Obesity facts for kids
Obesity means being much too heavy for your height, which can affect your health. It's also known as being very overweight or fat. Doctors consider obesity a disease, and it has become a widespread health issue.
To find out if someone is overweight, doctors often use something called the body mass index (BMI). You calculate BMI by taking a person's weight (in kilograms) and dividing it by their height (in meters) multiplied by itself. This measurement is mainly for adults who are fully grown. For children, doctors use special growth charts to check for obesity.
A BMI between 20 and 25 is usually seen as normal. If a person's BMI is 25 or more, they are considered overweight. If it's 30 or higher, they are considered obese. A BMI of 35 or more means someone is severely obese. Generally, BMI is a good way to measure how much a person weighs compared to their height. However, it might not be accurate for very athletic people. This is because muscles weigh more than fat, so a muscular person could have a high BMI even if they are very healthy.
Contents
What Causes Obesity?
The most common reason for obesity is taking in more calories than your body uses. This means eating more food than your body needs for energy. Many other things can also lead to obesity:
- Poor nutrition: Not eating enough healthy foods.
- Hormonal problems: Issues with body chemicals, like those caused by hypothyroidism.
- Problems with your metabolism: How your body turns food into energy. An example is the yo-yo effect, where weight goes up and down.
- Eating disorders: Such as binge eating disorder, where a person eats a lot of food quickly.
- Psychological problems: Like depression.
- Not getting enough sleep or having trouble sleeping.
- Not getting enough exercise.
Your genes can also play a part in obesity. For example, a hormone called leptin is linked to how your body stores fat.
Health Problems Linked to Obesity
Being obese can lead to many health problems. One example is Type 2 diabetes. A woman with a BMI higher than 35 is much more likely to get diabetes. Studies have shown that people with very high BMIs (40 to 50) are much more likely to die from diabetes than people with normal BMIs.
Obese women are also more likely to have an unhealthy baby. The risk of health problems also depends on where extra fat is stored. Fat around the belly, known as abdominal obesity, is especially risky.
Some people believe that the health risks of obesity are sometimes overstated. For example, a review of scientific papers in 2013 found that a mild form of obesity (BMI 30-34.9) might not increase deaths. However, more severe obesity (BMI 35 and above) is linked to much higher death rates.
Sometimes, people who are obese can still be metabolically healthy. This means their body processes food normally, and they might not have a higher risk of heart disease or death than non-obese people who are also metabolically healthy.
There's also something called the obesity paradox. This means that while obesity can increase the chance of getting heart disease, obese people who already have heart disease might be less likely to die from it over a certain period. This has also been seen in patients with stroke, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
How Is Obesity Treated?
Scientists are still working to find the best ways to treat obesity that everyone can use. It's often thought that people who lose weight will gain it back, but newer research shows that many people can keep the weight off.
The most common way to treat obesity is through diet and exercise. Eating healthier foods and being more active can help people lose weight and keep it off.
Surgery can also be used to treat severe obesity. Gastric bypass is a common weight loss surgery. It makes the stomach smaller, so a person feels full after eating less food. It also helps the body absorb fewer calories. This surgery is usually for people who are very obese.
Some people believe obesity should not be treated, but most medical research disagrees with this idea.
Weight loss medicines can help by making people feel less hungry or by helping their bodies absorb less energy from food. The only weight loss medicine approved by the FDA for long-term use is orlistat. Other medicines have not been approved because they can have side effects.
How Society Views Obesity
In Western countries, people sometimes link obesity with negative ideas like laziness or being unhealthy. These views are becoming more common. In the United States, it's legal to treat someone differently because of their weight. The fat acceptance movement argues that this is wrong and is a type of prejudice called fatphobia.
However, in some cultures, obesity is seen as a good thing. It can be linked to wealth, beauty, and being able to have children. But as Western ideas spread, some non-Western cultures are also starting to have more negative views about obesity.
Related pages
- Abdominal obesity
- Hypertrophy
- Healthy lifestyle
- Bariatrics (the part of medicine that deals with obesity)
Images for kids
-
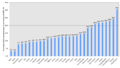
Percentage of the adult population with a BMI over 30, for the OECD countries
-
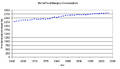
Obesity in developed countries is correlated with economic inequality.
-
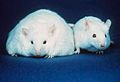
A comparison of a mouse unable to produce leptin thus resulting in obesity (left) and a normal mouse (right)
-
During the Middle Ages and the Renaissance obesity was often seen as a sign of wealth, and was relatively common among the elite: The Tuscan General Alessandro del Borro, attributed to Charles Mellin, 1645
-
United States President William Howard Taft was often ridiculed for being overweight.
See also
 In Spanish: Obesidad para niños
In Spanish: Obesidad para niños