2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Russo-Ukrainian War (outline) | |||||||
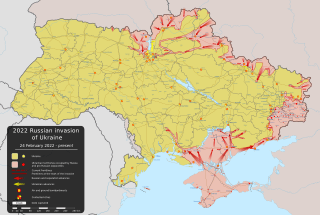 Military situation as of 31 October 2025 Controlled by Ukraine Controlled by Russia (Detailed map) |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Supported by: |
|||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Order of battle | Order of battle | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| Pre-invasion: 169,000–190,000 (including military, paramilitary, and 34,000 separatist militias) Since September 2022: + 300,000 mobilized + 50,000 mercenaries (including Wagner Group) |
Pre-invasion: 196,600 military 102,000 paramilitary In July 2022: 700,000 (active strength) |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Reports vary widely, see § Casualties for details. | |||||||
On February 24, 2022, Russia started a large-scale invasion of Ukraine. This invasion has caused many deaths on both sides. It is part of the larger Russo-Ukrainian War that began in 2014. The 2022 invasion followed a period of high tension between the two countries. Before the invasion, Russia supported two regions in eastern Ukraine, the Donetsk People's Republic and the Luhansk People's Republic.
More Russian soldiers moved into the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine on February 21, 2022. Many countries around the world strongly criticized this invasion. In Russia, groups against the war held protests, and many of these protesters were arrested.
Contents
Start of the Invasion
Around 6:00 AM Moscow time, Russian President Vladimir Putin announced a military operation in eastern Ukraine. Minutes later, missile attacks began in many parts of the country, including the capital city, Kyiv. The Ukrainian Border Service reported that its border posts with Russia and Belarus were attacked.
Explosions were heard in Kyiv, Kharkiv, Odessa, and the Donbas soon after Putin's announcement. Ukrainian officials said that Russia landed soldiers in Odessa and Mariupol. They also launched missiles at airfields, military centers, and supply depots in Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Dnipro. This was the largest attack by one country against another in Europe since World War II.
President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine declared martial law, which means the military takes control during an emergency. He then ordered the Ukrainian Army to fight back against the Russian forces.
Key Events in February 2022
On February 24, the Ukrainian government reported that Russia took control of Chernobyl and Pripyat. The US government said that Russian soldiers were holding the workers of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant captive. Later that day, Russian forces captured Snake Island after a sea and air attack. The thirteen border guards on the island were first thought to have died after refusing to surrender. President Zelenskyy announced they would receive the highest honor. However, it was later found that the border guards were alive and had been captured.
On February 25, as Russian soldiers got closer to Kyiv, Zelenskyy asked residents to make Molotov cocktails to defend their city. Meanwhile, Putin called on the Ukrainian military to overthrow their government. Ukraine gave 18,000 guns to Kyiv residents who wanted to fight. Some Russian soldiers did enter northern Kyiv.
On February 26, heavy fighting happened south of Kyiv, near the city of Vasylkiv and its air base. A Ukrainian fighter jet shot down a Russian transport plane carrying paratroopers near Vasylkiv. Hundreds of deaths were reported in Kyiv during this battle. Russia also claimed to have captured Melitopol, near the Sea of Azov.
On February 27, President Putin ordered Russia's nuclear forces to be on "special alert" because of "aggressive statements" from NATO. That same day, President Zelenskyy announced that Ukrainian and Russian officials had agreed to meet. A Russian airstrike also killed over 70 Ukrainian soldiers at a military base in Okhtyrka. Russian soldiers have been accused of actions that are against the rules of war, like harming civilians and using certain types of bombs on them.
Key Events in March
On March 1, Ukrainian sources said Belarus joined the invasion, sending soldiers to the Chernihiv region. Belarus denied this. On the same day, there was a rocket attack on Kyiv, hitting near the Kyiv Holocaust site. The next day, Russia claimed to have captured its first large city, the Black Sea port of Kherson. Fighting became more intense in many parts of Ukraine, including civilian areas. The International Criminal Court also started an investigation into possible war crimes in Ukraine.
On March 3, Ukraine passed a law saying that captured Russian military equipment and tanks would not be taxed. The next day, Russian forces attacked the Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant. The main reactor was not hit, and no dangerous radiation escaped. That same day, many foreign news outlets, including the BBC and CNN, stopped reporting from Russia. This was because new laws threatened long jail terms for spreading "fake news" about the war.
