Food security facts for kids
Food security means that people always have access to enough safe, healthy, and affordable food. When people are "food secure," they don't have to worry about going hungry or not knowing where their next meal will come from. It's about having a steady supply of good food to live an active and healthy life.
The opposite is food insecurity, which is when people aren't sure if they will have enough food. People who are food insecure do not live in hunger or fear of starvation. Food security also means being able to handle future problems that might disrupt the food supply, such as droughts, floods, wars, or economic troubles.
The idea of food security is built on six main ideas: availability, access, utilization, stability, agency (the power to make your own choices), and sustainability (protecting resources for the future). These ideas are also part of the right to food, which is a basic human right.
Contents
What is Food Security?
The World Food Summit in 1996 described food security as a situation where "all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food." This means everyone should be able to get the food they need to be healthy and active.
On the other hand, food insecurity is when people have "limited or uncertain availability" of healthy and safe food. This definition comes from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). It means people might not know how they will get their next meal.
Food insecurity can be temporary, for example, if someone loses their job. Or it can be long-term (chronic), where a household is always at risk of not having enough food.
The Four Pillars of Food Security
To understand food security better, experts talk about four "pillars" or main ideas. All four must be strong for people to be truly food secure.
1. Availability
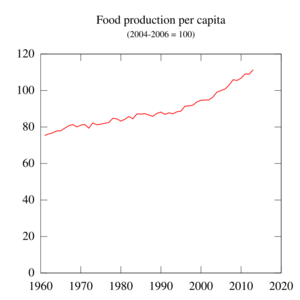
This is about the supply of food. Is there enough food being grown, produced, and sold in an area? This depends on things like farming, fishing, and how food is moved from farms to stores. A country doesn't have to grow all its own food to be food secure; it can also import food from other places, like Japan and Singapore do.
2. Access

This pillar is about whether people can actually get the food that is available. Do they have enough money to buy it? Do they have land to grow their own? Even if a country has a lot of food, poverty can stop people from being able to access it. A family's income and resources are key to having good access to food.
3. Utilization
Utilization means a person's body can use the food properly. This involves eating a healthy and balanced diet. It also means having clean water, good sanitation, and healthcare, so the body can absorb all the nutrients from the food without getting sick from diseases. Knowing how to prepare and cook food safely is also part of utilization.
4. Stability
Stability means having access to food all the time. People shouldn't have to worry about losing their food source because of a sudden problem like a drought, a war, or losing a job. Food security needs to be reliable day after day, not just for a short time.
What Causes Food Insecurity?
Many things can cause food insecurity and make it hard for people to get enough to eat.
High Food Prices and Conflict
When food becomes too expensive, poor families can't afford it. Wars and conflicts are also major causes. They can destroy farms, stop food from being delivered, and force people to leave their homes. The war in Ukraine, for example, disrupted the supply of wheat and other foods to many countries around the world.
Climate Change and Environmental Problems
Climate change leads to more extreme weather like droughts and floods. These events can ruin crops and make it very difficult to grow food. Problems like land degradation (when soil becomes unhealthy) and water scarcity (not enough water) also make farming harder. Many farms in places like Sub-Saharan Africa are at risk because of these issues.
Agricultural Diseases
Diseases that affect crops or farm animals can wipe out a food source for a whole region. For example, a disease called Ug99 affects wheat, which is a major food for millions of people. In 2025, an Avian Flu outbreak in the U.S. caused egg prices to rise sharply.
Food Loss and Waste
About one-third of all food produced in the world is lost or wasted. This can happen on the farm, during transport, in stores, or in our homes. Reducing food loss and waste could make more food available for everyone.
What Happens When People Are Food Insecure?
Food insecurity has serious effects on people and communities.
Hunger and Famines
The most direct effect of food insecurity is hunger. When it is very widespread and severe, it can lead to a famine, where many people die from lack of food.
Health Problems and Stunting
Not having enough healthy food, especially in childhood, can cause serious health issues. One major problem is stunted growth or stunting. This is when a child is too short for their age because they didn't get enough nutrients to grow properly. This can also affect their brain development and ability to learn. In 2020, about 149 million children under five were stunted.
Mental and Social Problems
Food insecurity is also linked to mental health problems like depression and anxiety. Hunger can make it hard for children to do well in school and for adults to work. This can trap families in a cycle of poverty. In desperate situations, people may be forced to do risky things to get money for food.
Who Is Most Affected by Food Insecurity?
While anyone can experience food insecurity, some groups are more vulnerable.
Children
Children need good nutrition to grow and develop. Food insecurity can harm their physical and mental growth for the rest of their lives. Households with children are more likely to be food insecure.
Women
Globally, women and girls often have a harder time getting enough food than men. According to the United Nations, the gap between men and women facing food insecurity has been growing. This is often due to gender inequality, which can mean they have less money, less control over land, and are expected to eat last or least in the family.
Racial and Ethnic Groups
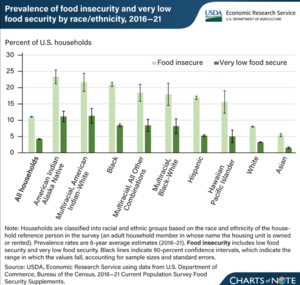
In many countries, certain racial and ethnic groups face higher rates of food insecurity. For example, a 2024 study in the United States found that households led by Black, Hispanic, and Native American individuals were much more likely to be food insecure than households led by White or Asian individuals.
How Can We Improve Food Security?
Many organizations and governments are working to solve food insecurity. Here are some of the main approaches.
Helping Farmers and Improving Agriculture
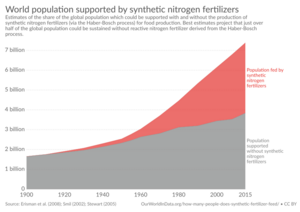
One of the best ways to fight hunger is to help farmers, especially small-scale farmers in poor countries, grow more food. This can be done by providing better seeds, tools, and training. Improving irrigation so crops have enough water is also very important.
Short-Term and Long-Term Aid
Organizations like the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Food Programme (WFP) use a "twin track" approach.
- Short-term help: In emergencies, they provide food aid, cash, or vouchers so people can get food right away.
- Long-term solutions: They also work on long-term projects, like building better roads and markets, to help communities become self-reliant.
Using New Technology
Scientists are developing new ways to grow food that use less water and land, such as vertical farming. There is also research into alternative food sources, like protein from insects or algae, which could help feed a growing world population.
Food Security Around the World
Food insecurity is a global problem, but it affects countries in different ways.
- Afghanistan: Following years of conflict and economic problems, more than half of the population faced severe food shortages in 2021. The country is experiencing a widespread hunger crisis.
- Canada: Even in a wealthy country like Canada, many people are food insecure. In 2018, the rate was especially high in the northern territory of Nunavut, where 57% of households were affected.
- Singapore: Singapore is a rich country that imports about 90% of its food. It is considered one of the most food-secure nations because it can afford to buy food. However, it is working on growing more of its own food through high-tech farming to be less dependent on other countries.
- United States: The U.S. is one of the world's largest food producers, but millions of Americans are food insecure. In 2022, about 1 in 8 households faced food insecurity.
See also
- Agricultural economics
- Food price crisis
- Food vs. fuel
- Integrated Food Security Phase Classification
- Sustainable Development Goal 2
- Theories of famines