.
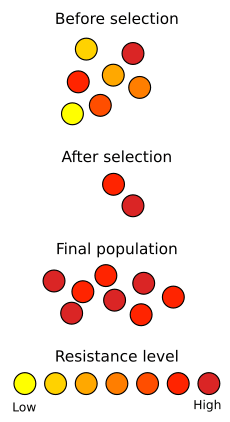
Think of a huge group of bacteria. Even though there are many of them, they are not all exactly the same. Some have tiny changes in their genetic material, called mutations. When an antibiotic is used, most bacteria die quickly. But some might have mutations that make them a little bit stronger against the medicine. If the antibiotic treatment is stopped too soon, these stronger bacteria survive. This process, where the weaker ones are removed and the stronger ones live on, is natural selection. The surviving bacteria then multiply, and their offspring inherit the resistance, making the next generation harder to kill.
A Warning from the Past
In 1945, when he received his Nobel Prize, Alexander Fleming gave a warning. He said it was easy to make microbes resistant to penicillin in a lab by using too little of the medicine. He also said it could happen in the human body. He worried that if penicillin became easily available, people might not use enough of it. This would allow the microbes to become resistant.
Before antibiotics, many infections were deadly. Maclyn McCarty, another scientist, explained that there were many infections from which no one ever recovered before these powerful medicines were found.
Why Resistance Matters for Health
Any surgery that involves cutting open the body carries a big risk of infection. Antibiotics given before and after surgery help surgeons perform operations that would have been too dangerous before. For example, open-heart surgery would be much riskier without effective antibiotics.
Treatments for cancer, like chemotherapy and radiotherapy, can weaken a person's immune system. Doctors give antibiotics to these patients to help protect them from infections. Also, people who receive organ transplants need medicines to stop their immune system from attacking the new organ. This also weakens their defenses, so antibiotics are needed to keep them safe. Without working antibiotics, these patients could die from infections their bodies can no longer fight.
Professor Richard James from the University of Nottingham said, "It's a pretty grim future, I think a lot of major surgery would be seriously threatened."
Other medical treatments are also at risk. For example, the number of cases where bacteria are resistant to carbapenems, which are very strong antibiotics, has grown a lot. In 2003, there were only a few cases, but by 2010, there were over 300. Some bacteria are even resistant to all known antibiotics.
Many infections that were almost gone are now coming back. Around the world, tuberculosis (TB) that is resistant to many drugs is a growing problem. Only a few medicines still work against it.
Infections that affect older people in hospitals are a big worry. In the UK, a common problem is bacteria like E. coli that live in the gut. These are now the most common infections patients get in hospitals, and they are becoming more and more resistant to antibiotics.
Official Warnings
The UK government has warned that "the number of infections complicated by antimicrobial resistance could increase markedly over the next 20 years." They also said, "Without effective antibiotics, even minor surgery and routine operations could become high-risk procedures, leading to increased duration of illness and ultimately premature mortality."
The WHO has also given similar warnings. They stated that using and misusing antibiotics for the past 70 years has led to a steady increase in resistant microorganisms. This causes more deaths, suffering, and higher healthcare costs. They noted that resistance to first-line drugs for many common diseases ranges from almost none to nearly 100%. This means that in some cases, even second and third-line medicines are not working well.
Examples of Resistant Bacteria
MRSA
If bacteria are exposed to an antibiotic many times over a long period, a group of bacteria that are resistant to that antibiotic will appear. This leads to a kind of "arms race" between bacteria and medicine. Bacteria keep developing ways to resist antibiotics, while scientists try to create new antibiotics to kill them. Doctors might use different, stronger antibiotics. However, new types of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) have appeared that are resistant even to these stronger drugs.
Tuberculosis (TB)
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease caused by bacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It often attacks the lungs, but it can affect other parts of the body too. The bacteria can spread through the air from one person to another. Experts believe that about one-third of the world population is infected with M. tuberculosis. New infections happen very often.
TB that is resistant to drugs is a big health problem in many countries. It takes longer to treat and needs more expensive medicines. MDR-TB means the bacteria are resistant to the two most important first-line TB drugs. Extensively drug-resistant TB is even worse, as it's resistant to three or more of the second-line drugs.
A type of TB that is totally resistant to all currently used drugs was first seen in Italy in 2003. It was widely reported in 2012.
A New Hope?
The first new antibiotic in forty years has been discovered! It's called teixobactin, and researchers are very hopeful about it. It still needs to be developed and tested, so it will be some time before doctors can use it. It only works on certain types of bacteria called gram-positive bacteria. However, this group includes important ones like MRSA and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Images for kids
-
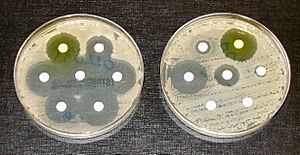
Antibiotic resistance tests: Bacteria are spread on dishes with white disks, each having a different antibiotic. Clear rings, like those on the left, show that bacteria have not grown—meaning these bacteria are not resistant. The bacteria on the right are fully resistant to all but two of the seven antibiotics tested.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: Small paper discs with an antibiotic have been placed on a dish where bacteria are growing. Bacteria cannot grow around antibiotics they are sensitive to.
See also
 In Spanish: Resistencia a antibióticos para niños
In Spanish: Resistencia a antibióticos para niños