On March 5, Russia announced a temporary ceasefire to let civilians leave Mariupol and Volnovakha. The next day, Vinnytsia International Airport was destroyed by Russian missiles. President Zelenskyy asked for a no-fly zone over Ukraine to stop future attacks.
On March 7, Ukraine rejected Russia's offer to open safe passages for refugees if they could only go to Belarus or Russia.
On March 13, 30 Russian missiles hit the Yavoriv military base, which was used for NATO training and was close to the border with Poland. This attack killed 35 people and injured 134 others.
On March 24, NATO announced that four new groups of soldiers, totaling 40,000, would be sent to Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, and Slovakia. They also prepared for possible chemical, biological, or nuclear threats.
On March 29, Russia's deputy defense minister said that Moscow decided to reduce military activity near Kyiv and Chernihiv. This was to build trust for future peace talks with Ukraine.
Key Events in April
On April 2, Russia said it would not work with Western countries on the International Space Station until all "illegal sanctions" were removed. The next day, Ukraine accused Russia and Putin of war crimes because of civilian killings, such as the Bucha massacre. U.S. President Joe Biden called for Putin to be tried for war crimes. On April 7, Russia was suspended from the United Nations Council on Human Rights after a vote supported by 97 nations.
On April 8, Russia attacked the Kramatorsk train station with missiles, killing many civilians, including children, who were trying to leave. On April 13, the Russian flagship cruiser Moskva sank after an explosion off the Ukrainian coast. This was the largest naval ship to be sunk since World War II.
On April 19, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov announced that Russia's military operation had entered a new phase, focusing on the entire front line of Eastern Ukraine. The city of Kreminna was reportedly the first to be captured in this new phase.
Key Events in May
On May 2, Russia announced it might leave the International Space Station in two years because of the economic sanctions placed on the country due to the invasion. On May 14, Russian forces withdrew from Ukraine's second-largest city, Kharkiv, in the north-east.
On May 16, the Siege of Mariupol ended with a Russian victory as Ukrainian soldiers were evacuated from Mariupol.
Key Events in June
The Battle of Sievierodonetsk was ongoing in the first week of June.
On June 27, the Russian Armed Forces fired missiles at a mall in Kremenchuk, Ukraine. This attack killed sixteen people and injured over 50 others.
Key Events in July
On July 3, Russia and the Luhansk People's Republic took control of the entire Luhansk Oblast after capturing Lysychansk. On July 14, a Russian missile attacked Vinnytsia in central Ukraine. This attack killed at least 22 people, including 3 children, and injured at least 100 others.
Key Events in August
According to the Kyiv School of Economics, the conflict has caused $113.5 billion in damages and destruction in Ukraine. Transportation and housing were the main areas affected.
Key Events in September
On September 30, 2022, Vladimir Putin announced that Russia was taking over Ukraine's Donetsk, Luhansk, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia regions. Ukraine, the United States, the European Union, and the United Nations all strongly disagreed with this action.
Key Events in October
On October 8, the Crimean Bridge was partly damaged due to an explosion. Russia blamed Ukraine for the blast and launched missile attacks against Ukrainian civilian areas in return.
Key Events in November
On November 9, Russian troops began to leave Kherson, the only regional capital they had captured since the invasion started. Ukrainian forces then recaptured the city two days later, on November 11.
Key Events in December
In early December, heavy fighting was still happening near Bakhmut and south of Bakhmut.
Key Events in January 2023
The British government announced on January 14, 2023, that Ukraine would receive 14 Challenger 2 tanks. These were the first Western main battle tanks given to Ukraine.
On January 25, 2023, the German government said that Germany would send Leopard 2 tanks to Ukraine. They also allowed other countries to send their Leopard 2 tanks. Later that day, the United States government announced that 31 Abrams tanks would be sent to Ukraine.
Key Events in February 2023
Poland's prime minister said that Poland could give some F-16 fighter jets to Ukraine. This could happen if all NATO member countries agreed.
Worldwide Reactions
U.S. President Joe Biden announced sanctions on Russian banks.
On February 24, 2022, the Prime Minister of Australia Scott Morrison announced travel bans and financial sanctions against eight members of Russia's national security council.
The United Kingdom, United Nations, France, Germany, Spain, Japan, Sweden, Turkey, Norway, Canada, and Italy all spoke out against the invasion.
On February 24, 2022, President of the European Commission Ursula von der Leyen said the European Union would take "massive" actions. These actions would target technology, Russian banks, and Russian assets. That same day, President Putin said Western countries that took part in these actions "will face consequences."
