Skeletal muscle facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Skeletal striated muscle |
|
|---|---|
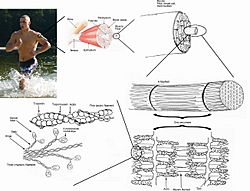 |
|
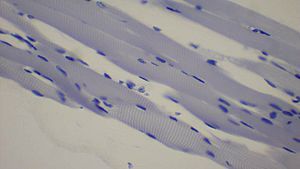
| A top-down view of skeletal muscle | |
| Latin | textus muscularis striatus skeletalis |
| Code | TH H2.00.05.2.00002 |
Skeletal muscle is a special type of muscle tissue that looks "striped" under a microscope. This is why it's called "striated" muscle. You can control these muscles with your mind, like when you decide to lift your arm or kick a ball. Most skeletal muscles are connected to your bones by strong, rope-like parts called tendons.
Your body has three main types of muscles. Skeletal muscle is one of them. The other two are cardiac muscle (which is in your heart) and smooth muscle (found in places like your stomach and intestines).
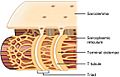
Skeletal muscles are made up of tiny individual muscle cells, also known as muscle fibres. These muscle fibres are the parts that do the work when your muscles contract, or shorten. Scientists know a lot about how they are built and how they work. They contract when they receive a signal, called a nerve impulse, from your brain.
Contents
What Are Skeletal Muscles?
Skeletal muscles are the muscles you use for all your movements, from walking and running to smiling and writing. They are called "skeletal" because they are usually attached to your skeleton (your bones).
These muscles are made of many long, thin cells called muscle fibres. These fibres are grouped together to form the muscle. When you want to move, your brain sends a message through your nerves to these muscle fibres, telling them to contract.
How Your Muscles Move
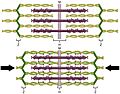
Inside each muscle fibre are even smaller parts called myofibrils. These myofibrils contain tiny protein threads called filaments. When your muscle gets a signal to contract, these filaments slide past each other. This action makes the muscle fibre shorter, which then makes the whole muscle contract. This is known as the "sliding filament model."
This amazing process allows you to pull, push, lift, and do all sorts of movements. Think about how your arm muscle shortens when you lift something heavy.
Fueling Your Muscles
Muscles need energy to work, just like a car needs fuel. This energy comes from a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Your body makes ATP mainly from the food you eat, especially sugars like glucose.
When you exercise, your muscles use up ATP very quickly. Your body has ways to make more ATP. For short, intense bursts of activity, muscles can use a stored energy source called creatine phosphate. For longer activities, your body breaks down glucose with oxygen to make a lot of ATP. This process happens in tiny powerhouses inside your cells called mitochondria.
Sometimes, during very hard exercise, your muscles might not get enough oxygen. When this happens, glucose is broken down differently, and a substance called lactic acid can build up. This can make your muscles feel tired or sore.
Keeping Your Muscles Strong
Regular exercise is important for keeping your skeletal muscles strong and healthy. Activities like jogging, swimming, and playing sports help your muscles grow and work better.
Sometimes, people can have conditions that affect their muscles. For example, muscular dystrophy is a group of diseases that cause muscles to become weak over time. Scientists are always learning more about these conditions to help people stay healthy.
Images for kids
-
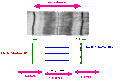
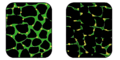
Structure of muscle fibre showing a sarcomere under electron microscope with schematic explanation.
-
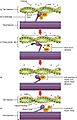
(a) Some ATP is stored in a resting muscle. As contraction starts, it is used up in seconds. More ATP is generated from creatine phosphate for about 15 seconds. (b) Each glucose molecule produces two ATP and two molecules of pyruvic acid, which can be used in aerobic respiration or converted to lactic acid. If oxygen is not available, pyruvic acid is converted to lactic acid, which may contribute to muscle fatigue. This occurs during strenuous exercise when high amounts of energy are needed but oxygen cannot be sufficiently delivered to muscle. (c) Aerobic respiration is the breakdown of glucose in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Approximately 95 percent of the ATP required for resting or moderately active muscles is provided by aerobic respiration, which takes place in mitochondria.
-
Jogging is one form of aerobic exercise.
-
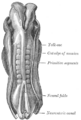
Human embryo showing somites labelled as primitive segments.
See also
 In Spanish: Músculo esquelético para niños
In Spanish: Músculo esquelético para niños