Fusion power facts for kids
Nuclear fusion is when two tiny atoms join together to make a new, bigger atom. When this happens, it creates a huge amount of energy. The idea behind a fusion reactor is to build a special kind of nuclear power plant. This plant would use fusion to produce electricity for our homes and schools. Today, most nuclear power plants use a different process called nuclear fission, which splits atoms instead of joining them.
Fusion is the same powerful process that makes our Sun shine and feel warm. It's also used in the most powerful nuclear weapons.
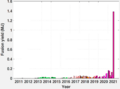
As of 2012, there were no commercial power plants using fusion to make electricity. However, there are several research facilities around the world. One famous example is the Joint European Torus (JET) in England. This reactor uses a special design called a Tokamak. A tokamak uses strong magnets shaped like a doughnut to squeeze the atoms together.
Contents
What is Nuclear Fusion?
Nuclear fusion is like a cosmic hug between atoms. It happens when two light atomic nuclei (the centers of atoms) combine. They form a heavier nucleus, and in doing so, they release a lot of energy. This is different from nuclear fission, where a heavy atom splits into lighter ones.
How Fusion Works in Stars
Our Sun and other stars are giant fusion reactors. Inside the Sun, hydrogen atoms combine to form helium. This process releases the enormous amount of heat and light that warms our planet. Scientists want to copy this process here on Earth to create clean energy.
Why Do We Need Fusion Power?
Fusion power could be a great way to make electricity in the future. It uses fuels that are easy to find, like forms of hydrogen from water. Fusion power plants would also produce very little radioactive waste. This makes them much safer for the environment than current nuclear power plants.
Challenges of Fusion Energy
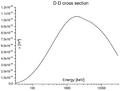
Making fusion work on Earth is very difficult. Atoms need to be incredibly hot (millions of degrees Celsius!) and squeezed together very tightly. This creates a super-hot gas called plasma. Scientists need to control this plasma for a long time to get energy out. It's like trying to hold onto a tiny piece of the Sun!
Types of Fusion Reactors
Scientists are trying different ways to build fusion reactors. The two main types are magnetic confinement and inertial confinement.
Magnetic Confinement Fusion
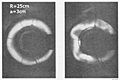
This method uses powerful magnetic fields to hold the hot plasma. The most common design is the Tokamak.
- Tokamaks: These machines have a doughnut shape. Strong magnets create a magnetic cage that keeps the super-hot plasma from touching the reactor walls. The Joint European Torus (JET) is a well-known tokamak.
- Stellarators: These are similar to tokamaks but have a more twisted shape. This design helps to keep the plasma stable for longer periods. The Wendelstein 7-X in Germany is a large stellarator.
Inertial Confinement Fusion
This method uses powerful lasers or particle beams to heat and compress a tiny pellet of fusion fuel.
- Laser Fusion: Giant lasers fire at a small fuel pellet, making it implode. This creates the extreme heat and pressure needed for fusion. The National Ignition Facility (NIF) in the United States uses this method.
The Future of Fusion Energy
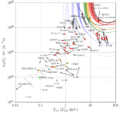
Scientists and engineers around the world are working hard to make fusion power a reality. Big projects like ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) are being built. ITER aims to show that fusion can produce more energy than it consumes. If successful, fusion could provide a nearly limitless and clean energy source for future generations.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Energía de fusión para niños
In Spanish: Energía de fusión para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |