Sustainable energy facts for kids
Sustainable energy is all about using energy wisely and getting it from sources that can be replaced naturally. This helps us slow down and reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the air, which is good for our planet.
Using energy efficiently means we don't need as much. This gives renewable energy sources time to grow and replace fossil fuels like coal and oil. If we use too much energy, it's hard for clean energy to catch up. So, both saving energy and using clean energy are super important for a sustainable future.
What are Renewable Energy Sources?
When we talk about energy, "sustainable energy" and "renewable energy" are often used together. Renewable energy comes from natural sources that refill themselves, like the sun or wind. These technologies are key to sustainable energy because they help countries have enough energy and rely less on fossil fuels. This also helps reduce gases that cause climate change.
Solar Power: Energy from the Sun
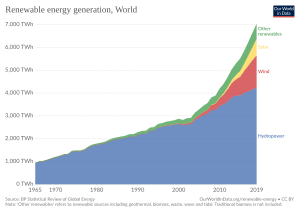
Solar power uses special panels called photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells turn sunlight directly into electricity. In 2018, solar power made up about 3% of the world's electricity.
You can see solar panels on buildings or in big solar farms connected to the power grid. They are also great for providing electricity to places that are far away from power lines. Solar panels are built to last a long time, often 25 years or more, and most parts can be recycled.
Right now, solar panels can turn about 24% of the sunlight they get into electricity. Scientists are always working to make them better and cheaper. For example, researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) found a way to store solar energy by using it to make hydrogen fuel from water. This helps solve the problem of needing energy when the sun isn't shining, like at night.
Scientists are also looking into space-based solar power. This idea involves putting solar panels in space and sending the energy back to Earth using microwaves. China is even building a test facility for this!
Using Solar for Heating
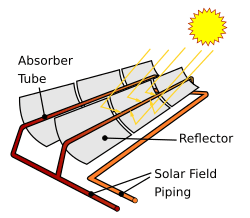
Solar heating systems use the sun's energy to heat water or buildings. They usually have special collectors that soak up sunlight. A fluid then carries this heat to where it's needed, like to heat water for showers, swimming pools, or even entire homes.
This heat can also be stored for later use. For example, you can store heat collected in the summer to warm your home in the winter. The same idea can be used to store winter cold for air conditioning in the summer. Solar heating can provide a lot of the energy needed for hot water in many places.
Wind Power: Harnessing the Breeze
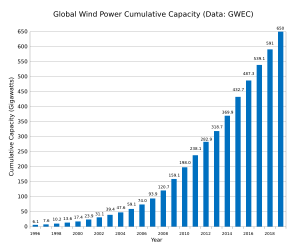
Wind power uses large wind turbines to turn the force of the wind into electricity. In 2018, wind power provided about 6% of the world's electricity.
Sometimes, it can be tricky to find good places for wind turbines because of how they look or their effect on the environment. A big wind farm might have hundreds of turbines spread out over a large area. But the land between the turbines can still be used for farming or other things. Wind farms can also be built offshore in the ocean.
After about 20 years, wind turbine blades need to be replaced. Scientists are working on ways to recycle these old blades and to make new ones that are easier to recycle.
Hydropower: Power from Moving Water

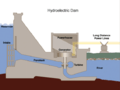
Hydroelectric plants use the power of moving water, usually from dams, to create electricity. These plants can last a very long time—some have been working for over 100 years! They are also clean and don't produce much pollution. Hydropower can help balance out energy from wind and solar, which can change depending on the weather.
Some people worry about very large hydroelectric dams because they can force people to move from their homes and might release some gases during construction. However, studies show that these problems are mostly with shallow dams in warm places. Newer technologies allow for smaller, less impactful projects called run-of-the-river hydroelectricity, which don't need big reservoirs. Overall, hydroelectric plants produce much less pollution than other types of power.
In 2015, hydropower made up 16% of the world's electricity. It's a very important energy source in countries like Canada (60% of electricity) and Brazil (nearly 80%).
Biomass: Energy from Living Things
Biomass is material that comes from living or recently living things, like plants, trees, or even waste. We can burn biomass to create heat and electricity, or turn it into biofuels like biodiesel and ethanol.
Biomass is very useful and is one of the most common renewable energy sources. It's found in many countries, which helps reduce the need for imported fossil fuels. If biomass is grown and managed well, the carbon dioxide released when it's burned can be balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by new plants as they grow. Also, using agricultural or city waste for energy helps us get rid of that waste.
However, if we grow crops specifically for biomass, it can sometimes mean less land for growing food. It can also affect natural areas, harm the soil, and use a lot of water.
Biofuels: Fuel from Plants
Biofuels are fuels made from different types of biomass, like corn or sugar beet. They are usually liquids and are used to power vehicles, often mixed with regular gasoline or diesel.
One type, Cellulosic ethanol, is made from wood, grasses, or parts of plants we don't eat. This means it doesn't compete with our food supply. Some studies show it could be cheaper and more sustainable than corn-based ethanol.
Using farmland to grow fuel crops can mean less land for food. For example, in the United States, corn-based ethanol uses about 40% of the yearly corn harvest but only replaces a small amount of gasoline. In places like Malaysia and Indonesia, clearing forests to grow palm oil for biodiesel has caused serious problems for the environment and endangered animals.
Geothermal Energy: Heat from Inside the Earth
Geothermal energy comes from the heat deep inside the Earth. This heat is always being made by natural processes. We can get this energy by drilling into the ground, similar to drilling for oil. Hot water or steam from underground then brings the heat to the surface.
Geothermal energy can be used to make electricity or to heat buildings. As of 2010, 24 countries use geothermal energy for electricity, and 70 countries use it for heating.
Geothermal power is considered a sustainable and renewable source because the amount of heat we take out is tiny compared to the Earth's total heat. Geothermal power plants also produce very little carbon dioxide pollution, much less than coal power plants.
Marine Energy: Power from the Ocean
Marine energy mainly comes from tides and wave power. As of 2020, there are a few small tidal power plants working in places like France and China. Engineers are still working to make wave power equipment strong enough to handle big ocean storms.
Non-Renewable Energy Sources
Nuclear Power: Splitting Atoms for Energy
Nuclear power plants have been making electricity since the 1950s. They provide a steady supply of power without causing local air pollution. In 2012, nuclear power made up 11% of the world's electricity. Experts consider nuclear power a low-carbon energy source, meaning it produces very few greenhouse gases over its lifetime.
There's a lot of discussion about whether nuclear power is truly sustainable. People talk about the risks of accidents, the high cost and long time to build new plants, the problem of radioactive waste, and the possibility of nuclear energy being used to make weapons.
Currently, all nuclear power plants use fission, which means splitting atoms. Another type, fusion, is what powers the sun, but it's not yet practical for use on Earth.
Thorium is another material that can be used for nuclear power. Some people think it could be more sustainable than uranium because there's more of it, it might be safer, and it could produce less dangerous waste.
Images for kids
-
A solar trough array, an example of green energy
See also
 In Spanish: Energía sostenible para niños
In Spanish: Energía sostenible para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |