Smooth muscle facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Smooth muscle tissues |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
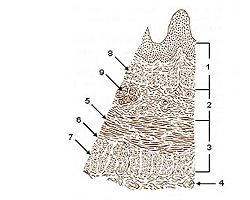
| Layers of Esophageal Wall: | |
| Latin | textus muscularis levis; textus muscularis nonstriatus |
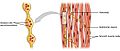
Smooth muscle is a special kind of muscle in your body that you don't have to think about to make it work. It's called "involuntary" because it moves all by itself! Unlike the muscles you use to lift your arm (which are "striated" or "skeletal" muscles), smooth muscle doesn't have stripes when you look at it closely.
These muscles are found in the walls of many hollow organs inside you. Think of your stomach, intestines, and urinary bladder. They also line the tubes and passageways in your body, like your arteries and veins (which carry blood), and the tubes in your breathing, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Smooth muscles do many important jobs. For example, they help push food through your digestive system. They also control how much blood flows through your blood vessels.
Contents
Where You Find Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is super important because it's in so many parts of your body, doing jobs you don't even notice!
In Your Organs
You can find smooth muscle in the walls of many of your internal organs. It helps these organs do their jobs.
- Digestive System: In your stomach and intestines, smooth muscle helps mix food and push it along. This is how your body digests what you eat.
- Urinary System: Your urinary bladder has smooth muscle that helps it hold urine and then push it out when you need to go to the bathroom.
- Reproductive System: In the uterus, smooth muscle helps with important processes like childbirth.
In Your Passageways
Smooth muscle also lines the tubes and pathways throughout your body.
- Blood Vessels: Your arteries and veins have smooth muscle in their walls. This muscle helps control your blood pressure by making the vessels wider or narrower.
- Breathing Tubes: In your lungs and airways, smooth muscle helps control how much air can pass through.
- Eyes: In your eyes, smooth muscle helps change the size of your iris (the colored part) to let in more or less light. It also helps change the shape of your lens so you can focus on things far away or up close.
- Skin: Have you ever gotten goosebumps when you're cold or scared? That's smooth muscle working! Tiny smooth muscles in your skin pull on your hair follicles, making your hairs stand up.
How Smooth Muscle Works
Smooth muscle works differently from the muscles you control. It gets signals from your nervous system that tell it what to do without you thinking about it. This is why it's called "involuntary."
Sometimes, a whole group of smooth muscle cells works together like one big team. This is called "single-unit" smooth muscle. When one cell gets a signal, the signal quickly spreads to all the cells around it, and they all contract at the same time. This is useful for organs like the stomach, where a big push is needed.
Other times, smooth muscle cells work more independently. This is called "multiunit" smooth muscle. Each cell gets its own signal, allowing for more precise and fine-tuned movements. This type is found in places like your eyes, where very exact movements are needed.
Smooth muscle is amazing because it can stay contracted for a long time without getting tired, which is perfect for jobs like keeping blood flowing or maintaining blood pressure.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Músculo liso para niños
In Spanish: Músculo liso para niños