Hypertrophy facts for kids
Hypertrophy is a scientific word that means an organ or tissue in your body gets bigger because its cells grow in size. Think of it like blowing up a balloon – the balloon itself gets larger because the air inside expands. In your body, the cells are like tiny balloons that get bigger.
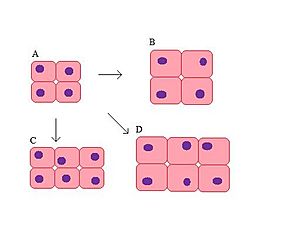
It's important to know the difference between hypertrophy and something called hyperplasia. With hyperplasia, the cells don't get bigger, but their number increases. Imagine having more balloons, but they stay the same size. Sometimes, hypertrophy and hyperplasia happen at the same time. For example, during pregnancy, a woman's uterus (womb) grows larger because its cells both increase in number and get bigger.
One of the most common ways you might see hypertrophy is when skeletal muscles (the muscles you use to move) grow larger. This often happens when people do strength training or bodybuilding.
Contents
What is Hypertrophy?
Hypertrophy happens when the individual cells that make up a tissue or organ become larger. This makes the whole tissue or organ grow in volume. It's a way your body adapts to different situations, like needing more strength or function.
How it Differs from Hyperplasia
It's easy to mix up hypertrophy and hyperplasia, but they are different.
- Hypertrophy: Cells get bigger in size.
- Hyperplasia: The number of cells increases, but their size stays about the same.
Even though they are different, these two processes often happen together. For example, when a woman is pregnant, her uterus grows a lot. This growth is due to both the cells getting larger (hypertrophy) and more cells being made (hyperplasia).
Why Do Cells Get Bigger?
Cells grow bigger in hypertrophy for different reasons. It can be a normal and healthy response, or it can be a sign of a problem.
Normal Growth (Physiological Hypertrophy)
Sometimes, hypertrophy is a normal and healthy process. This is called physiological hypertrophy.
- Muscle Growth: When you lift weights or do other strength exercises, your muscle cells work harder. To handle this extra work, they grow larger and stronger. This is why athletes and bodybuilders have big muscles.
- Heart Adaptation: An athlete's heart might also show some hypertrophy. Because they exercise a lot, their heart muscle cells grow slightly larger to pump blood more efficiently throughout the body.
Unhealthy Growth (Pathological Hypertrophy)
Hypertrophy can also happen when there's a problem in the body. This is called pathological hypertrophy.
- High Blood Pressure: If someone has high blood pressure for a long time, their heart has to work much harder to pump blood. This extra strain can cause the heart muscle cells to grow too large, which can lead to health problems over time.
- Organ Damage: Sometimes, if part of an organ is damaged, the remaining healthy cells might grow larger to try and make up for the lost function.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hipertrofia para niños
In Spanish: Hipertrofia para niños