On February 26, the European Union, the United States, and their allies supported removing Russian banks from the SWIFT payment system. SWIFT is a global system for sending money between banks. The next day, many European nations announced a ban on Russian flights in their airspace.
On February 28, Switzerland, Monaco, Singapore, and South Korea put economic sanctions on Russia, like controlling exports and assets. These countries were once known for being neutral in global conflicts.
Tugan Sokhiev, a musical director, resigned from his job because he wanted to remain neutral in the conflict.
In response to the invasion, on May 15, 2022, President of Finland Sauli Niinistö said Finland would apply to join NATO. The next day, Sweden also confirmed it would apply to join NATO, after many years of being neutral.
Chinese authorities stopped Russian Boeing and Airbus planes, owned by foreign companies, from flying through or landing in China. This rule started in May 2022.
About 60 military recruitment offices in Russia have been attacked as of January 2023. Some were set on fire, sometimes using Molotov cocktails.
Sanctions on Russia
The EU put sanctions on Putin and the Russian foreign minister, Sergey Lavrov, as of March 3, 2022.
The AIIB stopped giving loans to Russia and Belarus, according to media reports on March 4, 2022.
EU countries have closed their airspace to Russian aircraft. On June 6, 2022, Montenegro and North Macedonia closed their airspace for a plane carrying Russia's foreign minister to Serbia.
Other Protests
People have held pro-Ukrainian protests outside many Ukrainian and Russian embassies. There have been many protests in countries like Armenia, Australia, Bulgaria, Belgium, Canada, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Japan, Kazakhstan, Moldova, the Netherlands, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, Taiwan, Turkey, the UK, and the US. In the Czech Republic, about 3,000 people protested in Wenceslas Square in Prague.
On March 14, 2022, a woman held a sign with an anti-war message on a news program on Channel One Russia during prime time. The sign said: "NO WAR. Stop the war. Do not believe propaganda they tell you lies here." It also said "Russians against war." Marina Ovsyannikova was arrested by police. She received a fine the next day and was then released from jail.
Businesses React
On March 3, 2022, the board of directors for Lukoil, a large oil company, said they supported an immediate stop to the armed conflict. On March 8, international brands like McDonald's, Coca-Cola, and Starbucks stopped sales in Russia because of the attacks on Ukraine.
The production of Lada cars was stopped in March 2022.
On May 16, 2022, McDonald's announced it would permanently close its fast food restaurants in Russia. They said this was due to the "humanitarian crisis" and the difficult situation caused by the invasion.
Foreign Soldiers Joining Ukrainian Forces
Yevhen Yenin, the First Deputy Minister of Internal Affairs for Ukraine, said that foreign soldiers who fight for the International Legion might be able to get Ukrainian citizenship. The news agency Ukrinform reported this in March 2022.
In March 2022, the Ukrainian Armed Forces showed the first picture of International Legion soldiers. The picture showed some of these soldiers in a trench on the edge of Kyiv.
As of the same month, foreigners are receiving military training at the Yavoriv military base.
Supplying Weapons and Military Equipment
The United States and European countries are sending supplies to an airport near the Ukraine border, but outside Ukraine. These supplies include anti-tank rockets, Stinger rockets (which can be fired from a soldier's shoulder to hit aircraft), armored vehicles, automatic weapons, ammunition, MREs (food for soldiers that doesn't need cooking), and fuel. It does not take long for these rockets to be moved into Ukraine.
- On March 3, 2022, a transport plane flew from Norway with 2,000 M72 anti-tank weapons. Each of these rocket launchers weighs about 2 or 3 kilograms.
- By January 4, 2023, 10,000 shells for howitzers were sent. These shells are 155mm wide.
Rebuilding Infrastructure
Norway's authorities are sending and paying for 10 bridges, according to media reports in December 2022.
Weapons Used
Ukraine has and uses:
- M777 howitzers (a type of large cannon)
- M982 Excalibur shells that can travel up to 40 kilometers and be guided after being fired.
- NASAMS air defense system.
- Phoenix Ghost, a type of drone that can explode, also called a loitering munition.
- M109 howitzer and shells with a range of 30 km.
- HIMARS (officially M142 HIMARS), a type of rocket launcher.
- M270, another multiple rocket launcher.
- Bayraktar TB2, a combat drone used for fighting.
- Javelin anti-tank missile system.
- HARM, a missile that can find and destroy radar systems.
