Araza facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Araza |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eugenia |
| Species: |
E. stipitata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eugenia stipitata McVaugh
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
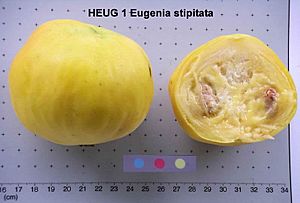
The Eugenia stipitata is a special fruit tree. It is also known as Araza. People in Brazil, Colombia, and Ecuador call it araçá or arazá. This tree grows naturally in the Amazon rainforest.
Contents
About the Araza Plant
The Araza tree first grew in the western part of the Amazon. It is not as well-known as some other fruits. But it has many good qualities that could make it a popular crop.
When you eat the fruit directly from the tree, it tastes very sour. But people use it to make many tasty things. These include juices, jams, ice creams, and other refreshing foods.
Wild Araza fruits are usually small, about 7 cm wide and 30 grams. But farmers in Peru have grown much larger ones. Some can be 12 cm wide and weigh up to 740 grams! This shows how much the plant can improve with careful growing.
You can find Araza trees mainly in the western Amazon. They grow on old, dry land with special white soils. Sometimes, they are also found in Bolivia and other parts of Brazil and Colombia. People also grow them in other warm places like Central America and Florida.
Plant Science (Botany)
The name Eugenia comes from Prince Eugene of Savoy. He was an Austrian general who loved art and science.
The Araza plant can be a small bush or a tree. It usually grows to be about 2.5 to 15 meters tall. It has many branches and reddish-brown bark that peels off.
Its leaves are dark green and shiny. They are about 8 to 19 cm long. The plant has small white flowers, about 1 cm wide. These flowers usually grow in groups of two to five.
The fruit is round and can be 2 to 12 cm wide. It can weigh up to 750 grams. When ripe, it turns bright yellow and has a soft, thin skin. Inside, there is juicy, sour, and fragrant pulp. Each fruit usually has about 12 seeds.
These seeds are "recalcitrant." This means they cannot survive if they get too dry or cold. So, they need special care to stay alive.
Healthy Goodness in Araza
Araza fruit is quite sour, with a low pH of about 2.4. This makes it great for processing into drinks and other foods. It is also rich in important nutrients.
The fruit contains a lot of nitrogen and potassium. Its dry weight has a good amount of protein (8-10%) and fiber (5-6.5%). It also has carbohydrates, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, and magnesium.
Araza is packed with vitamins! For every 100 grams of fruit, you get about:
- 775 mg of Vitamin A
- 9.84 mg of Vitamin B1
- 768 mg of Vitamin C (which is twice as much as an orange!)
The fruit's pulp also has sugars like glucose, fructose, and sucrose. The oil from the fruit has special compounds called sesquiterpenes. These give the fruit antioxidant power, which helps protect your body.
Studies also show that extracts from Araza fruit might help prevent certain types of cancer. This makes Araza a very healthy fruit!
How People Use Araza
You can eat fresh Araza fruit. But because it's so sour, most people add sugar to it.
In Colombia, Araza has become very popular since the late 1900s. Farmers now sell it in supermarkets. Some Araza is even exported to countries like the UK. The USA is also working to allow fresh Araza to be sold there.
Besides its fruit, the Araza tree has other uses. It can help bring life back to tired soil. It is also grown as a beautiful ornamental plant.
Growing Araza Trees
Araza trees can be grown alongside other crops. This is called intercropping. Young Araza trees grow well in the shade of taller trees.
Most fruit trees are grown from seeds, and Araza is no different. The best seeds for growing new plants come from fully ripe fruits. If you keep the seeds in water, about 80% of them will sprout within 60 days.
It's a good idea to prune young Araza trees. This helps them grow three or four strong branches. You should also prune them every year to keep them healthy.
Remember, Araza seeds are "recalcitrant." This means they lose their ability to grow if stored cold for too long. So, you should plant them within five days after harvesting.
Plant the seeds about 2 cm apart in a shady spot. Cover them lightly, as too much soil can stop them from sprouting. Using partly rotted wood in the seed bed is better than using regular earth. Seeds can take up to 80 days to sprout, but almost all of them will grow if cared for properly.
When the seedlings are 7 to 10 cm tall, move them into bags. Fill the bags with soil mixed with about 10% manure. Keep the plants in these bags for up to a year. Give them shade for six months, then partial shade for another six months.
After a year, the plants are ready for their final spot. Dig holes about 50 cm deep and 30 to 50 cm wide. Mix the soil with about 0.5 kg of manure. It's important to remove weeds every month and add organic material to the soil. Organic fertilizers, like manure, work better for Araza than chemical ones.
Fruit Growing and Picking
Araza trees produce fruit all year round. You can get 2 to 4 harvests each year! This is because the fruit grows quickly, taking about 84 days from flower to harvest.
Araza is a "climacteric" fruit. This means it continues to ripen after being picked, like bananas or avocados.
For Araza, you pick the fruit based on its size and color. You also check its texture. If you let the fruit ripen fully on the tree, it will only last about 72 hours after picking. This is because it can get bruised or develop a disease called anthracnose.
So, farmers usually pick Araza fruits while they are still green. This helps prevent bruising and makes them last longer. The fresh fruits are then carefully moved in plastic trays, with no more than three layers of fruit.
Future of Araza
Araza is still quite new as a farmed crop. So, scientists are still learning the best ways to grow it. We don't know much about its genetics yet.
If we learn more about growing and harvesting Araza, its production could increase. For Araza to become popular worldwide, new technologies are needed. These will help people outside the Amazon accept and enjoy this fruit.
Any efforts to improve Araza will focus on things like:
- How the fruit looks
- Its color and smell
- How good it tastes
- How well it handles being transported and stored
Pests and Fungi
Araza trees can be attacked by fruit flies. These flies lay eggs in the fruit. Their larvae eat the pulp and can destroy the fruit. Other insects like weevils also attack the fruit and seeds.
A type of black bee can also eat the skin, pulp, and sometimes even the seeds.
Finally, Araza is also sensitive to a fungus called anthracnose. This can cause spots and decay on the fruit.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Arazá para niños
In Spanish: Arazá para niños