- Hellfire rockets or surface-to-surface missiles. In Ukraine, each of these missiles is fired from a tripod on the ground and weighs 45 kg.
Reuters reported in January 2023 that U.S. officials said the United States would send more weapons to Ukraine in February. They expect to send the Ground Launched Small Diameter Bomb (or GLSDB), which has a range of 150 km (94 miles).
Russia uses:

- TOS-1 (ТОС-1), a multiple rocket launcher that can use rockets with thermobaric warheads. These warheads create a powerful pressure wave and then a vacuum, which can severely harm people.
- UR-77 Meteorit, a mine clearing vehicle. It has also been used to clear a path, 6 meters wide and up to 90 meters long, for Russian forces to enter Ukrainian trenches.
- Geran-2 and Shahed-136, a family of drones that can explode.
- T-90 tanks, including the T-90S, which is an export version sold to other countries.
- Lancet, a drone.
Russia also has:
- TOS-2, another thermobaric weapon.
- Khinzal ('dagger'), a missile that has been used three times as of early 2023.
Military Strength
Soldiers and Military Personnel
 Ukraine:
Ukraine:
- 209,000 in armed forces
- 102,000 in paramilitary groups
- 20,000 foreign volunteers
 Russia:
Russia:
- Around 175,000–190,000
 Donetsk PR:
Donetsk PR:
- 20,000
 Luhansk PR:
Luhansk PR:
- 14,000
In May 2022, Ukrainian authorities stated they had 700,000 active duty service members fighting the Russian invasion.
As of December 2022, 50,000 women have signed contracts to serve as soldiers in the Ukrainian Armed Forces.
Reserves (soldiers not on active duty):
 Ukraine:
Ukraine:
- 900,000 according to media in 2021
At the Start of the Invasion
 Russia:
Russia:
- 175,000–190,000 in armed forces
- 34,000 in separatist militias
 Ukraine:
Ukraine:
- 196,600 in armed forces
- 102,000 in paramilitary groups
Loss of Weapons and Equipment
According to Oryx, an organization that tracks military losses, Russia has lost at least 64 aircraft as of January 6, 2023.
Casualties
 Russia:
Russia:- Acc. to Russia (March 25, 2022): 1,351 soldiers killed, 3,825 wounded.
- Acc. to NATO (March 23): 30,000–40,000 soldiers killed, wounded, missing, or captured (7,000–15,000 killed).
- Acc. to the United States (March 25): 15,000–22,500 soldiers killed and wounded.
 Donetsk PR:
Donetsk PR:- Acc. to the Donetsk PR (March 17): 349 soldiers killed, 1,930 wounded.
 Ukraine:
Ukraine:- Acc. to Ukraine (March 12): 1,300 soldiers killed.
- Acc. to the United States (March 9, 2022): 2,000–4,000 soldiers killed.
Treating Wounded Soldiers in Other Countries
As of May 31, 2022, no injured Ukrainian soldiers had been taken to Norway. On that day, the Norwegian minister of justice was asked to explain this to parliament. That evening, the justice minister said that Norway would allow injured Ukrainian soldiers to come to Norway. These soldiers would be part of a total of 550 injured Ukrainian civilians and soldiers. On June 12, 2022, the first wounded soldiers arrived in Norway.
Civilians
- The UN reported on January 15, 2023, that at least 7,031 civilians had died because of the war.
- Acc. to Ukraine (partial figures; March 25, 2022): 3,909–4,275+ civilians killed.
Refugees
- Acc. to the UN (March 21, 2022): More than 4.3 million refugees and 6.5 million internally displaced people (people who had to leave their homes but stayed within Ukraine).
The President of Moldova, Maia Sandu, said over 4,000 Ukrainian citizens had crossed into Moldova since the invasion began. Poland prepared for a large number of refugees to enter the country. To make border crossings easier, Poland removed COVID-19 entry rules. Ukrainian refugees also started crossing into Romania, mostly through Siret in Suceava County. Romania said refugees did not need to quarantine or follow COVID rules.
Details about the Warfare
There have been reports of dead soldiers being buried in graves that are connected to booby traps. This means that when a grave is opened and a body is touched, a grenade or other explosive device blows up.
Images for kids
-
TOS-1A rocket launchers on the ground and two rockets in the air (Picture from 2011)
See also
 In Spanish: Invasión rusa de Ucrania para niños
In Spanish: Invasión rusa de Ucrania para niños






